YoctoHub-Wireless-SR : User's guide
2. Presentation
2.1 The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR components 3. First steps
3.1 Manual configuration 3.2 Automated configuration 3.3 Connections 4. Assembly
4.1 Fixing 4.2 Fixing a sub-module 5. Using the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR
5.1 Locating the modules 5.2 Testing the modules 5.3 Configuring modules 5.4 Upgrading firmware 6. Access control
6.1 Protected "admin" access 6.2 Protected "user" access 6.3 Access control and API 6.4 Deleting passwords 7. Interaction with external services
7.1 Configuration 7.2 Emoncms 7.3 Valarm.net 7.4 Xively (previously Cosm) 7.5 InfluxDB 7.6 PRTG 7.7 MQTT 7.8 Yocto-API callback 7.9 User defined callback 8. Programming
8.1 Accessing connected modules 8.2 Controlling the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR 9. Sleep mode
9.1 Manual configuration of the wake ups 9.2 Configuring the wake up system by software 10. Personalizing the web interface
10.1 Using the file system 10.2 Limitations 11. High-level API Reference
11.1 Class YHubPort 11.2 Class YWireless 11.3 Class YNetwork 11.4 Class YFiles 11.5 Class YRealTimeClock 11.6 Class YWakeUpMonitor 11.7 Class YWakeUpSchedule 12. Troubleshooting
12.1 Where to start? 12.2 Programming examples don't seem to work 12.3 Linux and USB 12.4 ARM Platforms: HF and EL 12.5 Powered module but invisible for the OS 12.6 Another process named xxx is already using yAPI 12.7 Disconnections, erratic behavior 12.8 Registering a VirtualHub disconnect an other one 12.9 Dropped commands 12.10 Can't contact sub devices by USB 12.11 Network Readiness stuck at 3- LAN ready 12.12 Damaged device 13. Characteristics
14. Index
1. Introduction
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is a 60x58mm electronic module enabling you to control other Yoctopuce modules through a wireless network connection. Seen from the outside, this module behaves exactly like a standard computer running a VirtualHub1: same interface, same functionalities.
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is designed to be easily deployed and to not require any specific maintenance. In the opposite to a mini-computer, it does not have a complex operating system. Some simple settings allow you to use it in many kinds of network environments. These settings can be modified manually or automatically through USB. Therefore, the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is much more suited to industrialization than a mini-computer. However, you cannot run additional software written by the user on the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR.
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is not a standard USB hub with network access. Although it uses USB cables, its down ports use a proprietary protocol, much simpler than USB. It is therefore not possible to control, or even to power, standard USB devices with a YoctoHub-Wireless-SR.
Yoctopuce thanks you for buying this YoctoHub-Wireless-SR and sincerely hopes that you will be satisfied with it. The Yoctopuce engineers have put a large amount of effort to ensure that your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is easy to install anywhere and easy to use in any circumstance. If you are nevertheless disappointed with this device, do not hesitate to contact Yoctopuce support2.
2. Presentation

| 1: | Yocto-button | 9: | Sleep neutralization |
| 2: | Control and power USB port | 10: | Back connection |
| 3: | Yocto-led | 11: | Down port 1 |
| 4: | Overload led | 12: | Down port 1 led |
| 5: | Network transfer led | 13: | Down port 2 |
| 6: | Wake up button | 14: | Down port 2 led |
| 7: | Sleep button | 15: | Down port 3 |
| 8: | Antenna | 16: | Down port 3 led |
2.1. The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR components
Serial number
Each Yocto-module has a unique serial number assigned to it at the factory. For YoctoHub-Wireless-SR modules, this number starts with YHUBWLN2. The module can be software driven using this serial number. The serial number cannot be modified.
Logical name
The logical name is similar to the serial number: it is a supposedly unique character string which allows you to reference your module by software. However, in the opposite of the serial number, the logical name can be modified at will. The advantage is to enable you to build several copies of the same project without needing to modify the driving software. You only need to program the same logical name in each copy. Warning: the behavior of a project becomes unpredictable when it contains several modules with the same logical name and when the driving software tries to access one of these modules through its logical name. When leaving the factory, modules do not have an assigned logical name. It is yours to define.
Yocto-button
The Yocto-button has two functionalities. First, it can activate the Yocto-beacon mode (see below under Yocto-led). Second, if you plug in a Yocto-module while keeping this button pressed, you can then reprogram its firmware with a new version. Note that there is a simpler UI-based method to update the firmware, but this one works even if the firmware on the module is incomplete or corrupted.
Yocto-led
Normally, the Yocto-led is used to indicate that the module is working smoothly. The Yocto-led then emits a low blue light which varies slowly, mimicking breathing. The Yocto-led stops breathing when the module is not communicating any more, as for instance when powered by a USB hub which is disconnected from any active computer.
When you press the Yocto-button, the Yocto-led switches to Yocto-beacon mode. It starts flashing faster with a stronger light, in order to facilitate the localization of a module when you have several identical ones. It is indeed possible to trigger off the Yocto-beacon by software, as it is possible to detect by software that a Yocto-beacon is on.
The Yocto-led has a third functionality, which is less pleasant: when the internal software which controls the module encounters a fatal error, the Yocto-led starts emitting an SOS in morse 3. If this happens, unplug and re-plug the module. If it happens again, check that the module contains the latest version of the firmware and, if it is the case, contact Yoctopuce support4.
Power / Control port
This port allows you to power the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR and the modules connected to it with a simple USB charger. This port also allows you to control the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR by USB, exactly like you can do it with a classic Yoctopuce module. It is particularly useful when you want to configure the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR without knowing its IP address.
Down ports
You can connect up to three Yoctopuce modules on these ports. They
will then be available as if they were connected to a computer running
a VirtualHub. Note that the protocol used between the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR and
the USB modules is not USB but a lighter proprietary protocol. Therefore,
the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR cannot manage devices other than Yoctopuce devices.
A standard USB hub does not work either5. If you want to connect
more than three Yoctopuce modules, just connect one or more
Warning: the USB connectors are simply soldered in surface and can be pulled out if the USB plug acts as a lever. In this case, if the tracks stayed in position, the connector can be soldered back with a good iron and flux to avoid bridges. Alternatively, you can solder a USB cable directly in the 1.27mm-spaced holes near the connector.
Integrated Antenna
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR features an antenna integrated on the board. So you won't have to use an external one. Because of that integrated antenna, device orientation will have an influence on performances. Make sure you don't mount your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR in a metallic enclosure.
Overload led
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR continuously monitors its power consumption. If it detects a global consumption of more that 2A, following an overload on one of the down ports for example, it automatically disables all the down ports and lights the overload led. To isolate the source of the issue, you can reactivate the ports one by one, monitoring the power consumption increase. Alternatively, if you know the source of the overload issue and know to have solved it, you can restart the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR to enable all its ports at once.
Note that the overload led is a protection measure which can prevent overheating, but it is not a protection guarantee against shorts.
Sleep
Usually, the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR consumes about 0.5 Watt (110mA), to which you must add the connected module consumption. But it is able to get into sleep to reduce its power consumption to a strict minimum, and to wake up at a precise time (or when an outside contact is closed). This functionality is very useful to build measuring installations working on a battery. When the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is in sleep mode, most of the electronics of the module as well as the connected Yoctopuce modules are switched off. This reduces the total consumption to 75 µW (15 µA).
Switching to sleep and waking up can be programmed based on a schedule, controlled by software, or controlled manually with two push buttons located on the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR circuit. You can find there two pairs of contacts which enable you to shunt these two buttons.
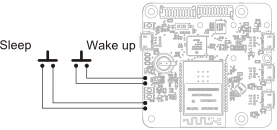
Sleep and wake up buttons deviation.
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR includes a switch with which you can disable the sleep mode at the hardware level. This functionality is particularly useful when developing and debugging your project, as well as when updating the firmware.
3. First steps
The aim of this chapter is to help you connect and configure your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR for the first time.
3.1. Manual configuration
You can configure your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR through its USB control port, by using the VirtualHub7.
Run the VirtualHub on your preferred computer and connect it to the power / control port of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR. You need a USB A-MicroB cable.

Configuration: connecting your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR by USB to a computer
Launch your preferred browser on the URL of your VirtualHub. It usually is http://127.0.0.1:4444. You obtain the list of Yoctopuce modules connected by USB, among which your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR.
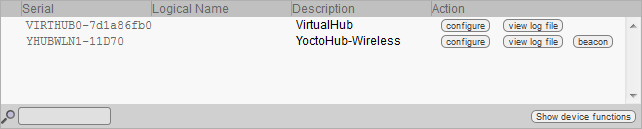
List of Yoctopuce modules connected by USB to your computer, among which your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR
Click on the configure button corresponding to your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR. You obtain the module configuration window. This window contains a Network configuration section.

YoctoHub-Wireless-SR module configuration window
Connection to the wireless network
You must first configure your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR to enable it to connect itself to your wifi network. To do so, click on the edit button corresponding to WLAN settings in the Network configuration section. The configuration window of the wireless network shows up:

Wireless network configuration window.
You can then decide if you wish to connect your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR to an existing network, or if you would rather manually enter the SSID of network you wish to use.
You can also configure the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR for it to generate its own wireless network in ad-hoc mode. You can then connect yourself directly on the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR without having to go through an infrastructure server (access point). However, be aware that the ad-hoc mode has important limitations compared to a real wifi network. In particular, devices under Android cannot connect themselves to it.
When you have set the wireless network parameters, and possibly tested them, you can click on the OK button to close this configuration window and go back to the main configuration window.
If needed, you can also configure which IP address must be assigned to the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR. To do so, click on the edit button opposite to the IP addressing line in the main window.
You can then choose between a DHCP assigned IP address or a fixed IP address for your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR module. The DHCP address is recommended in so much as this functionality is supported by most ADSL routers (its the default configuration). If you do not know what a DHCP server is but are used to connect machines on your network and to see them work without any problem, do not touch anything.
You can also choose the network name of your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR. You can then access your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR by using this name rather than its IP address. When the network part is configured, click on the Save button to save your changes and close the configuration window. These modifications are saved in the persistent memory of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR, they are kept even after the module has been powered off.
Click on the serial number corresponding to your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR. This opens your module property window:

The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR properties
This window contains a section indicating the state of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR network part. You can find there its MAC address, current IP address, and network name. This section also provides the state of the network connection. Possible states are:
- 0- search for link: The module is searching for a connection with the network. If this state persists, the sought wifi network is most likely not in the neighborhood.
- 1- network exists: The sought wifi network was detected.
- 2- network linked: The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR did connect to the network.
- 3- LAN ready: The local network is working (IP address obtained).
- 4- WWW ready: The module has checked Internet connectivity by connecting itself to a time server (NTP).
When you have checked that your module does indeed have a valid IP address, you can close the property window, stop your VirtualHub, and disconnect your USB cable. They are not needed anymore.
From now on, you can access your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR by typing its IP address directly in the address field of your preferred browser. The module answers to the standard HTTP port, but also to the 4444 port used by the VirtualHub. If your module IP address is 192.168.0.10, you can therefore access it with the http://192.168.0.10 URL.

The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR interface is identical to that of a VirtualHub.
If you have assigned a name to your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR, you can also use this name on the local network. For example, if your have used the yoctohub network name, you can contact the module with the http://yoctohub URL under Windows and the http://yoctohub.local URL under Mac OS X and Linux. Note that this technique is limited to the subnet of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR. If you want to contact the module by name from another network, you must use a classic DNS infrastructure.
3.2. Automated configuration
You can industrialize the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR network configuration. You can find in the following chapters of this documentation the description of the programming functions enabling you to read the Ethernet address (MAC address) of a module, and to configure all of its network parameters.
The network configuration functions are also available as command lines, using the YNetwork utility software available in the command line programming library 8.
After having set some parameters by software, make sure to call the saveToFlash() function to ensure that the new settings are saved permanently in the module flash memory.
3.3. Connections
Power supply
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR must be powered by the USB control socket.
USB
Simply connect a USB charger in the power / control port port, but make sure that the charger provides enough electric power. The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR consumes about 110mA, to which you must add the power consumption of each submodule. The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is designed to manage a maximum of 2A. Therefore, we recommend a USB charger able to deliver at least 2A. Moreover, you must make sure that the total power consumption of the set "hub + submodules" does not go above this limit.

The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR can be powered by a regular USB charger
Sub-modules
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is able to drive all the Yoctopuce modules of the Yocto range. These modules can be directly connected to the down ports. They are automatically detected. For this, you need Micro-B Micro-B USB cables. Whether you use OTG cables or not does not matter.
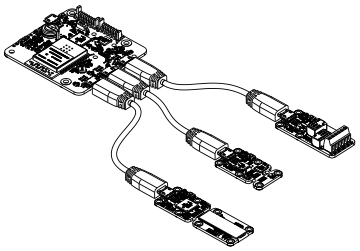
Connecting sub-modules with USB cables
Alternatively, you can connect your modules by directly soldering electric cables between the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR and its sub-modules. Indeed, all the Yoctopuce modules have contacts designed for direct cabling. We recommend you to use solid coper ribbon cables, with a 1.27mm pitch. Solid copper ribbon cable is less supple than threaded cable but easier to solder. Pay particular attention to polarity: the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR, like all modules in the Yoctopuce range, is not protected against polarity inversion. Such an inversion would likely destroy your devices. Make sure the positions of the square contacts on both sides of the cable correspond.
Sub-module connection with ribbon cable
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is designed so that you can fix a single width module directly on top of it. To do so, you need screws, spacers9, and a 1.27mm pitch connector10. You can thus transform your USB Yoctopuce module into a network module while keeping a very compact format.

Fixing a module directly on the hub
Beware, the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is designed to drive only Yoctopuce modules. Indeed, the protocol used between the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR and the sub-modules is not USB but a much lighter proprietary protocol. If, by chance, you connect a device other than a Yoctopuce module on one of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR down ports, this port is automatically disabled to prevent damages to the device.
4. Assembly
This chapter provides important information regarding the use of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR module in real-world situations. Make sure to read it carefully before going too far into your project if you want to avoid pitfalls.
4.1. Fixing
While developing your project, you can simply let the hub hang at the end of its cable. Check only that it does not come in contact with any conducting material (such as your tools). When your project is almost at an end, you need to find a way for your modules to stop moving around.
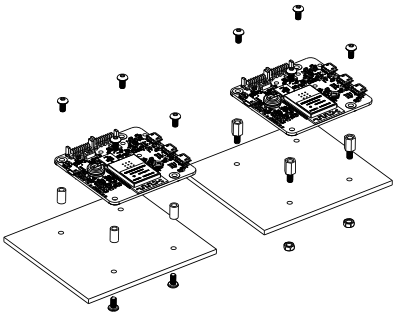
Examples of assembly on supports
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR module contains 3mm assembly holes. You can use these holes for screws. The screw head diameter must not be larger than 8mm or the heads will damage the module circuits.
Make sure that the lower surface of the module is not in contact with the support. We recommend using spacers. You can fix the module in any position that suits you: however be aware that the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR electronic components, in particular the network part, generate heat. You must not let this heat accumulate.
4.2. Fixing a sub-module
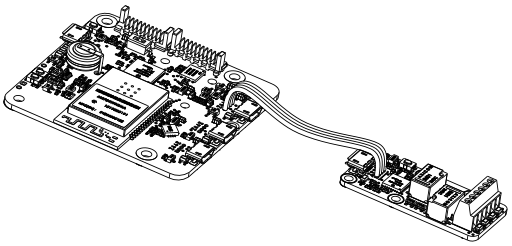
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is designed so that you can screw a single width module directly on top of it. By single width, we mean modules with a 20mm width. All the single width modules have their 5 assembly holes and the USB socket in the same position. The sub-module can be assembled with screws and spacers. At the back of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR and sub-module USB connectors, there are a set of 4 contacts enabling you to easily perform an electrical connection between the hub and the sub-module. If you do not feel sufficiently at ease with a soldering iron, you can also use a simple Micro-B Micro-B USB cable, OTG or not.

Fixing a module directly on the hub
Make sure to mount your module on the designed side, as illustrated above. The module 5 holes must correspond to the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR 5 holes, and the square contact on the module must be connected to the square contact on the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR down port. If you assemble a module on the other side or in another way, the connector polarity will be inverted and you risk to permanently damage your equipment.
All the accessories necessary to fix a module on your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR are relatively usual. You can find them on the Yoctopuce web site, as on most web sites selling electronic equipment. However, beware: the head of the screws used to assemble the sub-module must have a maximum head diameter of 4.5mm, otherwise they could damage the electronic components.
5. Using the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR
Apart from providing network access to the Yoctopuce devices, the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR enables you to test and configure your Yoctopuce modules. To do so, connect yourself to your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR with your favorite web browser11. Use the IP address of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR or its network name, for example http://192.168.0.10. The list of the connected modules should appear.

YoctoHub-Wireless-SR web interface
5.1. Locating the modules
The main interface displays a line per connected module; if you have several modules of the same model, you can locate a specific module by clicking on the corresponding beacon button: it makes the blue led of the module start blinking and displays a blue disk at the beginning of the corresponding line in the interface. Pressing the Yocto-button of a connected module has the same effect.

Yocto-button (1) and localization led (2) of the Yocto-Demo module.
These two elements are usually placed in the same location, whatever the module.
5.2. Testing the modules
To test a module, simply click on the serial number of a module in the interface, a window specific to the module opens. This window generally allows you to activate the main functions of the module. Refer to the User's guide of the corresponding module for more details 12.

Property window of the Yocto-Demo module, obtained from the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR interface
5.3. Configuring modules
You can configure a module by clicking on the corresponding configure button in the main interface. A window, specific to the module, then opens. This window allows you minimally to assign a logical name to the module and to update its firmware. Refer to the User's guide of the corresponding module for more details.
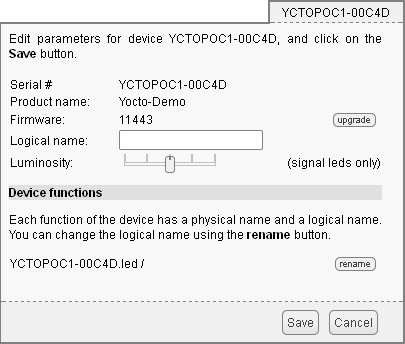
"Configuration" window of the Yocto-Demo module
5.4. Upgrading firmware
The Yoctopuce modules are in fact real computers, they even contain a small web server. And, as all computers, it is possible to update their control software (firmware). New firmware for each module are regularly published, they generally allow you to add new functionalities to the module, and/or to correct a hypothetical bug13.
To update a module firmware, you must first get the new firmware. It can be downloaded from the module product page on the Yoctopuce web site14. The interface offers also a direct link if it detects that the firmware is not up-to-date 15. Firmware is available as .byn files of a few tens of kilobytes. Save the one you are interested in on your local disk.
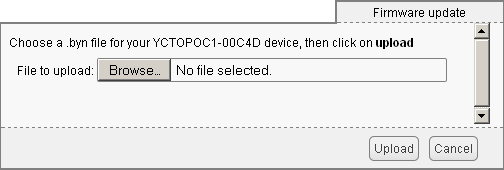
Firmware update window
When the firmware file is locally available, open the module configuration window and click on the upgrade button. The interface asks you to select the firmware file you wish to use. Enter the file name and click on Upload. From then on, everything is automatically performed: the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR restarts the module in "update" mode, updates the firmware, then restarts the module in normal mode. The module configuration settings are kept. Do not disconnect the module during the update process.
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR firmware can be updated in the same manner.
If control is lost during a firmware update (power failure or unwanted disconnection), it is always possible to manually force a firmware reload, even if the sub-module does not even appear in the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR window. In this case, disconnect the module, and reconnect it while keeping the Yocto-button pressed. This starts the module in "update" mode. You can restart the firmware update process.
6. Access control
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is able to perform access control to protect your Yoctopuce devices. Click on the configure button on the line matching the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR in the user interface.

Click on the "configure" button on the first line
Then the configuration window for the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR shows up.

The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR configuration window.
Access control can be configured from the Incoming connections section. There are two levels of access control.
6.1. Protected "admin" access
The admin password locks write access on the modules. When the admin password is set, only users using the admin login are allowed read and write access to the modules. The users using the admin login can configure the modules seen by this YoctoHub-Wireless-SR as they wish.
6.2. Protected "user" access
The user password locks read access to the Yoctopuce modules. When set, any use without password becomes impossible. The user access type allows only read-only access to the modules, that is only to consult the states of the modules. If you simultaneously create "admin" and "user" access controls, users with a "user" login cannot modify the configuration of modules seen by this YoctoHub-Wireless-SR.
If you configure an admin access, without configuring a user access, users are still able to read your device values without any password.
To set up YoctoHub-Wireless-SR access, click the edit button on the line Authentication to read the information from the devices or Authentication to write information to the devices
6.3. Access control and API
Warning, the access control has an impact on Yoctopuce API behavior when trying to connect to this YoctoHub-Wireless-SR. With Yoctopuce API, access control is handled at RegisterHub() function call level. You need to provide the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR address as follow: login:password@address:port, here is an exemple:
yRegisterHub("admin:mypass@192.168.0.10:4444",errmsg);
6.4. Deleting passwords
If you forget your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR password, the only way to regain control is to reset all the settings to the default value. To do so, find a USB cable for the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR and connect it to a computer running the VirtualHub16 while keeping the Yocto-button pressed. This forces the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR to start in firmware update mode. It then appears in the VirtualHub below the module list. Click on its serial number and select a firmware file to load on the module. When the firmware is reloaded with this method, the module is reset to the factory settings, without access control.
7. Interaction with external services
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR can publish the state of connected devices on any web server. The values are posted on a regular basis and each time one of them changes significantly. This feature, named HTTP Callback, enables you to interface your Yoctopuce devices with many web services.
7.1. Configuration
To use this feature, just click on the configure button located on the line matching the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR on the main user interface. Then look for the Outgoing calbacks section and click on the edit button.

Just click on the "Configure" button on the first line.

Then edit the "Outgoing callbacks" section.
The callback configuration window shows up. This window enables you to define how your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR interacts with an external web server. Several interaction types are at your disposal. For each type, a specific wizard will help you enter appropriate parameters
7.2. Emoncms
Emoncms.org is an open-source cloud service where you can register to upload your sensor data. It will let you view your measures in real-time over the Internet, and draw historical graphs, without writing a single line of code. You just have to enter in the configuration window your own API key, as provided by Emoncms, and allocate an arbitrary node number to YoctoHub-Wireless-SR.
It is also possible to install Emoncms on your own server, to keep control on your data. You will find more explanations about this on Yoctopuce blog17.
Yoctopuce is not affiliated with Emoncms.org.
7.3. Valarm.net
Valarm is a professional cloud service where you can register to upload your sensor data, with some advanced features like remote configuration of Yoctopuce devices and measure geolocation.
Valarm is a reseller for Yoctopuce products, but Yoctopuce is not otherwise affiliated with Valarm.
7.4. Xively (previously Cosm)
Xively is a commercial cloud service where you might be able to register to upload your sensor data. Note that since end of 2014, Xively is focusing on enterprise and OEM customers, and might therefore not be available to everyone. For more details, see xively.com.
Yoctopuce is not affiliated with Xively.
7.5. InfluxDB
InfluxDB is an open-source database for time series, metrics and events. It is very efficient to retrieve measure series for a given time range, even when averaging on-the-fly. You can easily install it on your own computer to record and graph your sensor data. There is a step-by-step guide on how to configure InfluxDB and Grafana to graph Yoctopuce sensors on the Yoctopuce blog 18.
Yoctopuce is not affiliated to InfluxData nor to Grafana.
7.6. PRTG
PRTG is a commercial system, device and application monitoring solution developped by PAESSLER. You can easily install it on windows to record and graph your sensor data. For more details, see www.paessler.com/prtg. Vous pouvez facilement l'installer sur Windows pour enregistrer les mesures et obtenir des graphiques de vos capteurs. Pour plus de détails, voir fr.paessler.com/prtg. There is a step-by-step guide on how to configure PRTG to graph Yoctopuce sensors on the Yoctopuce blog 19.
Yoctopuce is not affiliated to PAESSLER.
7.7. MQTT
MQTT is an "Internet of Things" protocol to push sensor data to a central repository, named MQTT broker. For more details, see mqtt.org. You can also find several examples of use of MQTT on Yoctopuce blog.
7.8. Yocto-API callback
With some programming environments, the full Yoctopuce API can be used to drive devices in HTTP callback mode. This way, a web server script can take control of Yoctopuce devices installed behind a NAT filter without having to open any port. Typically, this allows you to control Yoctopuce devices running on a LAN behind a private DSL router from a public web site. The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR then acts as a gateway. All you have to do is to define the HTTP server script URL and, if applicable, the credentials needed to access it. On the server script, you would initialize the library using the following call:
RegisterHub("http://callback");There are two possibilities to use the Yoctopuce API in callback mode. The first one, available in PHP, Java and Node.JS is using pure HTTP callbacks. The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR posts its complete state to the server, and receives commands in return from the server script. There are however some limitations with this mode: complex interactions, such as retrieving data from the datalogger, are not possible.
The second mode API callback mode is using WebSocket callbacks. It is currently only available in Java and Node.JS. WebSockets are a standard extension of HTTP, providing a full bidirectional exchange channel over an HTTP connection. When a server script is connected by a YoctoHub-Wireless-SR over a Websocket callback connection, the full Yoctopuce API can be used, without any limitation.
The GatewayHub webservice, available from Yoctopuce web site, uses this Websocket callback technology to provide remote access to the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR, even in the presence of a NAT filter or firewall. For more information, see Yoctopuce blog20.
7.9. User defined callback
The "User defined callback" allow you to fully customize the way the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR interacts with an external web site. You need to provide the URL of the web server where you want the hub to post data. Note that only HTTP protocol is supported (no HTTPS).

The callback configuration window.
If you want to secure access to your callback script, you can setup a standard HTTP authentication. The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR knows how to handle standard HTTP authentication schemes: simply fill in the user and and password fields needed to access the URL. Both Basic and Digest authentication are supported. However, Digest authentication is highly recommended, since it uses a challenge mechanism that avoids sending the password itself over the Internet, and prevents replays.
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR posts the advertised values21 on a regular basis, and each time one of these values changes significantly. You can change the default delay between posts.
Tests
To help you debug the process, you can visualize with the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR the answer to the callback sent by the web server. Click on the test button when all required fields are filled. When the result meets your expectations, close the debug window and then click on the "Ok" button.
Format
Values are posted in one of the following formats:
1. If the function has been assigned a logical name:
FUNCTION_NAME = VALUE2. If the module has been assigned a logical name, but not the function:
MODULE_NAME#HARDWARE_NAME = VALUE3. If no logical name has been set:
SERIAL_NUMBER#HARDWARE_NAME = VALUEHere is a short PHP script allowing you to visualize the data posted by the callback and the result in the debug window:
<?php
Print(Date('H:i:s')."\r\n");
foreach ($_POST as $key=>$value) {
Print("$key=$value\r\n");
}
?>

Callback test results with a Yocto-PowerRelay and a Yocto-Temperature.
8. Programming
8.1. Accessing connected modules
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR behaves itself exactly like a computer running a VirtualHub. The only difference between a program using the Yoctopuce API with modules in native USB and the same program with Yoctopuce modules connected to a YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is located at the level of the registerHub function call. To use USB modules connected natively, the registerHub parameter is usb. To use modules connected to a YoctoHub-Wireless-SR, you must simply replace this parameter by the IP address of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR. For instance, in Delphi:
YRegisterHub("usb",errmsg);
becomes
YRegisterHub("192.168.0.10",errmsg); // The hub IP address is 192.168.0.10
8.2. Controlling the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR
From the programming API standpoint, the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is a module like the others. You can perfectly manage it from the Yoctopuce API. To do so, you need the following classes:
Module
This class, shared by all Yoctopuce modules, enables you to control the module itself. You can drive the Yocto-led, know the USB power consumption of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR, and so on.
Network
This class enables you to manage the network part of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR. You can control the link state, read the MAC address, change the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR IP address, know the power consumption on PoE, and so on.
HubPort
This class enables you to manage the hub part. You can enable or disable the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR ports, you can also know which module is connected to which port.
Files
This class enables you to access files stored in the flash memory of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR. The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR contains a small file system which allows you to store, for example, a web application controlling the modules connected to the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR.
WakeUpMonitor
This class enables you to monitor the sleep mode of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR.
WakeUpSchedule
This class enables you to schedule one or several wake ups for the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR.
You can find some examples on how to drive the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR by software in the Yoctopuce programming libraries, available free of charge on the Yoctopuce web site.
9. Sleep mode
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR includes a real time clock (RTC) powered by a super capacitor. This capacitor charges itself automatically when the module is powered. But it is able to keep time without any power for several days. This RTC is used to drive a sleep and wake up system to save power. You can configure the sleep system manually through an interface or drive it through software.
9.1. Manual configuration of the wake ups
You can manually configure the wake up conditions by connecting yourself on the interface of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR. In the Wake-up scheduler section of the main configuration window, click on the setup button corresponding to one of the "wakeup-schedule". This opens a window enabling you to schedule more or less regular wake ups. Select the boxes corresponding to the wanted occurrences. Empty sections are ignored.
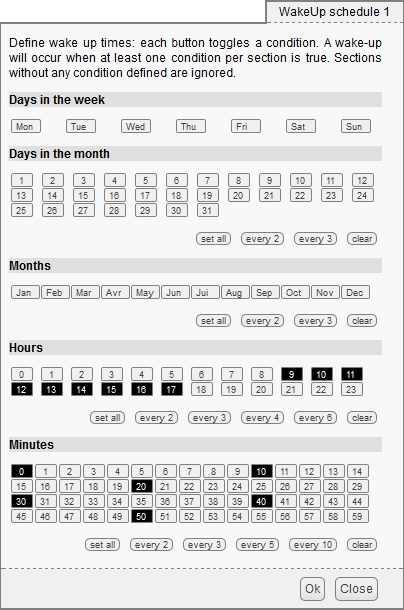
Wake up configuration window: here every 10 minutes between 9h and 17h.
Likewise, you can configure directly in the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR interface the maximal wake up duration, after which the module automatically goes back to sleep. If your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is running on batteries, this ensures they do not empty even if no explicit sleep command is received.
9.2. Configuring the wake up system by software
At the programming interface level, the wake up system is implemented with two types of functions: the wakeUpMonitor function and the wakeUpSchedule function.
wakeUpMonitor
The wakeUpMonitor function manages wake ups and sleep periods, proper. It provides all the instant managing functionalities : instant wake up, instant sleep, computing the date of the next wake up, and so on...
The wakeUpMonitor function enables you also to define the maximum duration during which the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR stays awake before automatically going back to sleep.
wakeUpSchedule
The wakeUpSchedule function enables you to program a wake up condition followed by a possible sleep. It includes five variables enabling you to define correspondences on minutes, hours, days of the week, days of the month, and months. These variables are integers where each bit defines a correspondence. Schematically, each set of minutes, hours, and days is represented as a set of boxes with each a coefficient which is a power of two, exactly like in the corresponding interface of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR.
For example, bit 0 for the hours corresponds to hour zero, bit 1 corresponds to hour 1, bit 2 to hour 2, and so on.

To each box is assigned a power of two
Thus, to program the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR for it to wake up every day at noon, you must set bit 12 to 1, which corresponds to the value 2^12 = 4096.

Example for a wake up at 12h
For the module to wake up at 0 hour, 6 hours, and 12 hours, you must set the 0, 6, and 12 bits to 1, which corresponds to the value 2^0 +2^6 +2^12 = 1 + 64 + 4096 = 4161

Example for wake ups at 0, 6, and 12h
Variables can be combined. For a wake up to happen every day at 6h05, 6h10, 12h05, and 12h10, you must set the hours to 2^6 + 2^12 = 4060, minutes to 2^5 and 2^10 = 1056. Variables remaining at the zero value are ignored.

Example for wake ups at 6H05, 6h10, 12h05, and 12h10
Note that if you want to program a wake up at 6h05 and 12h10, but not at 6h10 and 12h05, you need to use two distinct wakeUpSchedule functions.
This paradigm allows you to schedule complex wake ups. Thus, to program a wake up every first Tuesday of the month, you must set to 1 bit 1 of the days of the week and the first seven bits of the days of the month.

Example for a wake up every first Tuesday of the month
Some programming languages, among which JavaScript, do not support 64 bit integers. This is an issue for encoding minutes. Therefore, minutes are available both through a 64 bit integer minutes and two 32 bit integers minutesA and minutesB. These 32 bit integers are supposed to be available in any current programming language.

Minutes are also available in the shape of two 32 bit integers
The wakeUpSchedule function includes an additional variable to define the duration, in seconds, during which the module stays awake after a wake up. If this variable is set to zero, the modules stays awake.
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR includes two wakeUpSchedule functions, enabling you to program up to two independent wake up types.
10. Personalizing the web interface
Your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR contains a small embedded file system, allowing it to store personalized files for its own use. You can manipulate the file system thanks to the yocto_files library. You can store there the files you want to. If need be, you can store a web application enabling you to manage modules connected to your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR.
10.1. Using the file system
Interactive use
The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR web interface provides a succinct interface to manipulate the content of the file system: simply click the configuration button corresponding to your module in the hub interface, then the manage files button. The files are listed and you can view them, erase them, or add new ones (downloads).
Because of its small size, the file system does not have an explicit concept of directories. You can nevertheless use the slash sign "/" inside file names to sort them as if they were in directories.
Programmed use
Use the yocto_files library to manage the file system. Basic functions are available:
- upload creates a new file on the module, with a content that you provide;
- get_list lists the files on the module, including their content size and CRC32;
- download retrieves in a variable the content of a file present on the module;
- remove erases a file from the module;
- format resets the file system to an empty, not fragmented state.
A piece of software using a well designed file system should always start by making sure that all the files necessary for its working are available on the module and, if needed, upload them on the module. We can thus transparently manage software updates and application deployment on new modules. To make file versions easier to detect, the get_list method returns for each file a 32 bit signature called CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) which identifies in a reliable manner the file content. Thus, if the file CRC corresponds, there is less than one chance over 4 billions that the content is not the correct one. You can even compute in advance in your software the CRC of the content you want, and therefore check it without having to download the files. The CRC function used by the Yoctopuce file system is the same as Ethernet, Gzip, PNG, etc. Its characteristic value for the nine character string "123456789" is 0xCBF43926.
HTTP use
You can access the files that your have downloaded on your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR by HTTP at the root of the module (at the same level as the REST API). This allows you to load personalized HTML and Javascript interface pages, for example. You cannot, however, replace the content of a file preloaded on the module, you can only add new ones.
UI and optimisation
Since you can store files on the hub file system, you can easily build a web application to control the devices connected to the hub and store it directly on the hub. This is a very convenient way to build system remote controlled by tablets or smart phones. However the web server embedded in the hub have limited connectivity capabilities: only a few number of sockets can be opened at the same time. Since most web browsers tend to open as many connection as they can to load all elements in a web page, this might lead to very long loading time. To prevent this, try to keep your UI pages as compact as possible by embedding the javascript, CSS code and if possible, images in base64 code.
10.2. Limitations
The file system embedded on your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR has some technical limitations:
- Its maximal storage space is 3.5Mo, allocated in blocks enabling to store up to about 800 files.
- Erasing a file does not necessarily immediately free all the space used by the file. The non freed space is completely reused if you create a new file with the same name, but not necessarily if you create files with a distinct name each time. For this reason, it is not recommended to automatically create files with distinct names.
- You can recover the complete non freed space with the format command which frees all the files.
- Each firmware update implicitly provokes a complete reformatting of the file system.
- As all flash memories, the memory used to store the files has a life of about 100'000 erasing cycles. It is enough, but it is not infinite. Make sure that you do not write and erase files uselessly and very quickly in a loop, or you may destroy your module.
11. High-level API Reference
This chapter summarizes the high-level API functions to drive your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR. Syntax and exact type names may vary from one language to another, but, unless otherwise stated, all the functions are available in every language. For detailed information regarding the types of arguments and return values for a given language, refer to the definition file for this language (yocto_api.* as well as the other yocto_* files that define the function interfaces).
For languages which support exceptions, all of these functions throw exceptions in case of error by default, rather than returning the documented error value for each function. This is by design, to facilitate debugging. It is however possible to disable the use of exceptions using the yDisableExceptions() function, in case you prefer to work with functions that return error values.
This chapter does not explain Yoctopuce programming concepts, in order to stay as concise as possible. You will find more details in the documentation of the devices you plan to connect to your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR.
11.1. Class YHubPort
YoctoHub slave port control interface, available for instance in the YoctoHub-Ethernet, the YoctoHub-GSM-4G, the YoctoHub-Shield or the YoctoHub-Wireless-n
The YHubPort class provides control over the power supply for slave ports on a YoctoHub. It provide information about the device connected to it. The logical name of a YHubPort is always automatically set to the unique serial number of the Yoctopuce device connected to it.
In order to use the functions described here, you should include:
es | in HTML: <script src="../../lib/yocto_hubport.js"></script> in node.js: require('yoctolib-es2017/yocto_hubport.js'); |
js | <script type='text/javascript' src='yocto_hubport.js'></script> |
cpp | #include "yocto_hubport.h" |
m | #import "yocto_hubport.h" |
pas | uses yocto_hubport; |
vb | yocto_hubport.vb |
cs | yocto_hubport.cs |
java | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YHubPort; |
uwp | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YHubPort; |
py | from yocto_hubport import * |
php | require_once('yocto_hubport.php'); |
ts | in HTML: import { YHubPort } from '../../dist/esm/yocto_hubport.js'; in Node.js: import { YHubPort } from 'yoctolib-cjs/yocto_hubport.js'; |
dnp | import YoctoProxyAPI.YHubPortProxy |
cp | #include "yocto_hubport_proxy.h" |
vi | YHubPort.vi |
ml | import YoctoProxyAPI.YHubPortProxy |
| Global functions |
|---|
| YHubPort.FindHubPort(func) |
Retrieves a YoctoHub slave port for a given identifier. |
| YHubPort.FindHubPortInContext(yctx, func) |
Retrieves a YoctoHub slave port for a given identifier in a YAPI context. |
| YHubPort.FirstHubPort() |
Starts the enumeration of YoctoHub slave ports currently accessible. |
| YHubPort.FirstHubPortInContext(yctx) |
Starts the enumeration of YoctoHub slave ports currently accessible. |
| YHubPort.GetSimilarFunctions() |
Enumerates all functions of type HubPort available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID. |
| YHubPort properties |
| hubport→AdvertisedValue [read-only] |
Short string representing the current state of the function. |
| hubport→Enabled [writable] |
True if the YoctoHub port is powered, false otherwise. |
| hubport→FriendlyName [read-only] |
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| hubport→FunctionId [read-only] |
Hardware identifier of the YoctoHub slave port, without reference to the module. |
| hubport→HardwareId [read-only] |
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| hubport→IsOnline [read-only] |
Checks if the function is currently reachable. |
| hubport→LogicalName [writable] |
Logical name of the function. |
| hubport→PortState [read-only] |
Current state of the YoctoHub port. |
| hubport→SerialNumber [read-only] |
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| YHubPort methods |
| hubport→clearCache() |
Invalidates the cache. |
| hubport→describe() |
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the YoctoHub slave port in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| hubport→get_advertisedValue() |
Returns the current value of the YoctoHub slave port (no more than 6 characters). |
| hubport→get_baudRate() |
Returns the current baud rate used by this YoctoHub port, in kbps. |
| hubport→get_enabled() |
Returns true if the YoctoHub port is powered, false otherwise. |
| hubport→get_errorMessage() |
Returns the error message of the latest error with the YoctoHub slave port. |
| hubport→get_errorType() |
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the YoctoHub slave port. |
| hubport→get_friendlyName() |
Returns a global identifier of the YoctoHub slave port in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| hubport→get_functionDescriptor() |
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function. |
| hubport→get_functionId() |
Returns the hardware identifier of the YoctoHub slave port, without reference to the module. |
| hubport→get_hardwareId() |
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the YoctoHub slave port in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| hubport→get_logicalName() |
Returns the logical name of the YoctoHub slave port. |
| hubport→get_module() |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located. |
| hubport→get_module_async(callback, context) |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version). |
| hubport→get_portState() |
Returns the current state of the YoctoHub port. |
| hubport→get_serialNumber() |
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| hubport→get_userData() |
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData. |
| hubport→isOnline() |
Checks if the YoctoHub slave port is currently reachable, without raising any error. |
| hubport→isOnline_async(callback, context) |
Checks if the YoctoHub slave port is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version). |
| hubport→isReadOnly() |
Test if the function is readOnly. |
| hubport→load(msValidity) |
Preloads the YoctoHub slave port cache with a specified validity duration. |
| hubport→loadAttribute(attrName) |
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value. |
| hubport→load_async(msValidity, callback, context) |
Preloads the YoctoHub slave port cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version). |
| hubport→muteValueCallbacks() |
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| hubport→nextHubPort() |
Continues the enumeration of YoctoHub slave ports started using yFirstHubPort(). |
| hubport→registerValueCallback(callback) |
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value. |
| hubport→set_enabled(newval) |
Changes the activation of the YoctoHub port. |
| hubport→set_logicalName(newval) |
Changes the logical name of the YoctoHub slave port. |
| hubport→set_userData(data) |
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function. |
| hubport→unmuteValueCallbacks() |
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| hubport→wait_async(callback, context) |
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function. |
YHubPort.FindHubPort()
YHubPort.FindHubPort()yFindHubPort()YHubPort::FindHubPort()[YHubPort FindHubPort: ]yFindHubPort()YHubPort.FindHubPort()YHubPort.FindHubPort()YHubPort.FindHubPort()YHubPort.FindHubPort()YHubPort.FindHubPort()YHubPort::FindHubPort()YHubPort.FindHubPort()YHubPort.FindHubPort()YHubPort.FindHubPort()YHubPort.FindHubPort()
Retrieves a YoctoHub slave port for a given identifier.
js | function yFindHubPort( | func) |
cpp | YHubPort* FindHubPort( | string func) |
m | +(YHubPort*) FindHubPort | : (NSString*) func |
pas | TYHubPort yFindHubPort( | func: string): TYHubPort |
vb | function FindHubPort( | ByVal func As String) As YHubPort |
cs | static YHubPort FindHubPort( | string func) |
java | static YHubPort FindHubPort( | String func) |
uwp | static YHubPort FindHubPort( | string func) |
py | FindHubPort( | func) |
php | function FindHubPort( | $func) |
ts | static FindHubPort( | func: string): YHubPort |
es | static FindHubPort( | func) |
dnp | static YHubPortProxy FindHubPort( | string func) |
cp | static YHubPortProxy * FindHubPort( | string func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the YoctoHub slave port is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YHubPort.isOnline() to test if the YoctoHub slave port is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a YoctoHub slave port by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
If a call to this object's is_online() method returns FALSE although you are certain that the matching device is plugged, make sure that you did call registerHub() at application initialization time.
Parameters :
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the YoctoHub slave port, for instance YHUBETH1.hubPort1. |
Returns :
a YHubPort object allowing you to drive the YoctoHub slave port.
YHubPort.FindHubPortInContext()
YHubPort.FindHubPortInContext()YHubPort.FindHubPortInContext()YHubPort.FindHubPortInContext()YHubPort.FindHubPortInContext()YHubPort.FindHubPortInContext()
Retrieves a YoctoHub slave port for a given identifier in a YAPI context.
java | static YHubPort FindHubPortInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, String func) |
uwp | static YHubPort FindHubPortInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, string func) |
ts | static FindHubPortInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext, func: string): YHubPort |
es | static FindHubPortInContext( | yctx, func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the YoctoHub slave port is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YHubPort.isOnline() to test if the YoctoHub slave port is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a YoctoHub slave port by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context |
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the YoctoHub slave port, for instance YHUBETH1.hubPort1. |
Returns :
a YHubPort object allowing you to drive the YoctoHub slave port.
YHubPort.FirstHubPort()
YHubPort.FirstHubPort()yFirstHubPort()YHubPort::FirstHubPort()[YHubPort FirstHubPort]yFirstHubPort()YHubPort.FirstHubPort()YHubPort.FirstHubPort()YHubPort.FirstHubPort()YHubPort.FirstHubPort()YHubPort.FirstHubPort()YHubPort::FirstHubPort()YHubPort.FirstHubPort()YHubPort.FirstHubPort()
Starts the enumeration of YoctoHub slave ports currently accessible.
js | function yFirstHubPort( | ) |
cpp | YHubPort * FirstHubPort( | ) |
m | +(YHubPort*) FirstHubPort |
pas | TYHubPort yFirstHubPort( | ): TYHubPort |
vb | function FirstHubPort( | ) As YHubPort |
cs | static YHubPort FirstHubPort( | ) |
java | static YHubPort FirstHubPort( | ) |
uwp | static YHubPort FirstHubPort( | ) |
py | FirstHubPort( | ) |
php | function FirstHubPort( | ) |
ts | static FirstHubPort( | ): YHubPort | null |
es | static FirstHubPort( | ) |
Use the method YHubPort.nextHubPort() to iterate on next YoctoHub slave ports.
Returns :
a pointer to a YHubPort object, corresponding to the first YoctoHub slave port currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YHubPort.FirstHubPortInContext()
YHubPort.FirstHubPortInContext()YHubPort.FirstHubPortInContext()YHubPort.FirstHubPortInContext()YHubPort.FirstHubPortInContext()YHubPort.FirstHubPortInContext()
Starts the enumeration of YoctoHub slave ports currently accessible.
java | static YHubPort FirstHubPortInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
uwp | static YHubPort FirstHubPortInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
ts | static FirstHubPortInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext): YHubPort | null |
es | static FirstHubPortInContext( | yctx) |
Use the method YHubPort.nextHubPort() to iterate on next YoctoHub slave ports.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context. |
Returns :
a pointer to a YHubPort object, corresponding to the first YoctoHub slave port currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YHubPort.GetSimilarFunctions()
YHubPort.GetSimilarFunctions()YHubPort.GetSimilarFunctions()YHubPort.GetSimilarFunctions()
Enumerates all functions of type HubPort available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID.
dnp | static new string[] GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
cp | static vector<string> GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
Each of these IDs can be provided as argument to the method YHubPort.FindHubPort to obtain an object that can control the corresponding device.
Returns :
an array of strings, each string containing the unique hardwareId of a device function currently connected.
hubport→AdvertisedValuehubport.AdvertisedValue
Short string representing the current state of the function.
dnp | string AdvertisedValue |
hubport→Enabledhubport.Enabled
True if the YoctoHub port is powered, false otherwise.
dnp | int Enabled |
Writable. Changes the activation of the YoctoHub port. If the port is enabled, the connected module is powered. Otherwise, port power is shut down.
hubport→FriendlyNamehubport.FriendlyName
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
dnp | string FriendlyName |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the function if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the function (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
hubport→FunctionIdhubport.FunctionId
Hardware identifier of the YoctoHub slave port, without reference to the module.
dnp | string FunctionId |
For example relay1
hubport→HardwareIdhubport.HardwareId
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
dnp | string HardwareId |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the function (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
hubport→IsOnlinehubport.IsOnline
Checks if the function is currently reachable.
dnp | bool IsOnline |
If there is a cached value for the function in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the function.
hubport→LogicalNamehubport.LogicalName
Logical name of the function.
dnp | string LogicalName |
Writable. You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
hubport→PortStatehubport.PortState
Current state of the YoctoHub port.
dnp | int PortState |
hubport→SerialNumberhubport.SerialNumber
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
dnp | string SerialNumber |
hubport→clearCache()hubport.clearCache()hubport→clearCache()[hubport clearCache]hubport.clearCache()hubport.clearCache()hubport.clearCache()hubport.clearCache()hubport.clearCache()hubport→clearCache()hubport.clearCache()hubport.clearCache()
Invalidates the cache.
js | function clearCache( | ) |
cpp | void clearCache( | ) |
m | -(void) clearCache |
pas | clearCache( | ) |
vb | procedure clearCache( | ) |
cs | void clearCache( | ) |
java | void clearCache( | ) |
py | clearCache( | ) |
php | function clearCache( | ) |
ts | async clearCache( | ): Promise<void> |
es | async clearCache( | ) |
Invalidates the cache of the YoctoHub slave port attributes. Forces the next call to get_xxx() or loadxxx() to use values that come from the device.
hubport→describe()hubport.describe()hubport→describe()[hubport describe]hubport.describe()hubport.describe()hubport.describe()hubport.describe()hubport.describe()hubport→describe()hubport.describe()hubport.describe()
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the YoctoHub slave port in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function describe( | ) |
cpp | string describe( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) describe |
pas | string describe( | ): string |
vb | function describe( | ) As String |
cs | string describe( | ) |
java | String describe( | ) |
py | describe( | ) |
php | function describe( | ) |
ts | async describe( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async describe( | ) |
More precisely, TYPE is the type of the function, NAME it the name used for the first access to the function, SERIAL is the serial number of the module if the module is connected or "unresolved", and FUNCTIONID is the hardware identifier of the function if the module is connected. For example, this method returns Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1 if the module is already connected or Relay(BadCustomeName.relay1)=unresolved if the module has not yet been connected. This method does not trigger any USB or TCP transaction and can therefore be used in a debugger.
Returns :
a string that describes the YoctoHub slave port (ex: Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
hubport→get_advertisedValue()
hubport→advertisedValue()hubport.get_advertisedValue()hubport→get_advertisedValue()[hubport advertisedValue]hubport.get_advertisedValue()hubport.get_advertisedValue()hubport.get_advertisedValue()hubport.get_advertisedValue()hubport.get_advertisedValue()hubport.get_advertisedValue()hubport→get_advertisedValue()hubport.get_advertisedValue()hubport.get_advertisedValue()hubport.get_advertisedValue()hubport.get_advertisedValue()YHubPort get_advertisedValue
Returns the current value of the YoctoHub slave port (no more than 6 characters).
js | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cpp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) advertisedValue |
pas | string get_advertisedValue( | ): string |
vb | function get_advertisedValue( | ) As String |
cs | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
java | String get_advertisedValue( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_advertisedValue( | ) |
py | get_advertisedValue( | ) |
php | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
ts | async get_advertisedValue( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_advertisedValue( | ) |
dnp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cmd | YHubPort target get_advertisedValue |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the current value of the YoctoHub slave port (no more than 6 characters).
On failure, throws an exception or returns YHubPort.ADVERTISEDVALUE_INVALID.
hubport→get_baudRate()
hubport→baudRate()hubport.get_baudRate()hubport→get_baudRate()[hubport baudRate]hubport.get_baudRate()hubport.get_baudRate()hubport.get_baudRate()hubport.get_baudRate()hubport.get_baudRate()hubport.get_baudRate()hubport→get_baudRate()hubport.get_baudRate()hubport.get_baudRate()hubport.get_baudRate()hubport.get_baudRate()YHubPort get_baudRate
Returns the current baud rate used by this YoctoHub port, in kbps.
js | function get_baudRate( | ) |
cpp | int get_baudRate( | ) |
m | -(int) baudRate |
pas | LongInt get_baudRate( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_baudRate( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_baudRate( | ) |
java | int get_baudRate( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_baudRate( | ) |
py | get_baudRate( | ) |
php | function get_baudRate( | ) |
ts | async get_baudRate( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_baudRate( | ) |
dnp | int get_baudRate( | ) |
cp | int get_baudRate( | ) |
cmd | YHubPort target get_baudRate |
The default value is 1000 kbps, but a slower rate may be used if communication problems are encountered.
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the current baud rate used by this YoctoHub port, in kbps
On failure, throws an exception or returns YHubPort.BAUDRATE_INVALID.
hubport→get_enabled()
hubport→enabled()hubport.get_enabled()hubport→get_enabled()[hubport enabled]hubport.get_enabled()hubport.get_enabled()hubport.get_enabled()hubport.get_enabled()hubport.get_enabled()hubport.get_enabled()hubport→get_enabled()hubport.get_enabled()hubport.get_enabled()hubport.get_enabled()hubport.get_enabled()YHubPort get_enabled
Returns true if the YoctoHub port is powered, false otherwise.
js | function get_enabled( | ) |
cpp | Y_ENABLED_enum get_enabled( | ) |
m | -(Y_ENABLED_enum) enabled |
pas | Integer get_enabled( | ): Integer |
vb | function get_enabled( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_enabled( | ) |
java | int get_enabled( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_enabled( | ) |
py | get_enabled( | ) |
php | function get_enabled( | ) |
ts | async get_enabled( | ): Promise<YHubPort_Enabled> |
es | async get_enabled( | ) |
dnp | int get_enabled( | ) |
cp | int get_enabled( | ) |
cmd | YHubPort target get_enabled |
Returns :
either YHubPort.ENABLED_FALSE or YHubPort.ENABLED_TRUE, according to true if the YoctoHub port is powered, false otherwise
On failure, throws an exception or returns YHubPort.ENABLED_INVALID.
hubport→get_errorMessage()
hubport→errorMessage()hubport.get_errorMessage()hubport→get_errorMessage()[hubport errorMessage]hubport.get_errorMessage()hubport.get_errorMessage()hubport.get_errorMessage()hubport.get_errorMessage()hubport.get_errorMessage()hubport→get_errorMessage()hubport.get_errorMessage()hubport.get_errorMessage()
Returns the error message of the latest error with the YoctoHub slave port.
js | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
cpp | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) errorMessage |
pas | string get_errorMessage( | ): string |
vb | function get_errorMessage( | ) As String |
cs | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
java | String get_errorMessage( | ) |
py | get_errorMessage( | ) |
php | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
ts | get_errorMessage( | ): string |
es | get_errorMessage( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a string corresponding to the latest error message that occured while using the YoctoHub slave port object
hubport→get_errorType()
hubport→errorType()hubport.get_errorType()hubport→get_errorType()[hubport errorType]hubport.get_errorType()hubport.get_errorType()hubport.get_errorType()hubport.get_errorType()hubport.get_errorType()hubport→get_errorType()hubport.get_errorType()hubport.get_errorType()
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the YoctoHub slave port.
js | function get_errorType( | ) |
cpp | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
m | -(YRETCODE) errorType |
pas | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ): YRETCODE |
vb | function get_errorType( | ) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
java | int get_errorType( | ) |
py | get_errorType( | ) |
php | function get_errorType( | ) |
ts | get_errorType( | ): number |
es | get_errorType( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a number corresponding to the code of the latest error that occurred while using the YoctoHub slave port object
hubport→get_friendlyName()
hubport→friendlyName()hubport.get_friendlyName()hubport→get_friendlyName()[hubport friendlyName]hubport.get_friendlyName()hubport.get_friendlyName()hubport.get_friendlyName()hubport→get_friendlyName()hubport.get_friendlyName()hubport.get_friendlyName()hubport.get_friendlyName()hubport.get_friendlyName()
Returns a global identifier of the YoctoHub slave port in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
js | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
cpp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) friendlyName |
cs | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
java | String get_friendlyName( | ) |
py | get_friendlyName( | ) |
php | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
ts | async get_friendlyName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_friendlyName( | ) |
dnp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
cp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the YoctoHub slave port if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the YoctoHub slave port (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the YoctoHub slave port using logical names (ex: MyCustomName.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YHubPort.FRIENDLYNAME_INVALID.
hubport→get_functionDescriptor()
hubport→functionDescriptor()hubport.get_functionDescriptor()hubport→get_functionDescriptor()[hubport functionDescriptor]hubport.get_functionDescriptor()hubport.get_functionDescriptor()hubport.get_functionDescriptor()hubport.get_functionDescriptor()hubport.get_functionDescriptor()hubport→get_functionDescriptor()hubport.get_functionDescriptor()hubport.get_functionDescriptor()
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function.
js | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
cpp | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
m | -(YFUN_DESCR) functionDescriptor |
pas | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ): YFUN_DESCR |
vb | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) As YFUN_DESCR |
cs | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
java | String get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
py | get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
php | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
ts | async get_functionDescriptor( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
This identifier can be used to test if two instances of YFunction reference the same physical function on the same physical device.
Returns :
an identifier of type YFUN_DESCR.
If the function has never been contacted, the returned value is Y$CLASSNAME$.FUNCTIONDESCRIPTOR_INVALID.
hubport→get_functionId()
hubport→functionId()hubport.get_functionId()hubport→get_functionId()[hubport functionId]hubport.get_functionId()hubport.get_functionId()hubport.get_functionId()hubport.get_functionId()hubport→get_functionId()hubport.get_functionId()hubport.get_functionId()hubport.get_functionId()hubport.get_functionId()
Returns the hardware identifier of the YoctoHub slave port, without reference to the module.
js | function get_functionId( | ) |
cpp | string get_functionId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) functionId |
vb | function get_functionId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_functionId( | ) |
java | String get_functionId( | ) |
py | get_functionId( | ) |
php | function get_functionId( | ) |
ts | async get_functionId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionId( | ) |
dnp | string get_functionId( | ) |
cp | string get_functionId( | ) |
For example relay1
Returns :
a string that identifies the YoctoHub slave port (ex: relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YHubPort.FUNCTIONID_INVALID.
hubport→get_hardwareId()
hubport→hardwareId()hubport.get_hardwareId()hubport→get_hardwareId()[hubport hardwareId]hubport.get_hardwareId()hubport.get_hardwareId()hubport.get_hardwareId()hubport.get_hardwareId()hubport→get_hardwareId()hubport.get_hardwareId()hubport.get_hardwareId()hubport.get_hardwareId()hubport.get_hardwareId()
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the YoctoHub slave port in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
cpp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) hardwareId |
vb | function get_hardwareId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
java | String get_hardwareId( | ) |
py | get_hardwareId( | ) |
php | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
ts | async get_hardwareId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_hardwareId( | ) |
dnp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
cp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the YoctoHub slave port (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the YoctoHub slave port (ex: RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YHubPort.HARDWAREID_INVALID.
hubport→get_logicalName()
hubport→logicalName()hubport.get_logicalName()hubport→get_logicalName()[hubport logicalName]hubport.get_logicalName()hubport.get_logicalName()hubport.get_logicalName()hubport.get_logicalName()hubport.get_logicalName()hubport.get_logicalName()hubport→get_logicalName()hubport.get_logicalName()hubport.get_logicalName()hubport.get_logicalName()hubport.get_logicalName()YHubPort get_logicalName
Returns the logical name of the YoctoHub slave port.
js | function get_logicalName( | ) |
cpp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) logicalName |
pas | string get_logicalName( | ): string |
vb | function get_logicalName( | ) As String |
cs | string get_logicalName( | ) |
java | String get_logicalName( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_logicalName( | ) |
py | get_logicalName( | ) |
php | function get_logicalName( | ) |
ts | async get_logicalName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_logicalName( | ) |
dnp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cmd | YHubPort target get_logicalName |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the logical name of the YoctoHub slave port.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YHubPort.LOGICALNAME_INVALID.
hubport→get_module()
hubport→module()hubport.get_module()hubport→get_module()[hubport module]hubport.get_module()hubport.get_module()hubport.get_module()hubport.get_module()hubport.get_module()hubport→get_module()hubport.get_module()hubport.get_module()hubport.get_module()hubport.get_module()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located.
js | function get_module( | ) |
cpp | YModule * get_module( | ) |
m | -(YModule*) module |
pas | TYModule get_module( | ): TYModule |
vb | function get_module( | ) As YModule |
cs | YModule get_module( | ) |
java | YModule get_module( | ) |
py | get_module( | ) |
php | function get_module( | ) |
ts | async get_module( | ): Promise<YModule> |
es | async get_module( | ) |
dnp | YModuleProxy get_module( | ) |
cp | YModuleProxy * get_module( | ) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned instance of YModule is not shown as on-line.
Returns :
an instance of YModule
hubport→get_module_async()
hubport→module_async()hubport.get_module_async()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version).
js | function get_module_async( | callback, context) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned YModule object does not show as on-line.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking Firefox JavaScript VM that does not implement context switching during blocking I/O calls. See the documentation section on asynchronous JavasSript calls for more details.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the requested YModule object |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
hubport→get_portState()
hubport→portState()hubport.get_portState()hubport→get_portState()[hubport portState]hubport.get_portState()hubport.get_portState()hubport.get_portState()hubport.get_portState()hubport.get_portState()hubport.get_portState()hubport→get_portState()hubport.get_portState()hubport.get_portState()hubport.get_portState()hubport.get_portState()YHubPort get_portState
Returns the current state of the YoctoHub port.
js | function get_portState( | ) |
cpp | Y_PORTSTATE_enum get_portState( | ) |
m | -(Y_PORTSTATE_enum) portState |
pas | Integer get_portState( | ): Integer |
vb | function get_portState( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_portState( | ) |
java | int get_portState( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_portState( | ) |
py | get_portState( | ) |
php | function get_portState( | ) |
ts | async get_portState( | ): Promise<YHubPort_PortState> |
es | async get_portState( | ) |
dnp | int get_portState( | ) |
cp | int get_portState( | ) |
cmd | YHubPort target get_portState |
Returns :
a value among YHubPort.PORTSTATE_OFF, YHubPort.PORTSTATE_OVRLD, YHubPort.PORTSTATE_ON, YHubPort.PORTSTATE_RUN and YHubPort.PORTSTATE_PROG corresponding to the current state of the YoctoHub port
On failure, throws an exception or returns YHubPort.PORTSTATE_INVALID.
hubport→get_serialNumber()
hubport→serialNumber()hubport.get_serialNumber()hubport→get_serialNumber()[hubport serialNumber]hubport.get_serialNumber()hubport.get_serialNumber()hubport.get_serialNumber()hubport.get_serialNumber()hubport.get_serialNumber()hubport.get_serialNumber()hubport→get_serialNumber()hubport.get_serialNumber()hubport.get_serialNumber()hubport.get_serialNumber()hubport.get_serialNumber()YHubPort get_serialNumber
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
js | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
cpp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) serialNumber |
pas | string get_serialNumber( | ): string |
vb | function get_serialNumber( | ) As String |
cs | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
java | String get_serialNumber( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_serialNumber( | ) |
py | get_serialNumber( | ) |
php | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
ts | async get_serialNumber( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_serialNumber( | ) |
dnp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cmd | YHubPort target get_serialNumber |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFunction.SERIALNUMBER_INVALID.
hubport→get_userData()
hubport→userData()hubport.get_userData()hubport→get_userData()[hubport userData]hubport.get_userData()hubport.get_userData()hubport.get_userData()hubport.get_userData()hubport.get_userData()hubport→get_userData()hubport.get_userData()hubport.get_userData()
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData.
js | function get_userData( | ) |
cpp | void * get_userData( | ) |
m | -(id) userData |
pas | Tobject get_userData( | ): Tobject |
vb | function get_userData( | ) As Object |
cs | object get_userData( | ) |
java | Object get_userData( | ) |
py | get_userData( | ) |
php | function get_userData( | ) |
ts | async get_userData( | ): Promise<object|null> |
es | async get_userData( | ) |
This attribute is never touched directly by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Returns :
the object stored previously by the caller.
hubport→isOnline()hubport.isOnline()hubport→isOnline()[hubport isOnline]hubport.isOnline()hubport.isOnline()hubport.isOnline()hubport.isOnline()hubport.isOnline()hubport→isOnline()hubport.isOnline()hubport.isOnline()hubport.isOnline()hubport.isOnline()
Checks if the YoctoHub slave port is currently reachable, without raising any error.
js | function isOnline( | ) |
cpp | bool isOnline( | ) |
m | -(BOOL) isOnline |
pas | boolean isOnline( | ): boolean |
vb | function isOnline( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isOnline( | ) |
java | boolean isOnline( | ) |
py | isOnline( | ) |
php | function isOnline( | ) |
ts | async isOnline( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isOnline( | ) |
dnp | bool isOnline( | ) |
cp | bool isOnline( | ) |
If there is a cached value for the YoctoHub slave port in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the YoctoHub slave port.
Returns :
true if the YoctoHub slave port can be reached, and false otherwise
hubport→isOnline_async()hubport.isOnline_async()
Checks if the YoctoHub slave port is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version).
js | function isOnline_async( | callback, context) |
If there is a cached value for the YoctoHub slave port in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the requested function.
This asynchronous version exists only in Javascript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the Javascript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the boolean result |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
hubport→isReadOnly()hubport→isReadOnly()[hubport isReadOnly]hubport.isReadOnly()hubport.isReadOnly()hubport.isReadOnly()hubport.isReadOnly()hubport.isReadOnly()hubport.isReadOnly()hubport→isReadOnly()hubport.isReadOnly()hubport.isReadOnly()hubport.isReadOnly()hubport.isReadOnly()YHubPort isReadOnly
Test if the function is readOnly.
cpp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
m | -(bool) isReadOnly |
pas | boolean isReadOnly( | ): boolean |
vb | function isReadOnly( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
java | boolean isReadOnly( | ) |
uwp | async Task<bool> isReadOnly( | ) |
py | isReadOnly( | ) |
php | function isReadOnly( | ) |
ts | async isReadOnly( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isReadOnly( | ) |
dnp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cmd | YHubPort target isReadOnly |
Return true if the function is write protected or that the function is not available.
Returns :
true if the function is readOnly or not online.
hubport→load()hubport.load()hubport→load()[hubport load: ]hubport.load()hubport.load()hubport.load()hubport.load()hubport.load()hubport→load()hubport.load()hubport.load()
Preloads the YoctoHub slave port cache with a specified validity duration.
js | function load( | msValidity) |
cpp | YRETCODE load( | int msValidity) |
m | -(YRETCODE) load | : (u64) msValidity |
pas | YRETCODE load( | msValidity: u64): YRETCODE |
vb | function load( | ByVal msValidity As Long) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE load( | ulong msValidity) |
java | int load( | long msValidity) |
py | load( | msValidity) |
php | function load( | $msValidity) |
ts | async load( | msValidity: number): Promise<number> |
es | async load( | msValidity) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity attributed to the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
hubport→loadAttribute()hubport.loadAttribute()hubport→loadAttribute()[hubport loadAttribute: ]hubport.loadAttribute()hubport.loadAttribute()hubport.loadAttribute()hubport.loadAttribute()hubport.loadAttribute()hubport.loadAttribute()hubport→loadAttribute()hubport.loadAttribute()hubport.loadAttribute()hubport.loadAttribute()hubport.loadAttribute()
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value.
js | function loadAttribute( | attrName) |
cpp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
m | -(NSString*) loadAttribute | : (NSString*) attrName |
pas | string loadAttribute( | attrName: string): string |
vb | function loadAttribute( | ByVal attrName As String) As String |
cs | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
java | String loadAttribute( | String attrName) |
uwp | async Task<string> loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
py | loadAttribute( | attrName) |
php | function loadAttribute( | $attrName) |
ts | async loadAttribute( | attrName: string): Promise<string> |
es | async loadAttribute( | attrName) |
dnp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
cp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
Parameters :
| attrName | the name of the requested attribute |
Returns :
a string with the value of the the attribute
On failure, throws an exception or returns an empty string.
hubport→load_async()hubport.load_async()
Preloads the YoctoHub slave port cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version).
js | function load_async( | msValidity, callback, context) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the JavaScript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity of the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the error code (or YAPI.SUCCESS) |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
hubport→muteValueCallbacks()hubport.muteValueCallbacks()hubport→muteValueCallbacks()[hubport muteValueCallbacks]hubport.muteValueCallbacks()hubport.muteValueCallbacks()hubport.muteValueCallbacks()hubport.muteValueCallbacks()hubport.muteValueCallbacks()hubport.muteValueCallbacks()hubport→muteValueCallbacks()hubport.muteValueCallbacks()hubport.muteValueCallbacks()hubport.muteValueCallbacks()hubport.muteValueCallbacks()YHubPort muteValueCallbacks
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) muteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt muteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async muteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YHubPort target muteValueCallbacks |
You can use this function to save bandwidth and CPU on computers with limited resources, or to prevent unwanted invocations of the HTTP callback. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
hubport→nextHubPort()hubport.nextHubPort()hubport→nextHubPort()[hubport nextHubPort]hubport.nextHubPort()hubport.nextHubPort()hubport.nextHubPort()hubport.nextHubPort()hubport.nextHubPort()hubport.nextHubPort()hubport→nextHubPort()hubport.nextHubPort()hubport.nextHubPort()
Continues the enumeration of YoctoHub slave ports started using yFirstHubPort().
js | function nextHubPort( | ) |
cpp | YHubPort * nextHubPort( | ) |
m | -(nullable YHubPort*) nextHubPort |
pas | TYHubPort nextHubPort( | ): TYHubPort |
vb | function nextHubPort( | ) As YHubPort |
cs | YHubPort nextHubPort( | ) |
java | YHubPort nextHubPort( | ) |
uwp | YHubPort nextHubPort( | ) |
py | nextHubPort( | ) |
php | function nextHubPort( | ) |
ts | nextHubPort( | ): YHubPort | null |
es | nextHubPort( | ) |
Caution: You can't make any assumption about the returned YoctoHub slave ports order. If you want to find a specific a YoctoHub slave port, use HubPort.findHubPort() and a hardwareID or a logical name.
Returns :
a pointer to a YHubPort object, corresponding to a YoctoHub slave port currently online, or a null pointer if there are no more YoctoHub slave ports to enumerate.
hubport→registerValueCallback()hubport.registerValueCallback()hubport→registerValueCallback()[hubport registerValueCallback: ]hubport.registerValueCallback()hubport.registerValueCallback()hubport.registerValueCallback()hubport.registerValueCallback()hubport.registerValueCallback()hubport.registerValueCallback()hubport→registerValueCallback()hubport.registerValueCallback()hubport.registerValueCallback()
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value.
js | function registerValueCallback( | callback) |
cpp | int registerValueCallback( | YHubPortValueCallback callback) |
m | -(int) registerValueCallback | : (YHubPortValueCallback _Nullable) callback |
pas | LongInt registerValueCallback( | callback: TYHubPortValueCallback): LongInt |
vb | function registerValueCallback( | ByVal callback As YHubPortValueCallback) As Integer |
cs | int registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
java | int registerValueCallback( | UpdateCallback callback) |
uwp | async Task<int> registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
py | registerValueCallback( | callback) |
php | function registerValueCallback( | $callback) |
ts | async registerValueCallback( | callback: YHubPortValueCallback | null): Promise<number> |
es | async registerValueCallback( | callback) |
The callback is invoked only during the execution of ySleep or yHandleEvents. This provides control over the time when the callback is triggered. For good responsiveness, remember to call one of these two functions periodically. To unregister a callback, pass a null pointer as argument.
Parameters :
| callback | the callback function to call, or a null pointer. The callback function should take two arguments: the function object of which the value has changed, and the character string describing the new advertised value. |
hubport→set_enabled()
hubport→setEnabled()hubport.set_enabled()hubport→set_enabled()[hubport setEnabled: ]hubport.set_enabled()hubport.set_enabled()hubport.set_enabled()hubport.set_enabled()hubport.set_enabled()hubport.set_enabled()hubport→set_enabled()hubport.set_enabled()hubport.set_enabled()hubport.set_enabled()hubport.set_enabled()YHubPort set_enabled
Changes the activation of the YoctoHub port.
js | function set_enabled( | newval) |
cpp | int set_enabled( | Y_ENABLED_enum newval) |
m | -(int) setEnabled | : (Y_ENABLED_enum) newval |
pas | integer set_enabled( | newval: Integer): integer |
vb | function set_enabled( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_enabled( | int newval) |
java | int set_enabled( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_enabled( | int newval) |
py | set_enabled( | newval) |
php | function set_enabled( | $newval) |
ts | async set_enabled( | newval: YHubPort_Enabled): Promise<number> |
es | async set_enabled( | newval) |
dnp | int set_enabled( | int newval) |
cp | int set_enabled( | int newval) |
cmd | YHubPort target set_enabled | newval |
If the port is enabled, the connected module is powered. Otherwise, port power is shut down.
Parameters :
| newval | either YHubPort.ENABLED_FALSE or YHubPort.ENABLED_TRUE, according to the activation of the YoctoHub port |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
hubport→set_logicalName()
hubport→setLogicalName()hubport.set_logicalName()hubport→set_logicalName()[hubport setLogicalName: ]hubport.set_logicalName()hubport.set_logicalName()hubport.set_logicalName()hubport.set_logicalName()hubport.set_logicalName()hubport.set_logicalName()hubport→set_logicalName()hubport.set_logicalName()hubport.set_logicalName()hubport.set_logicalName()hubport.set_logicalName()YHubPort set_logicalName
Changes the logical name of the YoctoHub slave port.
js | function set_logicalName( | newval) |
cpp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setLogicalName | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_logicalName( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_logicalName( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
java | int set_logicalName( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_logicalName( | string newval) |
py | set_logicalName( | newval) |
php | function set_logicalName( | $newval) |
ts | async set_logicalName( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_logicalName( | newval) |
dnp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cmd | YHubPort target set_logicalName | newval |
You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the logical name of the YoctoHub slave port. |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
hubport→set_userData()
hubport→setUserData()hubport.set_userData()hubport→set_userData()[hubport setUserData: ]hubport.set_userData()hubport.set_userData()hubport.set_userData()hubport.set_userData()hubport.set_userData()hubport→set_userData()hubport.set_userData()hubport.set_userData()
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function.
js | function set_userData( | data) |
cpp | void set_userData( | void * data) |
m | -(void) setUserData | : (id) data |
pas | set_userData( | data: Tobject) |
vb | procedure set_userData( | ByVal data As Object) |
cs | void set_userData( | object data) |
java | void set_userData( | Object data) |
py | set_userData( | data) |
php | function set_userData( | $data) |
ts | async set_userData( | data: object|null): Promise<void> |
es | async set_userData( | data) |
This attribute is never touched by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Parameters :
| data | any kind of object to be stored |
hubport→unmuteValueCallbacks()hubport.unmuteValueCallbacks()hubport→unmuteValueCallbacks()[hubport unmuteValueCallbacks]hubport.unmuteValueCallbacks()hubport.unmuteValueCallbacks()hubport.unmuteValueCallbacks()hubport.unmuteValueCallbacks()hubport.unmuteValueCallbacks()hubport.unmuteValueCallbacks()hubport→unmuteValueCallbacks()hubport.unmuteValueCallbacks()hubport.unmuteValueCallbacks()hubport.unmuteValueCallbacks()hubport.unmuteValueCallbacks()YHubPort unmuteValueCallbacks
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) unmuteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YHubPort target unmuteValueCallbacks |
This function reverts the effect of a previous call to muteValueCallbacks(). Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
hubport→wait_async()hubport.wait_async()hubport.wait_async()hubport.wait_async()
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function.
js | function wait_async( | callback, context) |
ts | wait_async( | callback: Function, context: object) |
es | wait_async( | callback, context) |
The callback function can therefore freely issue synchronous or asynchronous commands, without risking to block the JavaScript VM.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when all pending commands on the module are completed. The callback function receives two arguments: the caller-specific context object and the receiving function object. |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing.
11.2. Class YWireless
Wireless LAN interface control interface, available for instance in the YoctoHub-Wireless, the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR, the YoctoHub-Wireless-g or the YoctoHub-Wireless-n
The YWireless class provides control over wireless network parameters and status for devices that are wireless-enabled. Note that TCP/IP parameters are configured separately, using class YNetwork.
In order to use the functions described here, you should include:
js | <script type='text/javascript' src='yocto_wireless.js'></script> |
cpp | #include "yocto_wireless.h" |
m | #import "yocto_wireless.h" |
pas | uses yocto_wireless; |
vb | yocto_wireless.vb |
cs | yocto_wireless.cs |
java | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YWireless; |
uwp | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YWireless; |
py | from yocto_wireless import * |
php | require_once('yocto_wireless.php'); |
ts | in HTML: import { YWireless } from '../../dist/esm/yocto_wireless.js'; in Node.js: import { YWireless } from 'yoctolib-cjs/yocto_wireless.js'; |
es | in HTML: <script src="../../lib/yocto_wireless.js"></script> in node.js: require('yoctolib-es2017/yocto_wireless.js'); |
dnp | import YoctoProxyAPI.YWirelessProxy |
cp | #include "yocto_wireless_proxy.h" |
vi | YWireless.vi |
ml | import YoctoProxyAPI.YWirelessProxy |
| Global functions |
|---|
| YWireless.FindWireless(func) |
Retrieves a wireless LAN interface for a given identifier. |
| YWireless.FindWirelessInContext(yctx, func) |
Retrieves a wireless LAN interface for a given identifier in a YAPI context. |
| YWireless.FirstWireless() |
Starts the enumeration of wireless LAN interfaces currently accessible. |
| YWireless.FirstWirelessInContext(yctx) |
Starts the enumeration of wireless LAN interfaces currently accessible. |
| YWireless.GetSimilarFunctions() |
Enumerates all functions of type Wireless available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID. |
| YWireless properties |
| wireless→AdvertisedValue [read-only] |
Short string representing the current state of the function. |
| wireless→FriendlyName [read-only] |
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| wireless→FunctionId [read-only] |
Hardware identifier of the wireless LAN interface, without reference to the module. |
| wireless→HardwareId [read-only] |
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| wireless→IsOnline [read-only] |
Checks if the function is currently reachable. |
| wireless→LinkQuality [read-only] |
Link quality, expressed in percent. |
| wireless→LogicalName [writable] |
Logical name of the function. |
| wireless→SerialNumber [read-only] |
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| wireless→Ssid [read-only] |
Wireless network name (SSID). |
| YWireless methods |
| wireless→adhocNetwork(ssid, securityKey) |
Changes the configuration of the wireless lan interface to create an ad-hoc wireless network, without using an access point. |
| wireless→clearCache() |
Invalidates the cache. |
| wireless→describe() |
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the wireless LAN interface in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| wireless→get_advertisedValue() |
Returns the current value of the wireless LAN interface (no more than 6 characters). |
| wireless→get_channel() |
Returns the 802.11 channel currently used, or 0 when the selected network has not been found. |
| wireless→get_detectedWlans() |
Returns a list of YWlanRecord objects that describe detected Wireless networks. |
| wireless→get_errorMessage() |
Returns the error message of the latest error with the wireless LAN interface. |
| wireless→get_errorType() |
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the wireless LAN interface. |
| wireless→get_friendlyName() |
Returns a global identifier of the wireless LAN interface in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| wireless→get_functionDescriptor() |
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function. |
| wireless→get_functionId() |
Returns the hardware identifier of the wireless LAN interface, without reference to the module. |
| wireless→get_hardwareId() |
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the wireless LAN interface in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| wireless→get_linkQuality() |
Returns the link quality, expressed in percent. |
| wireless→get_logicalName() |
Returns the logical name of the wireless LAN interface. |
| wireless→get_message() |
Returns the latest status message from the wireless interface. |
| wireless→get_module() |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located. |
| wireless→get_module_async(callback, context) |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version). |
| wireless→get_security() |
Returns the security algorithm used by the selected wireless network. |
| wireless→get_serialNumber() |
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| wireless→get_ssid() |
Returns the wireless network name (SSID). |
| wireless→get_userData() |
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData. |
| wireless→get_wlanState() |
Returns the current state of the wireless interface. |
| wireless→isOnline() |
Checks if the wireless LAN interface is currently reachable, without raising any error. |
| wireless→isOnline_async(callback, context) |
Checks if the wireless LAN interface is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version). |
| wireless→isReadOnly() |
Test if the function is readOnly. |
| wireless→joinNetwork(ssid, securityKey) |
Changes the configuration of the wireless lan interface to connect to an existing access point (infrastructure mode). |
| wireless→load(msValidity) |
Preloads the wireless LAN interface cache with a specified validity duration. |
| wireless→loadAttribute(attrName) |
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value. |
| wireless→load_async(msValidity, callback, context) |
Preloads the wireless LAN interface cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version). |
| wireless→muteValueCallbacks() |
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| wireless→nextWireless() |
Continues the enumeration of wireless LAN interfaces started using yFirstWireless(). |
| wireless→registerValueCallback(callback) |
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value. |
| wireless→set_logicalName(newval) |
Changes the logical name of the wireless LAN interface. |
| wireless→set_userData(data) |
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function. |
| wireless→softAPNetwork(ssid, securityKey) |
Changes the configuration of the wireless lan interface to create a new wireless network by emulating a WiFi access point (Soft AP). |
| wireless→startWlanScan() |
Triggers a scan of the wireless frequency and builds the list of available networks. |
| wireless→unmuteValueCallbacks() |
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| wireless→wait_async(callback, context) |
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function. |
YWireless.FindWireless()
YWireless.FindWireless()yFindWireless()YWireless::FindWireless()[YWireless FindWireless: ]yFindWireless()YWireless.FindWireless()YWireless.FindWireless()YWireless.FindWireless()YWireless.FindWireless()YWireless.FindWireless()YWireless::FindWireless()YWireless.FindWireless()YWireless.FindWireless()YWireless.FindWireless()YWireless.FindWireless()
Retrieves a wireless LAN interface for a given identifier.
js | function yFindWireless( | func) |
cpp | YWireless* FindWireless( | string func) |
m | +(YWireless*) FindWireless | : (NSString*) func |
pas | TYWireless yFindWireless( | func: string): TYWireless |
vb | function FindWireless( | ByVal func As String) As YWireless |
cs | static YWireless FindWireless( | string func) |
java | static YWireless FindWireless( | String func) |
uwp | static YWireless FindWireless( | string func) |
py | FindWireless( | func) |
php | function FindWireless( | $func) |
ts | static FindWireless( | func: string): YWireless |
es | static FindWireless( | func) |
dnp | static YWirelessProxy FindWireless( | string func) |
cp | static YWirelessProxy * FindWireless( | string func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the wireless LAN interface is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YWireless.isOnline() to test if the wireless LAN interface is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a wireless LAN interface by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
If a call to this object's is_online() method returns FALSE although you are certain that the matching device is plugged, make sure that you did call registerHub() at application initialization time.
Parameters :
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the wireless LAN interface, for instance YHUBWLN1.wireless. |
Returns :
a YWireless object allowing you to drive the wireless LAN interface.
YWireless.FindWirelessInContext()
YWireless.FindWirelessInContext()YWireless.FindWirelessInContext()YWireless.FindWirelessInContext()YWireless.FindWirelessInContext()YWireless.FindWirelessInContext()
Retrieves a wireless LAN interface for a given identifier in a YAPI context.
java | static YWireless FindWirelessInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, String func) |
uwp | static YWireless FindWirelessInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, string func) |
ts | static FindWirelessInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext, func: string): YWireless |
es | static FindWirelessInContext( | yctx, func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the wireless LAN interface is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YWireless.isOnline() to test if the wireless LAN interface is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a wireless LAN interface by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context |
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the wireless LAN interface, for instance YHUBWLN1.wireless. |
Returns :
a YWireless object allowing you to drive the wireless LAN interface.
YWireless.FirstWireless()
YWireless.FirstWireless()yFirstWireless()YWireless::FirstWireless()[YWireless FirstWireless]yFirstWireless()YWireless.FirstWireless()YWireless.FirstWireless()YWireless.FirstWireless()YWireless.FirstWireless()YWireless.FirstWireless()YWireless::FirstWireless()YWireless.FirstWireless()YWireless.FirstWireless()
Starts the enumeration of wireless LAN interfaces currently accessible.
js | function yFirstWireless( | ) |
cpp | YWireless * FirstWireless( | ) |
m | +(YWireless*) FirstWireless |
pas | TYWireless yFirstWireless( | ): TYWireless |
vb | function FirstWireless( | ) As YWireless |
cs | static YWireless FirstWireless( | ) |
java | static YWireless FirstWireless( | ) |
uwp | static YWireless FirstWireless( | ) |
py | FirstWireless( | ) |
php | function FirstWireless( | ) |
ts | static FirstWireless( | ): YWireless | null |
es | static FirstWireless( | ) |
Use the method YWireless.nextWireless() to iterate on next wireless LAN interfaces.
Returns :
a pointer to a YWireless object, corresponding to the first wireless LAN interface currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YWireless.FirstWirelessInContext()
YWireless.FirstWirelessInContext()YWireless.FirstWirelessInContext()YWireless.FirstWirelessInContext()YWireless.FirstWirelessInContext()YWireless.FirstWirelessInContext()
Starts the enumeration of wireless LAN interfaces currently accessible.
java | static YWireless FirstWirelessInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
uwp | static YWireless FirstWirelessInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
ts | static FirstWirelessInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext): YWireless | null |
es | static FirstWirelessInContext( | yctx) |
Use the method YWireless.nextWireless() to iterate on next wireless LAN interfaces.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context. |
Returns :
a pointer to a YWireless object, corresponding to the first wireless LAN interface currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YWireless.GetSimilarFunctions()
YWireless.GetSimilarFunctions()YWireless.GetSimilarFunctions()YWireless.GetSimilarFunctions()
Enumerates all functions of type Wireless available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID.
dnp | static new string[] GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
cp | static vector<string> GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
Each of these IDs can be provided as argument to the method YWireless.FindWireless to obtain an object that can control the corresponding device.
Returns :
an array of strings, each string containing the unique hardwareId of a device function currently connected.
wireless→AdvertisedValuewireless.AdvertisedValue
Short string representing the current state of the function.
dnp | string AdvertisedValue |
wireless→FriendlyNamewireless.FriendlyName
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
dnp | string FriendlyName |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the function if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the function (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
wireless→FunctionIdwireless.FunctionId
Hardware identifier of the wireless LAN interface, without reference to the module.
dnp | string FunctionId |
For example relay1
wireless→HardwareIdwireless.HardwareId
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
dnp | string HardwareId |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the function (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
wireless→IsOnlinewireless.IsOnline
Checks if the function is currently reachable.
dnp | bool IsOnline |
If there is a cached value for the function in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the function.
wireless→LinkQualitywireless.LinkQuality
Link quality, expressed in percent.
dnp | int LinkQuality |
wireless→LogicalNamewireless.LogicalName
Logical name of the function.
dnp | string LogicalName |
Writable. You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
wireless→SerialNumberwireless.SerialNumber
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
dnp | string SerialNumber |
wireless→Ssidwireless.Ssid
Wireless network name (SSID).
dnp | string Ssid |
wireless→adhocNetwork()wireless.adhocNetwork()wireless→adhocNetwork()[wireless adhocNetwork: ]wireless.adhocNetwork()wireless.adhocNetwork()wireless.adhocNetwork()wireless.adhocNetwork()wireless.adhocNetwork()wireless.adhocNetwork()wireless→adhocNetwork()wireless.adhocNetwork()wireless.adhocNetwork()wireless.adhocNetwork()wireless.adhocNetwork()YWireless adhocNetwork
Changes the configuration of the wireless lan interface to create an ad-hoc wireless network, without using an access point.
js | function adhocNetwork( | ssid, securityKey) |
cpp | int adhocNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
m | -(int) adhocNetwork | : (NSString*) ssid |
| : (NSString*) securityKey |
pas | LongInt adhocNetwork( | ssid: string, securityKey: string): LongInt |
vb | function adhocNetwork( | ByVal ssid As String, ByVal securityKey As String) As Integer |
cs | int adhocNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
java | int adhocNetwork( | String ssid, String securityKey) |
uwp | async Task<int> adhocNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
py | adhocNetwork( | ssid, securityKey) |
php | function adhocNetwork( | $ssid, $securityKey) |
ts | async adhocNetwork( | ssid: string, securityKey: string): Promise<number> |
es | async adhocNetwork( | ssid, securityKey) |
dnp | int adhocNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
cp | int adhocNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
cmd | YWireless target adhocNetwork | ssid securityKey |
On the YoctoHub-Wireless-g and YoctoHub-Wireless-n, you should use softAPNetwork() instead, which emulates an access point (Soft AP) which is more efficient and more widely supported than ad-hoc networks.
When a security key is specified for an ad-hoc network, the network is protected by a WEP40 key (5 characters or 10 hexadecimal digits) or WEP128 key (13 characters or 26 hexadecimal digits). It is recommended to use a well-randomized WEP128 key using 26 hexadecimal digits to maximize security. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method and then to reboot the module to apply this setting.
Parameters :
| ssid | the name of the network to connect to |
| securityKey | the network key, as a character string |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wireless→clearCache()wireless.clearCache()wireless→clearCache()[wireless clearCache]wireless.clearCache()wireless.clearCache()wireless.clearCache()wireless.clearCache()wireless.clearCache()wireless→clearCache()wireless.clearCache()wireless.clearCache()
Invalidates the cache.
js | function clearCache( | ) |
cpp | void clearCache( | ) |
m | -(void) clearCache |
pas | clearCache( | ) |
vb | procedure clearCache( | ) |
cs | void clearCache( | ) |
java | void clearCache( | ) |
py | clearCache( | ) |
php | function clearCache( | ) |
ts | async clearCache( | ): Promise<void> |
es | async clearCache( | ) |
Invalidates the cache of the wireless LAN interface attributes. Forces the next call to get_xxx() or loadxxx() to use values that come from the device.
wireless→describe()wireless.describe()wireless→describe()[wireless describe]wireless.describe()wireless.describe()wireless.describe()wireless.describe()wireless.describe()wireless→describe()wireless.describe()wireless.describe()
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the wireless LAN interface in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function describe( | ) |
cpp | string describe( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) describe |
pas | string describe( | ): string |
vb | function describe( | ) As String |
cs | string describe( | ) |
java | String describe( | ) |
py | describe( | ) |
php | function describe( | ) |
ts | async describe( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async describe( | ) |
More precisely, TYPE is the type of the function, NAME it the name used for the first access to the function, SERIAL is the serial number of the module if the module is connected or "unresolved", and FUNCTIONID is the hardware identifier of the function if the module is connected. For example, this method returns Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1 if the module is already connected or Relay(BadCustomeName.relay1)=unresolved if the module has not yet been connected. This method does not trigger any USB or TCP transaction and can therefore be used in a debugger.
Returns :
a string that describes the wireless LAN interface (ex: Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
wireless→get_advertisedValue()
wireless→advertisedValue()wireless.get_advertisedValue()wireless→get_advertisedValue()[wireless advertisedValue]wireless.get_advertisedValue()wireless.get_advertisedValue()wireless.get_advertisedValue()wireless.get_advertisedValue()wireless.get_advertisedValue()wireless.get_advertisedValue()wireless→get_advertisedValue()wireless.get_advertisedValue()wireless.get_advertisedValue()wireless.get_advertisedValue()wireless.get_advertisedValue()YWireless get_advertisedValue
Returns the current value of the wireless LAN interface (no more than 6 characters).
js | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cpp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) advertisedValue |
pas | string get_advertisedValue( | ): string |
vb | function get_advertisedValue( | ) As String |
cs | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
java | String get_advertisedValue( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_advertisedValue( | ) |
py | get_advertisedValue( | ) |
php | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
ts | async get_advertisedValue( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_advertisedValue( | ) |
dnp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target get_advertisedValue |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the current value of the wireless LAN interface (no more than 6 characters).
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWireless.ADVERTISEDVALUE_INVALID.
wireless→get_channel()
wireless→channel()wireless.get_channel()wireless→get_channel()[wireless channel]wireless.get_channel()wireless.get_channel()wireless.get_channel()wireless.get_channel()wireless.get_channel()wireless.get_channel()wireless→get_channel()wireless.get_channel()wireless.get_channel()wireless.get_channel()wireless.get_channel()YWireless get_channel
Returns the 802.11 channel currently used, or 0 when the selected network has not been found.
js | function get_channel( | ) |
cpp | int get_channel( | ) |
m | -(int) channel |
pas | LongInt get_channel( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_channel( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_channel( | ) |
java | int get_channel( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_channel( | ) |
py | get_channel( | ) |
php | function get_channel( | ) |
ts | async get_channel( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_channel( | ) |
dnp | int get_channel( | ) |
cp | int get_channel( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target get_channel |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the 802.11 channel currently used, or 0 when the selected network has not been found
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWireless.CHANNEL_INVALID.
wireless→get_detectedWlans()
wireless→detectedWlans()wireless.get_detectedWlans()wireless→get_detectedWlans()[wireless detectedWlans]wireless.get_detectedWlans()wireless.get_detectedWlans()wireless.get_detectedWlans()wireless.get_detectedWlans()wireless.get_detectedWlans()wireless.get_detectedWlans()wireless→get_detectedWlans()wireless.get_detectedWlans()wireless.get_detectedWlans()wireless.get_detectedWlans()wireless.get_detectedWlans()YWireless get_detectedWlans
Returns a list of YWlanRecord objects that describe detected Wireless networks.
js | function get_detectedWlans( | ) |
cpp | vector<YWlanRecord> get_detectedWlans( | ) |
m | -(NSMutableArray*) detectedWlans |
pas | TYWlanRecordArray get_detectedWlans( | ): TYWlanRecordArray |
vb | function get_detectedWlans( | ) As List |
cs | List<YWlanRecord> get_detectedWlans( | ) |
java | ArrayList<YWlanRecord> get_detectedWlans( | ) |
uwp | async Task<List<YWlanRecord>> get_detectedWlans( | ) |
py | get_detectedWlans( | ) |
php | function get_detectedWlans( | ) |
ts | async get_detectedWlans( | ): Promise<YWlanRecord[] |
es | async get_detectedWlans( | ) |
dnp | YWlanRecordProxy[] get_detectedWlans( | ) |
cp | vector<YWlanRecordProxy> get_detectedWlans( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target get_detectedWlans |
This list is not updated when the module is already connected to an access point (infrastructure mode). To force an update of this list, startWlanScan() must be called. Note that an languages without garbage collections, the returned list must be freed by the caller.
Returns :
a list of YWlanRecord objects, containing the SSID, channel, link quality and the type of security of the wireless network.
On failure, throws an exception or returns an empty list.
wireless→get_errorMessage()
wireless→errorMessage()wireless.get_errorMessage()wireless→get_errorMessage()[wireless errorMessage]wireless.get_errorMessage()wireless.get_errorMessage()wireless.get_errorMessage()wireless.get_errorMessage()wireless.get_errorMessage()wireless→get_errorMessage()wireless.get_errorMessage()wireless.get_errorMessage()
Returns the error message of the latest error with the wireless LAN interface.
js | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
cpp | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) errorMessage |
pas | string get_errorMessage( | ): string |
vb | function get_errorMessage( | ) As String |
cs | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
java | String get_errorMessage( | ) |
py | get_errorMessage( | ) |
php | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
ts | get_errorMessage( | ): string |
es | get_errorMessage( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a string corresponding to the latest error message that occured while using the wireless LAN interface object
wireless→get_errorType()
wireless→errorType()wireless.get_errorType()wireless→get_errorType()[wireless errorType]wireless.get_errorType()wireless.get_errorType()wireless.get_errorType()wireless.get_errorType()wireless.get_errorType()wireless→get_errorType()wireless.get_errorType()wireless.get_errorType()
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the wireless LAN interface.
js | function get_errorType( | ) |
cpp | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
m | -(YRETCODE) errorType |
pas | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ): YRETCODE |
vb | function get_errorType( | ) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
java | int get_errorType( | ) |
py | get_errorType( | ) |
php | function get_errorType( | ) |
ts | get_errorType( | ): number |
es | get_errorType( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a number corresponding to the code of the latest error that occurred while using the wireless LAN interface object
wireless→get_friendlyName()
wireless→friendlyName()wireless.get_friendlyName()wireless→get_friendlyName()[wireless friendlyName]wireless.get_friendlyName()wireless.get_friendlyName()wireless.get_friendlyName()wireless→get_friendlyName()wireless.get_friendlyName()wireless.get_friendlyName()wireless.get_friendlyName()wireless.get_friendlyName()
Returns a global identifier of the wireless LAN interface in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
js | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
cpp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) friendlyName |
cs | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
java | String get_friendlyName( | ) |
py | get_friendlyName( | ) |
php | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
ts | async get_friendlyName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_friendlyName( | ) |
dnp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
cp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the wireless LAN interface if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the wireless LAN interface (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the wireless LAN interface using logical names (ex: MyCustomName.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWireless.FRIENDLYNAME_INVALID.
wireless→get_functionDescriptor()
wireless→functionDescriptor()wireless.get_functionDescriptor()wireless→get_functionDescriptor()[wireless functionDescriptor]wireless.get_functionDescriptor()wireless.get_functionDescriptor()wireless.get_functionDescriptor()wireless.get_functionDescriptor()wireless.get_functionDescriptor()wireless→get_functionDescriptor()wireless.get_functionDescriptor()wireless.get_functionDescriptor()
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function.
js | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
cpp | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
m | -(YFUN_DESCR) functionDescriptor |
pas | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ): YFUN_DESCR |
vb | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) As YFUN_DESCR |
cs | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
java | String get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
py | get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
php | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
ts | async get_functionDescriptor( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
This identifier can be used to test if two instances of YFunction reference the same physical function on the same physical device.
Returns :
an identifier of type YFUN_DESCR.
If the function has never been contacted, the returned value is Y$CLASSNAME$.FUNCTIONDESCRIPTOR_INVALID.
wireless→get_functionId()
wireless→functionId()wireless.get_functionId()wireless→get_functionId()[wireless functionId]wireless.get_functionId()wireless.get_functionId()wireless.get_functionId()wireless.get_functionId()wireless→get_functionId()wireless.get_functionId()wireless.get_functionId()wireless.get_functionId()wireless.get_functionId()
Returns the hardware identifier of the wireless LAN interface, without reference to the module.
js | function get_functionId( | ) |
cpp | string get_functionId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) functionId |
vb | function get_functionId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_functionId( | ) |
java | String get_functionId( | ) |
py | get_functionId( | ) |
php | function get_functionId( | ) |
ts | async get_functionId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionId( | ) |
dnp | string get_functionId( | ) |
cp | string get_functionId( | ) |
For example relay1
Returns :
a string that identifies the wireless LAN interface (ex: relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWireless.FUNCTIONID_INVALID.
wireless→get_hardwareId()
wireless→hardwareId()wireless.get_hardwareId()wireless→get_hardwareId()[wireless hardwareId]wireless.get_hardwareId()wireless.get_hardwareId()wireless.get_hardwareId()wireless.get_hardwareId()wireless→get_hardwareId()wireless.get_hardwareId()wireless.get_hardwareId()wireless.get_hardwareId()wireless.get_hardwareId()
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the wireless LAN interface in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
cpp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) hardwareId |
vb | function get_hardwareId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
java | String get_hardwareId( | ) |
py | get_hardwareId( | ) |
php | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
ts | async get_hardwareId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_hardwareId( | ) |
dnp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
cp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the wireless LAN interface (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the wireless LAN interface (ex: RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWireless.HARDWAREID_INVALID.
wireless→get_linkQuality()
wireless→linkQuality()wireless.get_linkQuality()wireless→get_linkQuality()[wireless linkQuality]wireless.get_linkQuality()wireless.get_linkQuality()wireless.get_linkQuality()wireless.get_linkQuality()wireless.get_linkQuality()wireless.get_linkQuality()wireless→get_linkQuality()wireless.get_linkQuality()wireless.get_linkQuality()wireless.get_linkQuality()wireless.get_linkQuality()YWireless get_linkQuality
Returns the link quality, expressed in percent.
js | function get_linkQuality( | ) |
cpp | int get_linkQuality( | ) |
m | -(int) linkQuality |
pas | LongInt get_linkQuality( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_linkQuality( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_linkQuality( | ) |
java | int get_linkQuality( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_linkQuality( | ) |
py | get_linkQuality( | ) |
php | function get_linkQuality( | ) |
ts | async get_linkQuality( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_linkQuality( | ) |
dnp | int get_linkQuality( | ) |
cp | int get_linkQuality( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target get_linkQuality |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the link quality, expressed in percent
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWireless.LINKQUALITY_INVALID.
wireless→get_logicalName()
wireless→logicalName()wireless.get_logicalName()wireless→get_logicalName()[wireless logicalName]wireless.get_logicalName()wireless.get_logicalName()wireless.get_logicalName()wireless.get_logicalName()wireless.get_logicalName()wireless.get_logicalName()wireless→get_logicalName()wireless.get_logicalName()wireless.get_logicalName()wireless.get_logicalName()wireless.get_logicalName()YWireless get_logicalName
Returns the logical name of the wireless LAN interface.
js | function get_logicalName( | ) |
cpp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) logicalName |
pas | string get_logicalName( | ): string |
vb | function get_logicalName( | ) As String |
cs | string get_logicalName( | ) |
java | String get_logicalName( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_logicalName( | ) |
py | get_logicalName( | ) |
php | function get_logicalName( | ) |
ts | async get_logicalName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_logicalName( | ) |
dnp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target get_logicalName |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the logical name of the wireless LAN interface.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWireless.LOGICALNAME_INVALID.
wireless→get_message()
wireless→message()wireless.get_message()wireless→get_message()[wireless message]wireless.get_message()wireless.get_message()wireless.get_message()wireless.get_message()wireless.get_message()wireless.get_message()wireless→get_message()wireless.get_message()wireless.get_message()wireless.get_message()wireless.get_message()YWireless get_message
Returns the latest status message from the wireless interface.
js | function get_message( | ) |
cpp | string get_message( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) message |
pas | string get_message( | ): string |
vb | function get_message( | ) As String |
cs | string get_message( | ) |
java | String get_message( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_message( | ) |
py | get_message( | ) |
php | function get_message( | ) |
ts | async get_message( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_message( | ) |
dnp | string get_message( | ) |
cp | string get_message( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target get_message |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the latest status message from the wireless interface
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWireless.MESSAGE_INVALID.
wireless→get_module()
wireless→module()wireless.get_module()wireless→get_module()[wireless module]wireless.get_module()wireless.get_module()wireless.get_module()wireless.get_module()wireless.get_module()wireless→get_module()wireless.get_module()wireless.get_module()wireless.get_module()wireless.get_module()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located.
js | function get_module( | ) |
cpp | YModule * get_module( | ) |
m | -(YModule*) module |
pas | TYModule get_module( | ): TYModule |
vb | function get_module( | ) As YModule |
cs | YModule get_module( | ) |
java | YModule get_module( | ) |
py | get_module( | ) |
php | function get_module( | ) |
ts | async get_module( | ): Promise<YModule> |
es | async get_module( | ) |
dnp | YModuleProxy get_module( | ) |
cp | YModuleProxy * get_module( | ) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned instance of YModule is not shown as on-line.
Returns :
an instance of YModule
wireless→get_module_async()
wireless→module_async()wireless.get_module_async()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version).
js | function get_module_async( | callback, context) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned YModule object does not show as on-line.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking Firefox JavaScript VM that does not implement context switching during blocking I/O calls. See the documentation section on asynchronous JavasSript calls for more details.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the requested YModule object |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
wireless→get_security()
wireless→security()wireless.get_security()wireless→get_security()[wireless security]wireless.get_security()wireless.get_security()wireless.get_security()wireless.get_security()wireless.get_security()wireless.get_security()wireless→get_security()wireless.get_security()wireless.get_security()wireless.get_security()wireless.get_security()YWireless get_security
Returns the security algorithm used by the selected wireless network.
js | function get_security( | ) |
cpp | Y_SECURITY_enum get_security( | ) |
m | -(Y_SECURITY_enum) security |
pas | Integer get_security( | ): Integer |
vb | function get_security( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_security( | ) |
java | int get_security( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_security( | ) |
py | get_security( | ) |
php | function get_security( | ) |
ts | async get_security( | ): Promise<YWireless_Security> |
es | async get_security( | ) |
dnp | int get_security( | ) |
cp | int get_security( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target get_security |
Returns :
a value among YWireless.SECURITY_UNKNOWN, YWireless.SECURITY_OPEN, YWireless.SECURITY_WEP, YWireless.SECURITY_WPA and YWireless.SECURITY_WPA2 corresponding to the security algorithm used by the selected wireless network
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWireless.SECURITY_INVALID.
wireless→get_serialNumber()
wireless→serialNumber()wireless.get_serialNumber()wireless→get_serialNumber()[wireless serialNumber]wireless.get_serialNumber()wireless.get_serialNumber()wireless.get_serialNumber()wireless.get_serialNumber()wireless.get_serialNumber()wireless.get_serialNumber()wireless→get_serialNumber()wireless.get_serialNumber()wireless.get_serialNumber()wireless.get_serialNumber()wireless.get_serialNumber()YWireless get_serialNumber
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
js | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
cpp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) serialNumber |
pas | string get_serialNumber( | ): string |
vb | function get_serialNumber( | ) As String |
cs | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
java | String get_serialNumber( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_serialNumber( | ) |
py | get_serialNumber( | ) |
php | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
ts | async get_serialNumber( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_serialNumber( | ) |
dnp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target get_serialNumber |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFunction.SERIALNUMBER_INVALID.
wireless→get_ssid()
wireless→ssid()wireless.get_ssid()wireless→get_ssid()[wireless ssid]wireless.get_ssid()wireless.get_ssid()wireless.get_ssid()wireless.get_ssid()wireless.get_ssid()wireless.get_ssid()wireless→get_ssid()wireless.get_ssid()wireless.get_ssid()wireless.get_ssid()wireless.get_ssid()YWireless get_ssid
Returns the wireless network name (SSID).
js | function get_ssid( | ) |
cpp | string get_ssid( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) ssid |
pas | string get_ssid( | ): string |
vb | function get_ssid( | ) As String |
cs | string get_ssid( | ) |
java | String get_ssid( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_ssid( | ) |
py | get_ssid( | ) |
php | function get_ssid( | ) |
ts | async get_ssid( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_ssid( | ) |
dnp | string get_ssid( | ) |
cp | string get_ssid( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target get_ssid |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the wireless network name (SSID)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWireless.SSID_INVALID.
wireless→get_userData()
wireless→userData()wireless.get_userData()wireless→get_userData()[wireless userData]wireless.get_userData()wireless.get_userData()wireless.get_userData()wireless.get_userData()wireless.get_userData()wireless→get_userData()wireless.get_userData()wireless.get_userData()
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData.
js | function get_userData( | ) |
cpp | void * get_userData( | ) |
m | -(id) userData |
pas | Tobject get_userData( | ): Tobject |
vb | function get_userData( | ) As Object |
cs | object get_userData( | ) |
java | Object get_userData( | ) |
py | get_userData( | ) |
php | function get_userData( | ) |
ts | async get_userData( | ): Promise<object|null> |
es | async get_userData( | ) |
This attribute is never touched directly by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Returns :
the object stored previously by the caller.
wireless→get_wlanState()
wireless→wlanState()wireless.get_wlanState()wireless→get_wlanState()[wireless wlanState]wireless.get_wlanState()wireless.get_wlanState()wireless.get_wlanState()wireless.get_wlanState()wireless.get_wlanState()wireless.get_wlanState()wireless→get_wlanState()wireless.get_wlanState()wireless.get_wlanState()wireless.get_wlanState()wireless.get_wlanState()YWireless get_wlanState
Returns the current state of the wireless interface.
js | function get_wlanState( | ) |
cpp | Y_WLANSTATE_enum get_wlanState( | ) |
m | -(Y_WLANSTATE_enum) wlanState |
pas | Integer get_wlanState( | ): Integer |
vb | function get_wlanState( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_wlanState( | ) |
java | int get_wlanState( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_wlanState( | ) |
py | get_wlanState( | ) |
php | function get_wlanState( | ) |
ts | async get_wlanState( | ): Promise<YWireless_WlanState> |
es | async get_wlanState( | ) |
dnp | int get_wlanState( | ) |
cp | int get_wlanState( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target get_wlanState |
The state YWireless.WLANSTATE_DOWN means that the network interface is not connected to a network. The state YWireless.WLANSTATE_SCANNING means that the network interface is scanning available frequencies. During this stage, the device is not reachable, and the network settings are not yet applied. The state YWireless.WLANSTATE_CONNECTED means that the network settings have been successfully applied ant that the device is reachable from the wireless network. If the device is configured to use ad-hoc or Soft AP mode, it means that the wireless network is up and that other devices can join the network. The state YWireless.WLANSTATE_REJECTED means that the network interface has not been able to join the requested network. The description of the error can be obtain with the get_message() method.
Returns :
a value among YWireless.WLANSTATE_DOWN, YWireless.WLANSTATE_SCANNING, YWireless.WLANSTATE_CONNECTED and YWireless.WLANSTATE_REJECTED corresponding to the current state of the wireless interface
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWireless.WLANSTATE_INVALID.
wireless→isOnline()wireless.isOnline()wireless→isOnline()[wireless isOnline]wireless.isOnline()wireless.isOnline()wireless.isOnline()wireless.isOnline()wireless.isOnline()wireless→isOnline()wireless.isOnline()wireless.isOnline()wireless.isOnline()wireless.isOnline()
Checks if the wireless LAN interface is currently reachable, without raising any error.
js | function isOnline( | ) |
cpp | bool isOnline( | ) |
m | -(BOOL) isOnline |
pas | boolean isOnline( | ): boolean |
vb | function isOnline( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isOnline( | ) |
java | boolean isOnline( | ) |
py | isOnline( | ) |
php | function isOnline( | ) |
ts | async isOnline( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isOnline( | ) |
dnp | bool isOnline( | ) |
cp | bool isOnline( | ) |
If there is a cached value for the wireless LAN interface in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the wireless LAN interface.
Returns :
true if the wireless LAN interface can be reached, and false otherwise
wireless→isOnline_async()wireless.isOnline_async()
Checks if the wireless LAN interface is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version).
js | function isOnline_async( | callback, context) |
If there is a cached value for the wireless LAN interface in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the requested function.
This asynchronous version exists only in Javascript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the Javascript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the boolean result |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
wireless→isReadOnly()wireless→isReadOnly()[wireless isReadOnly]wireless.isReadOnly()wireless.isReadOnly()wireless.isReadOnly()wireless.isReadOnly()wireless.isReadOnly()wireless.isReadOnly()wireless→isReadOnly()wireless.isReadOnly()wireless.isReadOnly()wireless.isReadOnly()wireless.isReadOnly()YWireless isReadOnly
Test if the function is readOnly.
cpp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
m | -(bool) isReadOnly |
pas | boolean isReadOnly( | ): boolean |
vb | function isReadOnly( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
java | boolean isReadOnly( | ) |
uwp | async Task<bool> isReadOnly( | ) |
py | isReadOnly( | ) |
php | function isReadOnly( | ) |
ts | async isReadOnly( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isReadOnly( | ) |
dnp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target isReadOnly |
Return true if the function is write protected or that the function is not available.
Returns :
true if the function is readOnly or not online.
wireless→joinNetwork()wireless.joinNetwork()wireless→joinNetwork()[wireless joinNetwork: ]wireless.joinNetwork()wireless.joinNetwork()wireless.joinNetwork()wireless.joinNetwork()wireless.joinNetwork()wireless.joinNetwork()wireless→joinNetwork()wireless.joinNetwork()wireless.joinNetwork()wireless.joinNetwork()wireless.joinNetwork()YWireless joinNetwork
Changes the configuration of the wireless lan interface to connect to an existing access point (infrastructure mode).
js | function joinNetwork( | ssid, securityKey) |
cpp | int joinNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
m | -(int) joinNetwork | : (NSString*) ssid |
| : (NSString*) securityKey |
pas | LongInt joinNetwork( | ssid: string, securityKey: string): LongInt |
vb | function joinNetwork( | ByVal ssid As String, ByVal securityKey As String) As Integer |
cs | int joinNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
java | int joinNetwork( | String ssid, String securityKey) |
uwp | async Task<int> joinNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
py | joinNetwork( | ssid, securityKey) |
php | function joinNetwork( | $ssid, $securityKey) |
ts | async joinNetwork( | ssid: string, securityKey: string): Promise<number> |
es | async joinNetwork( | ssid, securityKey) |
dnp | int joinNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
cp | int joinNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
cmd | YWireless target joinNetwork | ssid securityKey |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method and then to reboot the module to apply this setting.
Parameters :
| ssid | the name of the network to connect to |
| securityKey | the network key, as a character string |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wireless→load()wireless.load()wireless→load()[wireless load: ]wireless.load()wireless.load()wireless.load()wireless.load()wireless.load()wireless→load()wireless.load()wireless.load()
Preloads the wireless LAN interface cache with a specified validity duration.
js | function load( | msValidity) |
cpp | YRETCODE load( | int msValidity) |
m | -(YRETCODE) load | : (u64) msValidity |
pas | YRETCODE load( | msValidity: u64): YRETCODE |
vb | function load( | ByVal msValidity As Long) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE load( | ulong msValidity) |
java | int load( | long msValidity) |
py | load( | msValidity) |
php | function load( | $msValidity) |
ts | async load( | msValidity: number): Promise<number> |
es | async load( | msValidity) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity attributed to the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wireless→loadAttribute()wireless.loadAttribute()wireless→loadAttribute()[wireless loadAttribute: ]wireless.loadAttribute()wireless.loadAttribute()wireless.loadAttribute()wireless.loadAttribute()wireless.loadAttribute()wireless.loadAttribute()wireless→loadAttribute()wireless.loadAttribute()wireless.loadAttribute()wireless.loadAttribute()wireless.loadAttribute()
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value.
js | function loadAttribute( | attrName) |
cpp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
m | -(NSString*) loadAttribute | : (NSString*) attrName |
pas | string loadAttribute( | attrName: string): string |
vb | function loadAttribute( | ByVal attrName As String) As String |
cs | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
java | String loadAttribute( | String attrName) |
uwp | async Task<string> loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
py | loadAttribute( | attrName) |
php | function loadAttribute( | $attrName) |
ts | async loadAttribute( | attrName: string): Promise<string> |
es | async loadAttribute( | attrName) |
dnp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
cp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
Parameters :
| attrName | the name of the requested attribute |
Returns :
a string with the value of the the attribute
On failure, throws an exception or returns an empty string.
wireless→load_async()wireless.load_async()
Preloads the wireless LAN interface cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version).
js | function load_async( | msValidity, callback, context) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the JavaScript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity of the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the error code (or YAPI.SUCCESS) |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
wireless→muteValueCallbacks()wireless.muteValueCallbacks()wireless→muteValueCallbacks()[wireless muteValueCallbacks]wireless.muteValueCallbacks()wireless.muteValueCallbacks()wireless.muteValueCallbacks()wireless.muteValueCallbacks()wireless.muteValueCallbacks()wireless.muteValueCallbacks()wireless→muteValueCallbacks()wireless.muteValueCallbacks()wireless.muteValueCallbacks()wireless.muteValueCallbacks()wireless.muteValueCallbacks()YWireless muteValueCallbacks
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) muteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt muteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async muteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target muteValueCallbacks |
You can use this function to save bandwidth and CPU on computers with limited resources, or to prevent unwanted invocations of the HTTP callback. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wireless→nextWireless()wireless.nextWireless()wireless→nextWireless()[wireless nextWireless]wireless.nextWireless()wireless.nextWireless()wireless.nextWireless()wireless.nextWireless()wireless.nextWireless()wireless.nextWireless()wireless→nextWireless()wireless.nextWireless()wireless.nextWireless()
Continues the enumeration of wireless LAN interfaces started using yFirstWireless().
js | function nextWireless( | ) |
cpp | YWireless * nextWireless( | ) |
m | -(nullable YWireless*) nextWireless |
pas | TYWireless nextWireless( | ): TYWireless |
vb | function nextWireless( | ) As YWireless |
cs | YWireless nextWireless( | ) |
java | YWireless nextWireless( | ) |
uwp | YWireless nextWireless( | ) |
py | nextWireless( | ) |
php | function nextWireless( | ) |
ts | nextWireless( | ): YWireless | null |
es | nextWireless( | ) |
Caution: You can't make any assumption about the returned wireless LAN interfaces order. If you want to find a specific a wireless LAN interface, use Wireless.findWireless() and a hardwareID or a logical name.
Returns :
a pointer to a YWireless object, corresponding to a wireless LAN interface currently online, or a null pointer if there are no more wireless LAN interfaces to enumerate.
wireless→registerValueCallback()wireless.registerValueCallback()wireless→registerValueCallback()[wireless registerValueCallback: ]wireless.registerValueCallback()wireless.registerValueCallback()wireless.registerValueCallback()wireless.registerValueCallback()wireless.registerValueCallback()wireless.registerValueCallback()wireless→registerValueCallback()wireless.registerValueCallback()wireless.registerValueCallback()
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value.
js | function registerValueCallback( | callback) |
cpp | int registerValueCallback( | YWirelessValueCallback callback) |
m | -(int) registerValueCallback | : (YWirelessValueCallback _Nullable) callback |
pas | LongInt registerValueCallback( | callback: TYWirelessValueCallback): LongInt |
vb | function registerValueCallback( | ByVal callback As YWirelessValueCallback) As Integer |
cs | int registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
java | int registerValueCallback( | UpdateCallback callback) |
uwp | async Task<int> registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
py | registerValueCallback( | callback) |
php | function registerValueCallback( | $callback) |
ts | async registerValueCallback( | callback: YWirelessValueCallback | null): Promise<number> |
es | async registerValueCallback( | callback) |
The callback is invoked only during the execution of ySleep or yHandleEvents. This provides control over the time when the callback is triggered. For good responsiveness, remember to call one of these two functions periodically. To unregister a callback, pass a null pointer as argument.
Parameters :
| callback | the callback function to call, or a null pointer. The callback function should take two arguments: the function object of which the value has changed, and the character string describing the new advertised value. |
wireless→set_logicalName()
wireless→setLogicalName()wireless.set_logicalName()wireless→set_logicalName()[wireless setLogicalName: ]wireless.set_logicalName()wireless.set_logicalName()wireless.set_logicalName()wireless.set_logicalName()wireless.set_logicalName()wireless.set_logicalName()wireless→set_logicalName()wireless.set_logicalName()wireless.set_logicalName()wireless.set_logicalName()wireless.set_logicalName()YWireless set_logicalName
Changes the logical name of the wireless LAN interface.
js | function set_logicalName( | newval) |
cpp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setLogicalName | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_logicalName( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_logicalName( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
java | int set_logicalName( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_logicalName( | string newval) |
py | set_logicalName( | newval) |
php | function set_logicalName( | $newval) |
ts | async set_logicalName( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_logicalName( | newval) |
dnp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cmd | YWireless target set_logicalName | newval |
You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the logical name of the wireless LAN interface. |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wireless→set_userData()
wireless→setUserData()wireless.set_userData()wireless→set_userData()[wireless setUserData: ]wireless.set_userData()wireless.set_userData()wireless.set_userData()wireless.set_userData()wireless.set_userData()wireless→set_userData()wireless.set_userData()wireless.set_userData()
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function.
js | function set_userData( | data) |
cpp | void set_userData( | void * data) |
m | -(void) setUserData | : (id) data |
pas | set_userData( | data: Tobject) |
vb | procedure set_userData( | ByVal data As Object) |
cs | void set_userData( | object data) |
java | void set_userData( | Object data) |
py | set_userData( | data) |
php | function set_userData( | $data) |
ts | async set_userData( | data: object|null): Promise<void> |
es | async set_userData( | data) |
This attribute is never touched by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Parameters :
| data | any kind of object to be stored |
wireless→softAPNetwork()wireless.softAPNetwork()wireless→softAPNetwork()[wireless softAPNetwork: ]wireless.softAPNetwork()wireless.softAPNetwork()wireless.softAPNetwork()wireless.softAPNetwork()wireless.softAPNetwork()wireless.softAPNetwork()wireless→softAPNetwork()wireless.softAPNetwork()wireless.softAPNetwork()wireless.softAPNetwork()wireless.softAPNetwork()YWireless softAPNetwork
Changes the configuration of the wireless lan interface to create a new wireless network by emulating a WiFi access point (Soft AP).
js | function softAPNetwork( | ssid, securityKey) |
cpp | int softAPNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
m | -(int) softAPNetwork | : (NSString*) ssid |
| : (NSString*) securityKey |
pas | LongInt softAPNetwork( | ssid: string, securityKey: string): LongInt |
vb | function softAPNetwork( | ByVal ssid As String, ByVal securityKey As String) As Integer |
cs | int softAPNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
java | int softAPNetwork( | String ssid, String securityKey) |
uwp | async Task<int> softAPNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
py | softAPNetwork( | ssid, securityKey) |
php | function softAPNetwork( | $ssid, $securityKey) |
ts | async softAPNetwork( | ssid: string, securityKey: string): Promise<number> |
es | async softAPNetwork( | ssid, securityKey) |
dnp | int softAPNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
cp | int softAPNetwork( | string ssid, string securityKey) |
cmd | YWireless target softAPNetwork | ssid securityKey |
This function can only be used with the YoctoHub-Wireless-g and the YoctoHub-Wireless-n.
On the YoctoHub-Wireless-g, when a security key is specified for a SoftAP network, the network is protected by a WEP40 key (5 characters or 10 hexadecimal digits) or WEP128 key (13 characters or 26 hexadecimal digits). It is recommended to use a well-randomized WEP128 key using 26 hexadecimal digits to maximize security.
On the YoctoHub-Wireless-n, when a security key is specified for a SoftAP network, the network will be protected by WPA2.
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method and then to reboot the module to apply this setting.
Parameters :
| ssid | the name of the network to connect to |
| securityKey | the network key, as a character string |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wireless→startWlanScan()wireless.startWlanScan()wireless→startWlanScan()[wireless startWlanScan]wireless.startWlanScan()wireless.startWlanScan()wireless.startWlanScan()wireless.startWlanScan()wireless.startWlanScan()wireless.startWlanScan()wireless→startWlanScan()wireless.startWlanScan()wireless.startWlanScan()wireless.startWlanScan()wireless.startWlanScan()YWireless startWlanScan
Triggers a scan of the wireless frequency and builds the list of available networks.
js | function startWlanScan( | ) |
cpp | int startWlanScan( | ) |
m | -(int) startWlanScan |
pas | LongInt startWlanScan( | ): LongInt |
vb | function startWlanScan( | ) As Integer |
cs | int startWlanScan( | ) |
java | int startWlanScan( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> startWlanScan( | ) |
py | startWlanScan( | ) |
php | function startWlanScan( | ) |
ts | async startWlanScan( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async startWlanScan( | ) |
dnp | int startWlanScan( | ) |
cp | int startWlanScan( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target startWlanScan |
The scan forces a disconnection from the current network. At then end of the process, the the network interface attempts to reconnect to the previous network. During the scan, the wlanState switches to YWireless.WLANSTATE_DOWN, then to YWireless.WLANSTATE_SCANNING. When the scan is completed, get_wlanState() returns either YWireless.WLANSTATE_DOWN or YWireless.WLANSTATE_SCANNING. At this point, the list of detected network can be retrieved with the get_detectedWlans() method.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wireless→unmuteValueCallbacks()wireless.unmuteValueCallbacks()wireless→unmuteValueCallbacks()[wireless unmuteValueCallbacks]wireless.unmuteValueCallbacks()wireless.unmuteValueCallbacks()wireless.unmuteValueCallbacks()wireless.unmuteValueCallbacks()wireless.unmuteValueCallbacks()wireless.unmuteValueCallbacks()wireless→unmuteValueCallbacks()wireless.unmuteValueCallbacks()wireless.unmuteValueCallbacks()wireless.unmuteValueCallbacks()wireless.unmuteValueCallbacks()YWireless unmuteValueCallbacks
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) unmuteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YWireless target unmuteValueCallbacks |
This function reverts the effect of a previous call to muteValueCallbacks(). Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wireless→wait_async()wireless.wait_async()wireless.wait_async()wireless.wait_async()
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function.
js | function wait_async( | callback, context) |
ts | wait_async( | callback: Function, context: object) |
es | wait_async( | callback, context) |
The callback function can therefore freely issue synchronous or asynchronous commands, without risking to block the JavaScript VM.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when all pending commands on the module are completed. The callback function receives two arguments: the caller-specific context object and the receiving function object. |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing.
11.3. Class YNetwork
Network interface control interface, available for instance in the YoctoHub-Ethernet, the YoctoHub-GSM-3G-NA, the YoctoHub-GSM-4G or the YoctoHub-Wireless-n
YNetwork objects provide access to TCP/IP parameters of Yoctopuce devices that include a built-in network interface.
In order to use the functions described here, you should include:
es | in HTML: <script src="../../lib/yocto_network.js"></script> in node.js: require('yoctolib-es2017/yocto_network.js'); |
js | <script type='text/javascript' src='yocto_network.js'></script> |
cpp | #include "yocto_network.h" |
m | #import "yocto_network.h" |
pas | uses yocto_network; |
vb | yocto_network.vb |
cs | yocto_network.cs |
java | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YNetwork; |
uwp | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YNetwork; |
py | from yocto_network import * |
php | require_once('yocto_network.php'); |
ts | in HTML: import { YNetwork } from '../../dist/esm/yocto_network.js'; in Node.js: import { YNetwork } from 'yoctolib-cjs/yocto_network.js'; |
dnp | import YoctoProxyAPI.YNetworkProxy |
cp | #include "yocto_network_proxy.h" |
vi | YNetwork.vi |
ml | import YoctoProxyAPI.YNetworkProxy |
| Global functions |
|---|
| YNetwork.FindNetwork(func) |
Retrieves a network interface for a given identifier. |
| YNetwork.FindNetworkInContext(yctx, func) |
Retrieves a network interface for a given identifier in a YAPI context. |
| YNetwork.FirstNetwork() |
Starts the enumeration of network interfaces currently accessible. |
| YNetwork.FirstNetworkInContext(yctx) |
Starts the enumeration of network interfaces currently accessible. |
| YNetwork.GetSimilarFunctions() |
Enumerates all functions of type Network available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID. |
| YNetwork properties |
| network→AdminPassword [writable] |
Hash string if a password has been set for user "admin", or an empty string otherwise. |
| network→AdvertisedValue [read-only] |
Short string representing the current state of the function. |
| network→CallbackCredentials [writable] |
Hashed version of the notification callback credentials if set, or an empty string otherwise. |
| network→CallbackEncoding [writable] |
Encoding standard to use for representing notification values. |
| network→CallbackInitialDelay [writable] |
Initial waiting time before first callback notifications, in seconds. |
| network→CallbackMaxDelay [writable] |
Waiting time between two HTTP callbacks when there is nothing new. |
| network→CallbackMethod [writable] |
HTTP method used to notify callbacks for significant state changes. |
| network→CallbackMinDelay [writable] |
Minimum waiting time between two HTTP callbacks, in seconds. |
| network→CallbackSchedule [writable] |
HTTP callback schedule strategy, as a text string. |
| network→CallbackUrl [writable] |
Callback URL to notify of significant state changes. |
| network→DefaultPage [writable] |
HTML page to serve for the URL "/"" of the hub. |
| network→Discoverable [writable] |
Activation state of the multicast announce protocols to allow easy discovery of the module in the network neighborhood (uPnP/Bonjour protocol). |
| network→FriendlyName [read-only] |
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| network→FunctionId [read-only] |
Hardware identifier of the network interface, without reference to the module. |
| network→HardwareId [read-only] |
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| network→HttpPort [writable] |
TCP port used to serve the hub web UI. |
| network→IpAddress [read-only] |
IP address currently in use by the device. |
| network→IsOnline [read-only] |
Checks if the function is currently reachable. |
| network→LogicalName [writable] |
Logical name of the function. |
| network→MacAddress [read-only] |
MAC address of the network interface. |
| network→NtpServer [writable] |
IP address of the NTP server to be used by the device. |
| network→PrimaryDNS [writable] |
IP address of the primary name server to be used by the module. |
| network→Readiness [read-only] |
Current established working mode of the network interface. |
| network→SecondaryDNS [writable] |
IP address of the secondary name server to be used by the module. |
| network→SerialNumber [read-only] |
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| network→UserPassword [writable] |
Hash string if a password has been set for "user" user, or an empty string otherwise. |
| network→WwwWatchdogDelay [writable] |
Allowed downtime of the WWW link (in seconds) before triggering an automated reboot to try to recover Internet connectivity. |
| YNetwork methods |
| network→callbackLogin(username, password) |
Connects to the notification callback and saves the credentials required to log into it. |
| network→clearCache() |
Invalidates the cache. |
| network→describe() |
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the network interface in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| network→get_adminPassword() |
Returns a hash string if a password has been set for user "admin", or an empty string otherwise. |
| network→get_advertisedValue() |
Returns the current value of the network interface (no more than 6 characters). |
| network→get_callbackCredentials() |
Returns a hashed version of the notification callback credentials if set, or an empty string otherwise. |
| network→get_callbackEncoding() |
Returns the encoding standard to use for representing notification values. |
| network→get_callbackInitialDelay() |
Returns the initial waiting time before first callback notifications, in seconds. |
| network→get_callbackMaxDelay() |
Returns the waiting time between two HTTP callbacks when there is nothing new. |
| network→get_callbackMethod() |
Returns the HTTP method used to notify callbacks for significant state changes. |
| network→get_callbackMinDelay() |
Returns the minimum waiting time between two HTTP callbacks, in seconds. |
| network→get_callbackSchedule() |
Returns the HTTP callback schedule strategy, as a text string. |
| network→get_callbackUrl() |
Returns the callback URL to notify of significant state changes. |
| network→get_defaultPage() |
Returns the HTML page to serve for the URL "/"" of the hub. |
| network→get_discoverable() |
Returns the activation state of the multicast announce protocols to allow easy discovery of the module in the network neighborhood (uPnP/Bonjour protocol). |
| network→get_errorMessage() |
Returns the error message of the latest error with the network interface. |
| network→get_errorType() |
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the network interface. |
| network→get_friendlyName() |
Returns a global identifier of the network interface in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| network→get_functionDescriptor() |
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function. |
| network→get_functionId() |
Returns the hardware identifier of the network interface, without reference to the module. |
| network→get_hardwareId() |
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the network interface in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| network→get_httpPort() |
Returns the TCP port used to serve the hub web UI. |
| network→get_ipAddress() |
Returns the IP address currently in use by the device. |
| network→get_ipConfig() |
Returns the IP configuration of the network interface. |
| network→get_logicalName() |
Returns the logical name of the network interface. |
| network→get_macAddress() |
Returns the MAC address of the network interface. |
| network→get_module() |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located. |
| network→get_module_async(callback, context) |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version). |
| network→get_ntpServer() |
Returns the IP address of the NTP server to be used by the device. |
| network→get_poeCurrent() |
Returns the current consumed by the module from Power-over-Ethernet (PoE), in milliamps. |
| network→get_primaryDNS() |
Returns the IP address of the primary name server to be used by the module. |
| network→get_readiness() |
Returns the current established working mode of the network interface. |
| network→get_router() |
Returns the IP address of the router on the device subnet (default gateway). |
| network→get_secondaryDNS() |
Returns the IP address of the secondary name server to be used by the module. |
| network→get_serialNumber() |
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| network→get_subnetMask() |
Returns the subnet mask currently used by the device. |
| network→get_userData() |
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData. |
| network→get_userPassword() |
Returns a hash string if a password has been set for "user" user, or an empty string otherwise. |
| network→get_wwwWatchdogDelay() |
Returns the allowed downtime of the WWW link (in seconds) before triggering an automated reboot to try to recover Internet connectivity. |
| network→isOnline() |
Checks if the network interface is currently reachable, without raising any error. |
| network→isOnline_async(callback, context) |
Checks if the network interface is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version). |
| network→isReadOnly() |
Test if the function is readOnly. |
| network→load(msValidity) |
Preloads the network interface cache with a specified validity duration. |
| network→loadAttribute(attrName) |
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value. |
| network→load_async(msValidity, callback, context) |
Preloads the network interface cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version). |
| network→muteValueCallbacks() |
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| network→nextNetwork() |
Continues the enumeration of network interfaces started using yFirstNetwork(). |
| network→ping(host) |
Pings host to test the network connectivity. |
| network→registerValueCallback(callback) |
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value. |
| network→set_adminPassword(newval) |
Changes the password for the "admin" user. |
| network→set_callbackCredentials(newval) |
Changes the credentials required to connect to the callback address. |
| network→set_callbackEncoding(newval) |
Changes the encoding standard to use for representing notification values. |
| network→set_callbackInitialDelay(newval) |
Changes the initial waiting time before first callback notifications, in seconds. |
| network→set_callbackMaxDelay(newval) |
Changes the waiting time between two HTTP callbacks when there is nothing new. |
| network→set_callbackMethod(newval) |
Changes the HTTP method used to notify callbacks for significant state changes. |
| network→set_callbackMinDelay(newval) |
Changes the minimum waiting time between two HTTP callbacks, in seconds. |
| network→set_callbackSchedule(newval) |
Changes the HTTP callback schedule strategy, as a text string. |
| network→set_callbackUrl(newval) |
Changes the callback URL to notify significant state changes. |
| network→set_defaultPage(newval) |
Changes the default HTML page returned by the hub. |
| network→set_discoverable(newval) |
Changes the activation state of the multicast announce protocols to allow easy discovery of the module in the network neighborhood (uPnP/Bonjour protocol). |
| network→set_httpPort(newval) |
Changes the the TCP port used to serve the hub web UI. |
| network→set_logicalName(newval) |
Changes the logical name of the network interface. |
| network→set_ntpServer(newval) |
Changes the IP address of the NTP server to be used by the module. |
| network→set_periodicCallbackSchedule(interval, offset) |
Setup periodic HTTP callbacks (simplified function). |
| network→set_primaryDNS(newval) |
Changes the IP address of the primary name server to be used by the module. |
| network→set_secondaryDNS(newval) |
Changes the IP address of the secondary name server to be used by the module. |
| network→set_userData(data) |
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function. |
| network→set_userPassword(newval) |
Changes the password for the "user" user. |
| network→set_wwwWatchdogDelay(newval) |
Changes the allowed downtime of the WWW link (in seconds) before triggering an automated reboot to try to recover Internet connectivity. |
| network→triggerCallback() |
Trigger an HTTP callback quickly. |
| network→unmuteValueCallbacks() |
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| network→useDHCP(fallbackIpAddr, fallbackSubnetMaskLen, fallbackRouter) |
Changes the configuration of the network interface to enable the use of an IP address received from a DHCP server. |
| network→useDHCPauto() |
Changes the configuration of the network interface to enable the use of an IP address received from a DHCP server. |
| network→useStaticIP(ipAddress, subnetMaskLen, router) |
Changes the configuration of the network interface to use a static IP address. |
| network→wait_async(callback, context) |
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function. |
YNetwork.FindNetwork()
YNetwork.FindNetwork()yFindNetwork()YNetwork::FindNetwork()[YNetwork FindNetwork: ]yFindNetwork()YNetwork.FindNetwork()YNetwork.FindNetwork()YNetwork.FindNetwork()YNetwork.FindNetwork()YNetwork.FindNetwork()YNetwork::FindNetwork()YNetwork.FindNetwork()YNetwork.FindNetwork()YNetwork.FindNetwork()YNetwork.FindNetwork()
Retrieves a network interface for a given identifier.
js | function yFindNetwork( | func) |
cpp | YNetwork* FindNetwork( | string func) |
m | +(YNetwork*) FindNetwork | : (NSString*) func |
pas | TYNetwork yFindNetwork( | func: string): TYNetwork |
vb | function FindNetwork( | ByVal func As String) As YNetwork |
cs | static YNetwork FindNetwork( | string func) |
java | static YNetwork FindNetwork( | String func) |
uwp | static YNetwork FindNetwork( | string func) |
py | FindNetwork( | func) |
php | function FindNetwork( | $func) |
ts | static FindNetwork( | func: string): YNetwork |
es | static FindNetwork( | func) |
dnp | static YNetworkProxy FindNetwork( | string func) |
cp | static YNetworkProxy * FindNetwork( | string func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the network interface is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YNetwork.isOnline() to test if the network interface is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a network interface by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
If a call to this object's is_online() method returns FALSE although you are certain that the matching device is plugged, make sure that you did call registerHub() at application initialization time.
Parameters :
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the network interface, for instance YHUBETH1.network. |
Returns :
a YNetwork object allowing you to drive the network interface.
YNetwork.FindNetworkInContext()
YNetwork.FindNetworkInContext()YNetwork.FindNetworkInContext()YNetwork.FindNetworkInContext()YNetwork.FindNetworkInContext()YNetwork.FindNetworkInContext()
Retrieves a network interface for a given identifier in a YAPI context.
java | static YNetwork FindNetworkInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, String func) |
uwp | static YNetwork FindNetworkInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, string func) |
ts | static FindNetworkInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext, func: string): YNetwork |
es | static FindNetworkInContext( | yctx, func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the network interface is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YNetwork.isOnline() to test if the network interface is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a network interface by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context |
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the network interface, for instance YHUBETH1.network. |
Returns :
a YNetwork object allowing you to drive the network interface.
YNetwork.FirstNetwork()
YNetwork.FirstNetwork()yFirstNetwork()YNetwork::FirstNetwork()[YNetwork FirstNetwork]yFirstNetwork()YNetwork.FirstNetwork()YNetwork.FirstNetwork()YNetwork.FirstNetwork()YNetwork.FirstNetwork()YNetwork.FirstNetwork()YNetwork::FirstNetwork()YNetwork.FirstNetwork()YNetwork.FirstNetwork()
Starts the enumeration of network interfaces currently accessible.
js | function yFirstNetwork( | ) |
cpp | YNetwork * FirstNetwork( | ) |
m | +(YNetwork*) FirstNetwork |
pas | TYNetwork yFirstNetwork( | ): TYNetwork |
vb | function FirstNetwork( | ) As YNetwork |
cs | static YNetwork FirstNetwork( | ) |
java | static YNetwork FirstNetwork( | ) |
uwp | static YNetwork FirstNetwork( | ) |
py | FirstNetwork( | ) |
php | function FirstNetwork( | ) |
ts | static FirstNetwork( | ): YNetwork | null |
es | static FirstNetwork( | ) |
Use the method YNetwork.nextNetwork() to iterate on next network interfaces.
Returns :
a pointer to a YNetwork object, corresponding to the first network interface currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YNetwork.FirstNetworkInContext()
YNetwork.FirstNetworkInContext()YNetwork.FirstNetworkInContext()YNetwork.FirstNetworkInContext()YNetwork.FirstNetworkInContext()YNetwork.FirstNetworkInContext()
Starts the enumeration of network interfaces currently accessible.
java | static YNetwork FirstNetworkInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
uwp | static YNetwork FirstNetworkInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
ts | static FirstNetworkInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext): YNetwork | null |
es | static FirstNetworkInContext( | yctx) |
Use the method YNetwork.nextNetwork() to iterate on next network interfaces.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context. |
Returns :
a pointer to a YNetwork object, corresponding to the first network interface currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YNetwork.GetSimilarFunctions()
YNetwork.GetSimilarFunctions()YNetwork.GetSimilarFunctions()YNetwork.GetSimilarFunctions()
Enumerates all functions of type Network available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID.
dnp | static new string[] GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
cp | static vector<string> GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
Each of these IDs can be provided as argument to the method YNetwork.FindNetwork to obtain an object that can control the corresponding device.
Returns :
an array of strings, each string containing the unique hardwareId of a device function currently connected.
network→AdminPasswordnetwork.AdminPassword
Hash string if a password has been set for user "admin", or an empty string otherwise.
dnp | string AdminPassword |
Writable. Changes the password for the "admin" user. This password becomes instantly required to perform any change of the module state. If the specified value is an empty string, a password is not required anymore. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→AdvertisedValuenetwork.AdvertisedValue
Short string representing the current state of the function.
dnp | string AdvertisedValue |
network→CallbackCredentialsnetwork.CallbackCredentials
Hashed version of the notification callback credentials if set, or an empty string otherwise.
dnp | string CallbackCredentials |
Writable. Changes the credentials required to connect to the callback address. The credentials must be provided as returned by function get_callbackCredentials, in the form username:hash. The method used to compute the hash varies according to the the authentication scheme implemented by the callback, For Basic authentication, the hash is the MD5 of the string username:password. For Digest authentication, the hash is the MD5 of the string username:realm:password. For a simpler way to configure callback credentials, use function callbackLogin instead. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→CallbackEncodingnetwork.CallbackEncoding
Encoding standard to use for representing notification values.
dnp | int CallbackEncoding |
Writable. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→CallbackInitialDelaynetwork.CallbackInitialDelay
Initial waiting time before first callback notifications, in seconds.
dnp | int CallbackInitialDelay |
Writable. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→CallbackMaxDelaynetwork.CallbackMaxDelay
Waiting time between two HTTP callbacks when there is nothing new.
dnp | int CallbackMaxDelay |
Writable. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→CallbackMethodnetwork.CallbackMethod
HTTP method used to notify callbacks for significant state changes.
dnp | int CallbackMethod |
Writable. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→CallbackMinDelaynetwork.CallbackMinDelay
Minimum waiting time between two HTTP callbacks, in seconds.
dnp | int CallbackMinDelay |
Writable. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→CallbackSchedulenetwork.CallbackSchedule
HTTP callback schedule strategy, as a text string.
dnp | string CallbackSchedule |
Writable. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→CallbackUrlnetwork.CallbackUrl
Callback URL to notify of significant state changes.
dnp | string CallbackUrl |
Writable. Changes the callback URL to notify significant state changes. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→DefaultPagenetwork.DefaultPage
HTML page to serve for the URL "/"" of the hub.
dnp | string DefaultPage |
Writable. Changes the default HTML page returned by the hub. If not value are set the hub return "index.html" which is the web interface of the hub. It is possible to change this page for file that has been uploaded on the hub. The maximum filename size is 15 characters. When you change this parameter, remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→Discoverablenetwork.Discoverable
Activation state of the multicast announce protocols to allow easy discovery of the module in the network neighborhood (uPnP/Bonjour protocol).
dnp | int Discoverable |
Writable. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→FriendlyNamenetwork.FriendlyName
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
dnp | string FriendlyName |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the function if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the function (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
network→FunctionIdnetwork.FunctionId
Hardware identifier of the network interface, without reference to the module.
dnp | string FunctionId |
For example relay1
network→HardwareIdnetwork.HardwareId
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
dnp | string HardwareId |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the function (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
network→HttpPortnetwork.HttpPort
TCP port used to serve the hub web UI.
dnp | int HttpPort |
Writable. Changes the the TCP port used to serve the hub web UI. The default value is port 80, which is the default for all Web servers. Regardless of the value set here, the hub will always reply on port 4444, which is used by default by Yoctopuce API library. When you change this parameter, remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→IpAddressnetwork.IpAddress
IP address currently in use by the device.
dnp | string IpAddress |
The address may have been configured statically, or provided by a DHCP server.
network→IsOnlinenetwork.IsOnline
Checks if the function is currently reachable.
dnp | bool IsOnline |
If there is a cached value for the function in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the function.
network→LogicalNamenetwork.LogicalName
Logical name of the function.
dnp | string LogicalName |
Writable. You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→MacAddressnetwork.MacAddress
MAC address of the network interface.
dnp | string MacAddress |
The MAC address is also available on a sticker on the module, in both numeric and barcode forms.
network→NtpServernetwork.NtpServer
IP address of the NTP server to be used by the device.
dnp | string NtpServer |
Writable. Changes the IP address of the NTP server to be used by the module. Use an empty string to restore the factory set address. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method and then to reboot the module to apply this setting.
network→PrimaryDNSnetwork.PrimaryDNS
IP address of the primary name server to be used by the module.
dnp | string PrimaryDNS |
Writable. When using DHCP, if a value is specified, it overrides the value received from the DHCP server. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method and then to reboot the module to apply this setting.
network→Readinessnetwork.Readiness
Current established working mode of the network interface.
dnp | int Readiness |
Level zero (DOWN_0) means that no hardware link has been detected. Either there is no signal on the network cable, or the selected wireless access point cannot be detected. Level 1 (LIVE_1) is reached when the network is detected, but is not yet connected. For a wireless network, this shows that the requested SSID is present. Level 2 (LINK_2) is reached when the hardware connection is established. For a wired network connection, level 2 means that the cable is attached at both ends. For a connection to a wireless access point, it shows that the security parameters are properly configured. For an ad-hoc wireless connection, it means that there is at least one other device connected on the ad-hoc network. Level 3 (DHCP_3) is reached when an IP address has been obtained using DHCP. Level 4 (DNS_4) is reached when the DNS server is reachable on the network. Level 5 (WWW_5) is reached when global connectivity is demonstrated by properly loading the current time from an NTP server.
network→SecondaryDNSnetwork.SecondaryDNS
IP address of the secondary name server to be used by the module.
dnp | string SecondaryDNS |
Writable. When using DHCP, if a value is specified, it overrides the value received from the DHCP server. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method and then to reboot the module to apply this setting.
network→SerialNumbernetwork.SerialNumber
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
dnp | string SerialNumber |
network→UserPasswordnetwork.UserPassword
Hash string if a password has been set for "user" user, or an empty string otherwise.
dnp | string UserPassword |
Writable. Changes the password for the "user" user. This password becomes instantly required to perform any use of the module. If the specified value is an empty string, a password is not required anymore. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→WwwWatchdogDelaynetwork.WwwWatchdogDelay
Allowed downtime of the WWW link (in seconds) before triggering an automated reboot to try to recover Internet connectivity.
dnp | int WwwWatchdogDelay |
A zero value disables automated reboot in case of Internet connectivity loss.
Writable. A zero value disables automated reboot in case of Internet connectivity loss. The smallest valid non-zero timeout is 90 seconds. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
network→callbackLogin()network.callbackLogin()network→callbackLogin()[network callbackLogin: ]network.callbackLogin()network.callbackLogin()network.callbackLogin()network.callbackLogin()network.callbackLogin()network→callbackLogin()network.callbackLogin()network.callbackLogin()network.callbackLogin()network.callbackLogin()YNetwork callbackLogin
Connects to the notification callback and saves the credentials required to log into it.
js | function callbackLogin( | username, password) |
cpp | int callbackLogin( | string username, string password) |
m | -(int) callbackLogin | : (NSString*) username |
| : (NSString*) password |
pas | integer callbackLogin( | username: string, password: string): integer |
vb | function callbackLogin( | ByVal username As String, |
| ByVal password As String) As Integer |
cs | int callbackLogin( | string username, string password) |
java | int callbackLogin( | String username, String password) |
py | callbackLogin( | username, password) |
php | function callbackLogin( | $username, $password) |
ts | async callbackLogin( | username: string, password: string): Promise<number> |
es | async callbackLogin( | username, password) |
dnp | int callbackLogin( | string username, string password) |
cp | int callbackLogin( | string username, string password) |
cmd | YNetwork target callbackLogin | username password |
The password is not stored into the module, only a hashed copy of the credentials are saved. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| username | username required to log to the callback |
| password | password required to log to the callback |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→clearCache()network.clearCache()network→clearCache()[network clearCache]network.clearCache()network.clearCache()network.clearCache()network.clearCache()network.clearCache()network→clearCache()network.clearCache()network.clearCache()
Invalidates the cache.
js | function clearCache( | ) |
cpp | void clearCache( | ) |
m | -(void) clearCache |
pas | clearCache( | ) |
vb | procedure clearCache( | ) |
cs | void clearCache( | ) |
java | void clearCache( | ) |
py | clearCache( | ) |
php | function clearCache( | ) |
ts | async clearCache( | ): Promise<void> |
es | async clearCache( | ) |
Invalidates the cache of the network interface attributes. Forces the next call to get_xxx() or loadxxx() to use values that come from the device.
network→describe()network.describe()network→describe()[network describe]network.describe()network.describe()network.describe()network.describe()network.describe()network→describe()network.describe()network.describe()
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the network interface in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function describe( | ) |
cpp | string describe( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) describe |
pas | string describe( | ): string |
vb | function describe( | ) As String |
cs | string describe( | ) |
java | String describe( | ) |
py | describe( | ) |
php | function describe( | ) |
ts | async describe( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async describe( | ) |
More precisely, TYPE is the type of the function, NAME it the name used for the first access to the function, SERIAL is the serial number of the module if the module is connected or "unresolved", and FUNCTIONID is the hardware identifier of the function if the module is connected. For example, this method returns Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1 if the module is already connected or Relay(BadCustomeName.relay1)=unresolved if the module has not yet been connected. This method does not trigger any USB or TCP transaction and can therefore be used in a debugger.
Returns :
a string that describes the network interface (ex: Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
network→get_adminPassword()
network→adminPassword()network.get_adminPassword()network→get_adminPassword()[network adminPassword]network.get_adminPassword()network.get_adminPassword()network.get_adminPassword()network.get_adminPassword()network.get_adminPassword()network.get_adminPassword()network→get_adminPassword()network.get_adminPassword()network.get_adminPassword()network.get_adminPassword()network.get_adminPassword()YNetwork get_adminPassword
Returns a hash string if a password has been set for user "admin", or an empty string otherwise.
js | function get_adminPassword( | ) |
cpp | string get_adminPassword( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) adminPassword |
pas | string get_adminPassword( | ): string |
vb | function get_adminPassword( | ) As String |
cs | string get_adminPassword( | ) |
java | String get_adminPassword( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_adminPassword( | ) |
py | get_adminPassword( | ) |
php | function get_adminPassword( | ) |
ts | async get_adminPassword( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_adminPassword( | ) |
dnp | string get_adminPassword( | ) |
cp | string get_adminPassword( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_adminPassword |
Returns :
a string corresponding to a hash string if a password has been set for user "admin", or an empty string otherwise
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.ADMINPASSWORD_INVALID.
network→get_advertisedValue()
network→advertisedValue()network.get_advertisedValue()network→get_advertisedValue()[network advertisedValue]network.get_advertisedValue()network.get_advertisedValue()network.get_advertisedValue()network.get_advertisedValue()network.get_advertisedValue()network.get_advertisedValue()network→get_advertisedValue()network.get_advertisedValue()network.get_advertisedValue()network.get_advertisedValue()network.get_advertisedValue()YNetwork get_advertisedValue
Returns the current value of the network interface (no more than 6 characters).
js | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cpp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) advertisedValue |
pas | string get_advertisedValue( | ): string |
vb | function get_advertisedValue( | ) As String |
cs | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
java | String get_advertisedValue( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_advertisedValue( | ) |
py | get_advertisedValue( | ) |
php | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
ts | async get_advertisedValue( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_advertisedValue( | ) |
dnp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_advertisedValue |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the current value of the network interface (no more than 6 characters).
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.ADVERTISEDVALUE_INVALID.
network→get_callbackCredentials()
network→callbackCredentials()network.get_callbackCredentials()network→get_callbackCredentials()[network callbackCredentials]network.get_callbackCredentials()network.get_callbackCredentials()network.get_callbackCredentials()network.get_callbackCredentials()network.get_callbackCredentials()network.get_callbackCredentials()network→get_callbackCredentials()network.get_callbackCredentials()network.get_callbackCredentials()network.get_callbackCredentials()network.get_callbackCredentials()YNetwork get_callbackCredentials
Returns a hashed version of the notification callback credentials if set, or an empty string otherwise.
js | function get_callbackCredentials( | ) |
cpp | string get_callbackCredentials( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) callbackCredentials |
pas | string get_callbackCredentials( | ): string |
vb | function get_callbackCredentials( | ) As String |
cs | string get_callbackCredentials( | ) |
java | String get_callbackCredentials( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_callbackCredentials( | ) |
py | get_callbackCredentials( | ) |
php | function get_callbackCredentials( | ) |
ts | async get_callbackCredentials( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_callbackCredentials( | ) |
dnp | string get_callbackCredentials( | ) |
cp | string get_callbackCredentials( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_callbackCredentials |
Returns :
a string corresponding to a hashed version of the notification callback credentials if set, or an empty string otherwise
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.CALLBACKCREDENTIALS_INVALID.
network→get_callbackEncoding()
network→callbackEncoding()network.get_callbackEncoding()network→get_callbackEncoding()[network callbackEncoding]network.get_callbackEncoding()network.get_callbackEncoding()network.get_callbackEncoding()network.get_callbackEncoding()network.get_callbackEncoding()network.get_callbackEncoding()network→get_callbackEncoding()network.get_callbackEncoding()network.get_callbackEncoding()network.get_callbackEncoding()network.get_callbackEncoding()YNetwork get_callbackEncoding
Returns the encoding standard to use for representing notification values.
js | function get_callbackEncoding( | ) |
cpp | Y_CALLBACKENCODING_enum get_callbackEncoding( | ) |
m | -(Y_CALLBACKENCODING_enum) callbackEncoding |
pas | Integer get_callbackEncoding( | ): Integer |
vb | function get_callbackEncoding( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_callbackEncoding( | ) |
java | int get_callbackEncoding( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_callbackEncoding( | ) |
py | get_callbackEncoding( | ) |
php | function get_callbackEncoding( | ) |
ts | async get_callbackEncoding( | ): Promise<YNetwork_CallbackEncoding> |
es | async get_callbackEncoding( | ) |
dnp | int get_callbackEncoding( | ) |
cp | int get_callbackEncoding( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_callbackEncoding |
Returns :
a value among YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_FORM, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_JSON, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_JSON_ARRAY, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_CSV, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_YOCTO_API, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_JSON_NUM, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_EMONCMS, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_AZURE, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_INFLUXDB, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_MQTT, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_YOCTO_API_JZON, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_PRTG and YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_INFLUXDB_V2 corresponding to the encoding standard to use for representing notification values
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_INVALID.
network→get_callbackInitialDelay()
network→callbackInitialDelay()network.get_callbackInitialDelay()network→get_callbackInitialDelay()[network callbackInitialDelay]network.get_callbackInitialDelay()network.get_callbackInitialDelay()network.get_callbackInitialDelay()network.get_callbackInitialDelay()network.get_callbackInitialDelay()network.get_callbackInitialDelay()network→get_callbackInitialDelay()network.get_callbackInitialDelay()network.get_callbackInitialDelay()network.get_callbackInitialDelay()network.get_callbackInitialDelay()YNetwork get_callbackInitialDelay
Returns the initial waiting time before first callback notifications, in seconds.
js | function get_callbackInitialDelay( | ) |
cpp | int get_callbackInitialDelay( | ) |
m | -(int) callbackInitialDelay |
pas | LongInt get_callbackInitialDelay( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_callbackInitialDelay( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_callbackInitialDelay( | ) |
java | int get_callbackInitialDelay( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_callbackInitialDelay( | ) |
py | get_callbackInitialDelay( | ) |
php | function get_callbackInitialDelay( | ) |
ts | async get_callbackInitialDelay( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_callbackInitialDelay( | ) |
dnp | int get_callbackInitialDelay( | ) |
cp | int get_callbackInitialDelay( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_callbackInitialDelay |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the initial waiting time before first callback notifications, in seconds
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.CALLBACKINITIALDELAY_INVALID.
network→get_callbackMaxDelay()
network→callbackMaxDelay()network.get_callbackMaxDelay()network→get_callbackMaxDelay()[network callbackMaxDelay]network.get_callbackMaxDelay()network.get_callbackMaxDelay()network.get_callbackMaxDelay()network.get_callbackMaxDelay()network.get_callbackMaxDelay()network.get_callbackMaxDelay()network→get_callbackMaxDelay()network.get_callbackMaxDelay()network.get_callbackMaxDelay()network.get_callbackMaxDelay()network.get_callbackMaxDelay()YNetwork get_callbackMaxDelay
Returns the waiting time between two HTTP callbacks when there is nothing new.
js | function get_callbackMaxDelay( | ) |
cpp | int get_callbackMaxDelay( | ) |
m | -(int) callbackMaxDelay |
pas | LongInt get_callbackMaxDelay( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_callbackMaxDelay( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_callbackMaxDelay( | ) |
java | int get_callbackMaxDelay( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_callbackMaxDelay( | ) |
py | get_callbackMaxDelay( | ) |
php | function get_callbackMaxDelay( | ) |
ts | async get_callbackMaxDelay( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_callbackMaxDelay( | ) |
dnp | int get_callbackMaxDelay( | ) |
cp | int get_callbackMaxDelay( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_callbackMaxDelay |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the waiting time between two HTTP callbacks when there is nothing new
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.CALLBACKMAXDELAY_INVALID.
network→get_callbackMethod()
network→callbackMethod()network.get_callbackMethod()network→get_callbackMethod()[network callbackMethod]network.get_callbackMethod()network.get_callbackMethod()network.get_callbackMethod()network.get_callbackMethod()network.get_callbackMethod()network.get_callbackMethod()network→get_callbackMethod()network.get_callbackMethod()network.get_callbackMethod()network.get_callbackMethod()network.get_callbackMethod()YNetwork get_callbackMethod
Returns the HTTP method used to notify callbacks for significant state changes.
js | function get_callbackMethod( | ) |
cpp | Y_CALLBACKMETHOD_enum get_callbackMethod( | ) |
m | -(Y_CALLBACKMETHOD_enum) callbackMethod |
pas | Integer get_callbackMethod( | ): Integer |
vb | function get_callbackMethod( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_callbackMethod( | ) |
java | int get_callbackMethod( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_callbackMethod( | ) |
py | get_callbackMethod( | ) |
php | function get_callbackMethod( | ) |
ts | async get_callbackMethod( | ): Promise<YNetwork_CallbackMethod> |
es | async get_callbackMethod( | ) |
dnp | int get_callbackMethod( | ) |
cp | int get_callbackMethod( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_callbackMethod |
Returns :
a value among YNetwork.CALLBACKMETHOD_POST, YNetwork.CALLBACKMETHOD_GET and YNetwork.CALLBACKMETHOD_PUT corresponding to the HTTP method used to notify callbacks for significant state changes
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.CALLBACKMETHOD_INVALID.
network→get_callbackMinDelay()
network→callbackMinDelay()network.get_callbackMinDelay()network→get_callbackMinDelay()[network callbackMinDelay]network.get_callbackMinDelay()network.get_callbackMinDelay()network.get_callbackMinDelay()network.get_callbackMinDelay()network.get_callbackMinDelay()network.get_callbackMinDelay()network→get_callbackMinDelay()network.get_callbackMinDelay()network.get_callbackMinDelay()network.get_callbackMinDelay()network.get_callbackMinDelay()YNetwork get_callbackMinDelay
Returns the minimum waiting time between two HTTP callbacks, in seconds.
js | function get_callbackMinDelay( | ) |
cpp | int get_callbackMinDelay( | ) |
m | -(int) callbackMinDelay |
pas | LongInt get_callbackMinDelay( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_callbackMinDelay( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_callbackMinDelay( | ) |
java | int get_callbackMinDelay( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_callbackMinDelay( | ) |
py | get_callbackMinDelay( | ) |
php | function get_callbackMinDelay( | ) |
ts | async get_callbackMinDelay( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_callbackMinDelay( | ) |
dnp | int get_callbackMinDelay( | ) |
cp | int get_callbackMinDelay( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_callbackMinDelay |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the minimum waiting time between two HTTP callbacks, in seconds
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.CALLBACKMINDELAY_INVALID.
network→get_callbackSchedule()
network→callbackSchedule()network.get_callbackSchedule()network→get_callbackSchedule()[network callbackSchedule]network.get_callbackSchedule()network.get_callbackSchedule()network.get_callbackSchedule()network.get_callbackSchedule()network.get_callbackSchedule()network.get_callbackSchedule()network→get_callbackSchedule()network.get_callbackSchedule()network.get_callbackSchedule()network.get_callbackSchedule()network.get_callbackSchedule()YNetwork get_callbackSchedule
Returns the HTTP callback schedule strategy, as a text string.
js | function get_callbackSchedule( | ) |
cpp | string get_callbackSchedule( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) callbackSchedule |
pas | string get_callbackSchedule( | ): string |
vb | function get_callbackSchedule( | ) As String |
cs | string get_callbackSchedule( | ) |
java | String get_callbackSchedule( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_callbackSchedule( | ) |
py | get_callbackSchedule( | ) |
php | function get_callbackSchedule( | ) |
ts | async get_callbackSchedule( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_callbackSchedule( | ) |
dnp | string get_callbackSchedule( | ) |
cp | string get_callbackSchedule( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_callbackSchedule |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the HTTP callback schedule strategy, as a text string
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.CALLBACKSCHEDULE_INVALID.
network→get_callbackUrl()
network→callbackUrl()network.get_callbackUrl()network→get_callbackUrl()[network callbackUrl]network.get_callbackUrl()network.get_callbackUrl()network.get_callbackUrl()network.get_callbackUrl()network.get_callbackUrl()network.get_callbackUrl()network→get_callbackUrl()network.get_callbackUrl()network.get_callbackUrl()network.get_callbackUrl()network.get_callbackUrl()YNetwork get_callbackUrl
Returns the callback URL to notify of significant state changes.
js | function get_callbackUrl( | ) |
cpp | string get_callbackUrl( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) callbackUrl |
pas | string get_callbackUrl( | ): string |
vb | function get_callbackUrl( | ) As String |
cs | string get_callbackUrl( | ) |
java | String get_callbackUrl( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_callbackUrl( | ) |
py | get_callbackUrl( | ) |
php | function get_callbackUrl( | ) |
ts | async get_callbackUrl( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_callbackUrl( | ) |
dnp | string get_callbackUrl( | ) |
cp | string get_callbackUrl( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_callbackUrl |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the callback URL to notify of significant state changes
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.CALLBACKURL_INVALID.
network→get_defaultPage()
network→defaultPage()network.get_defaultPage()network→get_defaultPage()[network defaultPage]network.get_defaultPage()network.get_defaultPage()network.get_defaultPage()network.get_defaultPage()network.get_defaultPage()network.get_defaultPage()network→get_defaultPage()network.get_defaultPage()network.get_defaultPage()network.get_defaultPage()network.get_defaultPage()YNetwork get_defaultPage
Returns the HTML page to serve for the URL "/"" of the hub.
js | function get_defaultPage( | ) |
cpp | string get_defaultPage( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) defaultPage |
pas | string get_defaultPage( | ): string |
vb | function get_defaultPage( | ) As String |
cs | string get_defaultPage( | ) |
java | String get_defaultPage( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_defaultPage( | ) |
py | get_defaultPage( | ) |
php | function get_defaultPage( | ) |
ts | async get_defaultPage( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_defaultPage( | ) |
dnp | string get_defaultPage( | ) |
cp | string get_defaultPage( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_defaultPage |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the HTML page to serve for the URL "/"" of the hub
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.DEFAULTPAGE_INVALID.
network→get_discoverable()
network→discoverable()network.get_discoverable()network→get_discoverable()[network discoverable]network.get_discoverable()network.get_discoverable()network.get_discoverable()network.get_discoverable()network.get_discoverable()network.get_discoverable()network→get_discoverable()network.get_discoverable()network.get_discoverable()network.get_discoverable()network.get_discoverable()YNetwork get_discoverable
Returns the activation state of the multicast announce protocols to allow easy discovery of the module in the network neighborhood (uPnP/Bonjour protocol).
js | function get_discoverable( | ) |
cpp | Y_DISCOVERABLE_enum get_discoverable( | ) |
m | -(Y_DISCOVERABLE_enum) discoverable |
pas | Integer get_discoverable( | ): Integer |
vb | function get_discoverable( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_discoverable( | ) |
java | int get_discoverable( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_discoverable( | ) |
py | get_discoverable( | ) |
php | function get_discoverable( | ) |
ts | async get_discoverable( | ): Promise<YNetwork_Discoverable> |
es | async get_discoverable( | ) |
dnp | int get_discoverable( | ) |
cp | int get_discoverable( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_discoverable |
Returns :
either YNetwork.DISCOVERABLE_FALSE or YNetwork.DISCOVERABLE_TRUE, according to the activation state of the multicast announce protocols to allow easy discovery of the module in the network neighborhood (uPnP/Bonjour protocol)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.DISCOVERABLE_INVALID.
network→get_errorMessage()
network→errorMessage()network.get_errorMessage()network→get_errorMessage()[network errorMessage]network.get_errorMessage()network.get_errorMessage()network.get_errorMessage()network.get_errorMessage()network.get_errorMessage()network→get_errorMessage()network.get_errorMessage()network.get_errorMessage()
Returns the error message of the latest error with the network interface.
js | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
cpp | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) errorMessage |
pas | string get_errorMessage( | ): string |
vb | function get_errorMessage( | ) As String |
cs | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
java | String get_errorMessage( | ) |
py | get_errorMessage( | ) |
php | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
ts | get_errorMessage( | ): string |
es | get_errorMessage( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a string corresponding to the latest error message that occured while using the network interface object
network→get_errorType()
network→errorType()network.get_errorType()network→get_errorType()[network errorType]network.get_errorType()network.get_errorType()network.get_errorType()network.get_errorType()network.get_errorType()network→get_errorType()network.get_errorType()network.get_errorType()
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the network interface.
js | function get_errorType( | ) |
cpp | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
m | -(YRETCODE) errorType |
pas | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ): YRETCODE |
vb | function get_errorType( | ) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
java | int get_errorType( | ) |
py | get_errorType( | ) |
php | function get_errorType( | ) |
ts | get_errorType( | ): number |
es | get_errorType( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a number corresponding to the code of the latest error that occurred while using the network interface object
network→get_friendlyName()
network→friendlyName()network.get_friendlyName()network→get_friendlyName()[network friendlyName]network.get_friendlyName()network.get_friendlyName()network.get_friendlyName()network→get_friendlyName()network.get_friendlyName()network.get_friendlyName()network.get_friendlyName()network.get_friendlyName()
Returns a global identifier of the network interface in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
js | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
cpp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) friendlyName |
cs | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
java | String get_friendlyName( | ) |
py | get_friendlyName( | ) |
php | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
ts | async get_friendlyName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_friendlyName( | ) |
dnp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
cp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the network interface if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the network interface (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the network interface using logical names (ex: MyCustomName.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.FRIENDLYNAME_INVALID.
network→get_functionDescriptor()
network→functionDescriptor()network.get_functionDescriptor()network→get_functionDescriptor()[network functionDescriptor]network.get_functionDescriptor()network.get_functionDescriptor()network.get_functionDescriptor()network.get_functionDescriptor()network.get_functionDescriptor()network→get_functionDescriptor()network.get_functionDescriptor()network.get_functionDescriptor()
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function.
js | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
cpp | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
m | -(YFUN_DESCR) functionDescriptor |
pas | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ): YFUN_DESCR |
vb | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) As YFUN_DESCR |
cs | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
java | String get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
py | get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
php | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
ts | async get_functionDescriptor( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
This identifier can be used to test if two instances of YFunction reference the same physical function on the same physical device.
Returns :
an identifier of type YFUN_DESCR.
If the function has never been contacted, the returned value is Y$CLASSNAME$.FUNCTIONDESCRIPTOR_INVALID.
network→get_functionId()
network→functionId()network.get_functionId()network→get_functionId()[network functionId]network.get_functionId()network.get_functionId()network.get_functionId()network.get_functionId()network→get_functionId()network.get_functionId()network.get_functionId()network.get_functionId()network.get_functionId()
Returns the hardware identifier of the network interface, without reference to the module.
js | function get_functionId( | ) |
cpp | string get_functionId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) functionId |
vb | function get_functionId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_functionId( | ) |
java | String get_functionId( | ) |
py | get_functionId( | ) |
php | function get_functionId( | ) |
ts | async get_functionId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionId( | ) |
dnp | string get_functionId( | ) |
cp | string get_functionId( | ) |
For example relay1
Returns :
a string that identifies the network interface (ex: relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.FUNCTIONID_INVALID.
network→get_hardwareId()
network→hardwareId()network.get_hardwareId()network→get_hardwareId()[network hardwareId]network.get_hardwareId()network.get_hardwareId()network.get_hardwareId()network.get_hardwareId()network→get_hardwareId()network.get_hardwareId()network.get_hardwareId()network.get_hardwareId()network.get_hardwareId()
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the network interface in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
cpp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) hardwareId |
vb | function get_hardwareId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
java | String get_hardwareId( | ) |
py | get_hardwareId( | ) |
php | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
ts | async get_hardwareId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_hardwareId( | ) |
dnp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
cp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the network interface (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the network interface (ex: RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.HARDWAREID_INVALID.
network→get_httpPort()
network→httpPort()network.get_httpPort()network→get_httpPort()[network httpPort]network.get_httpPort()network.get_httpPort()network.get_httpPort()network.get_httpPort()network.get_httpPort()network.get_httpPort()network→get_httpPort()network.get_httpPort()network.get_httpPort()network.get_httpPort()network.get_httpPort()YNetwork get_httpPort
Returns the TCP port used to serve the hub web UI.
js | function get_httpPort( | ) |
cpp | int get_httpPort( | ) |
m | -(int) httpPort |
pas | LongInt get_httpPort( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_httpPort( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_httpPort( | ) |
java | int get_httpPort( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_httpPort( | ) |
py | get_httpPort( | ) |
php | function get_httpPort( | ) |
ts | async get_httpPort( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_httpPort( | ) |
dnp | int get_httpPort( | ) |
cp | int get_httpPort( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_httpPort |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the TCP port used to serve the hub web UI
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.HTTPPORT_INVALID.
network→get_ipAddress()
network→ipAddress()network.get_ipAddress()network→get_ipAddress()[network ipAddress]network.get_ipAddress()network.get_ipAddress()network.get_ipAddress()network.get_ipAddress()network.get_ipAddress()network.get_ipAddress()network→get_ipAddress()network.get_ipAddress()network.get_ipAddress()network.get_ipAddress()network.get_ipAddress()YNetwork get_ipAddress
Returns the IP address currently in use by the device.
js | function get_ipAddress( | ) |
cpp | string get_ipAddress( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) ipAddress |
pas | string get_ipAddress( | ): string |
vb | function get_ipAddress( | ) As String |
cs | string get_ipAddress( | ) |
java | String get_ipAddress( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_ipAddress( | ) |
py | get_ipAddress( | ) |
php | function get_ipAddress( | ) |
ts | async get_ipAddress( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_ipAddress( | ) |
dnp | string get_ipAddress( | ) |
cp | string get_ipAddress( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_ipAddress |
The address may have been configured statically, or provided by a DHCP server.
Returns :
a string corresponding to the IP address currently in use by the device
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.IPADDRESS_INVALID.
network→get_ipConfig()
network→ipConfig()network.get_ipConfig()network→get_ipConfig()[network ipConfig]network.get_ipConfig()network.get_ipConfig()network.get_ipConfig()network.get_ipConfig()network.get_ipConfig()network.get_ipConfig()network→get_ipConfig()network.get_ipConfig()network.get_ipConfig()network.get_ipConfig()network.get_ipConfig()YNetwork get_ipConfig
Returns the IP configuration of the network interface.
js | function get_ipConfig( | ) |
cpp | string get_ipConfig( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) ipConfig |
pas | string get_ipConfig( | ): string |
vb | function get_ipConfig( | ) As String |
cs | string get_ipConfig( | ) |
java | String get_ipConfig( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_ipConfig( | ) |
py | get_ipConfig( | ) |
php | function get_ipConfig( | ) |
ts | async get_ipConfig( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_ipConfig( | ) |
dnp | string get_ipConfig( | ) |
cp | string get_ipConfig( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_ipConfig |
If the network interface is setup to use a static IP address, the string starts with "STATIC:" and is followed by three parameters, separated by "/". The first is the device IP address, followed by the subnet mask length, and finally the router IP address (default gateway). For instance: "STATIC:192.168.1.14/16/192.168.1.1"
If the network interface is configured to receive its IP from a DHCP server, the string start with "DHCP:" and is followed by three parameters separated by "/". The first is the fallback IP address, then the fallback subnet mask length and finally the fallback router IP address. These three parameters are used when no DHCP reply is received.
Returns :
a string corresponding to the IP configuration of the network interface
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.IPCONFIG_INVALID.
network→get_logicalName()
network→logicalName()network.get_logicalName()network→get_logicalName()[network logicalName]network.get_logicalName()network.get_logicalName()network.get_logicalName()network.get_logicalName()network.get_logicalName()network.get_logicalName()network→get_logicalName()network.get_logicalName()network.get_logicalName()network.get_logicalName()network.get_logicalName()YNetwork get_logicalName
Returns the logical name of the network interface.
js | function get_logicalName( | ) |
cpp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) logicalName |
pas | string get_logicalName( | ): string |
vb | function get_logicalName( | ) As String |
cs | string get_logicalName( | ) |
java | String get_logicalName( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_logicalName( | ) |
py | get_logicalName( | ) |
php | function get_logicalName( | ) |
ts | async get_logicalName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_logicalName( | ) |
dnp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_logicalName |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the logical name of the network interface.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.LOGICALNAME_INVALID.
network→get_macAddress()
network→macAddress()network.get_macAddress()network→get_macAddress()[network macAddress]network.get_macAddress()network.get_macAddress()network.get_macAddress()network.get_macAddress()network.get_macAddress()network.get_macAddress()network→get_macAddress()network.get_macAddress()network.get_macAddress()network.get_macAddress()network.get_macAddress()YNetwork get_macAddress
Returns the MAC address of the network interface.
js | function get_macAddress( | ) |
cpp | string get_macAddress( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) macAddress |
pas | string get_macAddress( | ): string |
vb | function get_macAddress( | ) As String |
cs | string get_macAddress( | ) |
java | String get_macAddress( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_macAddress( | ) |
py | get_macAddress( | ) |
php | function get_macAddress( | ) |
ts | async get_macAddress( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_macAddress( | ) |
dnp | string get_macAddress( | ) |
cp | string get_macAddress( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_macAddress |
The MAC address is also available on a sticker on the module, in both numeric and barcode forms.
Returns :
a string corresponding to the MAC address of the network interface
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.MACADDRESS_INVALID.
network→get_module()
network→module()network.get_module()network→get_module()[network module]network.get_module()network.get_module()network.get_module()network.get_module()network.get_module()network→get_module()network.get_module()network.get_module()network.get_module()network.get_module()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located.
js | function get_module( | ) |
cpp | YModule * get_module( | ) |
m | -(YModule*) module |
pas | TYModule get_module( | ): TYModule |
vb | function get_module( | ) As YModule |
cs | YModule get_module( | ) |
java | YModule get_module( | ) |
py | get_module( | ) |
php | function get_module( | ) |
ts | async get_module( | ): Promise<YModule> |
es | async get_module( | ) |
dnp | YModuleProxy get_module( | ) |
cp | YModuleProxy * get_module( | ) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned instance of YModule is not shown as on-line.
Returns :
an instance of YModule
network→get_module_async()
network→module_async()network.get_module_async()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version).
js | function get_module_async( | callback, context) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned YModule object does not show as on-line.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking Firefox JavaScript VM that does not implement context switching during blocking I/O calls. See the documentation section on asynchronous JavasSript calls for more details.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the requested YModule object |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
network→get_ntpServer()
network→ntpServer()network.get_ntpServer()network→get_ntpServer()[network ntpServer]network.get_ntpServer()network.get_ntpServer()network.get_ntpServer()network.get_ntpServer()network.get_ntpServer()network.get_ntpServer()network→get_ntpServer()network.get_ntpServer()network.get_ntpServer()network.get_ntpServer()network.get_ntpServer()YNetwork get_ntpServer
Returns the IP address of the NTP server to be used by the device.
js | function get_ntpServer( | ) |
cpp | string get_ntpServer( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) ntpServer |
pas | string get_ntpServer( | ): string |
vb | function get_ntpServer( | ) As String |
cs | string get_ntpServer( | ) |
java | String get_ntpServer( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_ntpServer( | ) |
py | get_ntpServer( | ) |
php | function get_ntpServer( | ) |
ts | async get_ntpServer( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_ntpServer( | ) |
dnp | string get_ntpServer( | ) |
cp | string get_ntpServer( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_ntpServer |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the IP address of the NTP server to be used by the device
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.NTPSERVER_INVALID.
network→get_poeCurrent()
network→poeCurrent()network.get_poeCurrent()network→get_poeCurrent()[network poeCurrent]network.get_poeCurrent()network.get_poeCurrent()network.get_poeCurrent()network.get_poeCurrent()network.get_poeCurrent()network.get_poeCurrent()network→get_poeCurrent()network.get_poeCurrent()network.get_poeCurrent()network.get_poeCurrent()network.get_poeCurrent()YNetwork get_poeCurrent
Returns the current consumed by the module from Power-over-Ethernet (PoE), in milliamps.
js | function get_poeCurrent( | ) |
cpp | int get_poeCurrent( | ) |
m | -(int) poeCurrent |
pas | LongInt get_poeCurrent( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_poeCurrent( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_poeCurrent( | ) |
java | int get_poeCurrent( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_poeCurrent( | ) |
py | get_poeCurrent( | ) |
php | function get_poeCurrent( | ) |
ts | async get_poeCurrent( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_poeCurrent( | ) |
dnp | int get_poeCurrent( | ) |
cp | int get_poeCurrent( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_poeCurrent |
The current consumption is measured after converting PoE source to 5 Volt, and should never exceed 1800 mA.
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the current consumed by the module from Power-over-Ethernet (PoE), in milliamps
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.POECURRENT_INVALID.
network→get_primaryDNS()
network→primaryDNS()network.get_primaryDNS()network→get_primaryDNS()[network primaryDNS]network.get_primaryDNS()network.get_primaryDNS()network.get_primaryDNS()network.get_primaryDNS()network.get_primaryDNS()network.get_primaryDNS()network→get_primaryDNS()network.get_primaryDNS()network.get_primaryDNS()network.get_primaryDNS()network.get_primaryDNS()YNetwork get_primaryDNS
Returns the IP address of the primary name server to be used by the module.
js | function get_primaryDNS( | ) |
cpp | string get_primaryDNS( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) primaryDNS |
pas | string get_primaryDNS( | ): string |
vb | function get_primaryDNS( | ) As String |
cs | string get_primaryDNS( | ) |
java | String get_primaryDNS( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_primaryDNS( | ) |
py | get_primaryDNS( | ) |
php | function get_primaryDNS( | ) |
ts | async get_primaryDNS( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_primaryDNS( | ) |
dnp | string get_primaryDNS( | ) |
cp | string get_primaryDNS( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_primaryDNS |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the IP address of the primary name server to be used by the module
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.PRIMARYDNS_INVALID.
network→get_readiness()
network→readiness()network.get_readiness()network→get_readiness()[network readiness]network.get_readiness()network.get_readiness()network.get_readiness()network.get_readiness()network.get_readiness()network.get_readiness()network→get_readiness()network.get_readiness()network.get_readiness()network.get_readiness()network.get_readiness()YNetwork get_readiness
Returns the current established working mode of the network interface.
js | function get_readiness( | ) |
cpp | Y_READINESS_enum get_readiness( | ) |
m | -(Y_READINESS_enum) readiness |
pas | Integer get_readiness( | ): Integer |
vb | function get_readiness( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_readiness( | ) |
java | int get_readiness( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_readiness( | ) |
py | get_readiness( | ) |
php | function get_readiness( | ) |
ts | async get_readiness( | ): Promise<YNetwork_Readiness> |
es | async get_readiness( | ) |
dnp | int get_readiness( | ) |
cp | int get_readiness( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_readiness |
Level zero (DOWN_0) means that no hardware link has been detected. Either there is no signal on the network cable, or the selected wireless access point cannot be detected. Level 1 (LIVE_1) is reached when the network is detected, but is not yet connected. For a wireless network, this shows that the requested SSID is present. Level 2 (LINK_2) is reached when the hardware connection is established. For a wired network connection, level 2 means that the cable is attached at both ends. For a connection to a wireless access point, it shows that the security parameters are properly configured. For an ad-hoc wireless connection, it means that there is at least one other device connected on the ad-hoc network. Level 3 (DHCP_3) is reached when an IP address has been obtained using DHCP. Level 4 (DNS_4) is reached when the DNS server is reachable on the network. Level 5 (WWW_5) is reached when global connectivity is demonstrated by properly loading the current time from an NTP server.
Returns :
a value among YNetwork.READINESS_DOWN, YNetwork.READINESS_EXISTS, YNetwork.READINESS_LINKED, YNetwork.READINESS_LAN_OK and YNetwork.READINESS_WWW_OK corresponding to the current established working mode of the network interface
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.READINESS_INVALID.
network→get_router()
network→router()network.get_router()network→get_router()[network router]network.get_router()network.get_router()network.get_router()network.get_router()network.get_router()network.get_router()network→get_router()network.get_router()network.get_router()network.get_router()network.get_router()YNetwork get_router
Returns the IP address of the router on the device subnet (default gateway).
js | function get_router( | ) |
cpp | string get_router( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) router |
pas | string get_router( | ): string |
vb | function get_router( | ) As String |
cs | string get_router( | ) |
java | String get_router( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_router( | ) |
py | get_router( | ) |
php | function get_router( | ) |
ts | async get_router( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_router( | ) |
dnp | string get_router( | ) |
cp | string get_router( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_router |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the IP address of the router on the device subnet (default gateway)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.ROUTER_INVALID.
network→get_secondaryDNS()
network→secondaryDNS()network.get_secondaryDNS()network→get_secondaryDNS()[network secondaryDNS]network.get_secondaryDNS()network.get_secondaryDNS()network.get_secondaryDNS()network.get_secondaryDNS()network.get_secondaryDNS()network.get_secondaryDNS()network→get_secondaryDNS()network.get_secondaryDNS()network.get_secondaryDNS()network.get_secondaryDNS()network.get_secondaryDNS()YNetwork get_secondaryDNS
Returns the IP address of the secondary name server to be used by the module.
js | function get_secondaryDNS( | ) |
cpp | string get_secondaryDNS( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) secondaryDNS |
pas | string get_secondaryDNS( | ): string |
vb | function get_secondaryDNS( | ) As String |
cs | string get_secondaryDNS( | ) |
java | String get_secondaryDNS( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_secondaryDNS( | ) |
py | get_secondaryDNS( | ) |
php | function get_secondaryDNS( | ) |
ts | async get_secondaryDNS( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_secondaryDNS( | ) |
dnp | string get_secondaryDNS( | ) |
cp | string get_secondaryDNS( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_secondaryDNS |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the IP address of the secondary name server to be used by the module
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.SECONDARYDNS_INVALID.
network→get_serialNumber()
network→serialNumber()network.get_serialNumber()network→get_serialNumber()[network serialNumber]network.get_serialNumber()network.get_serialNumber()network.get_serialNumber()network.get_serialNumber()network.get_serialNumber()network.get_serialNumber()network→get_serialNumber()network.get_serialNumber()network.get_serialNumber()network.get_serialNumber()network.get_serialNumber()YNetwork get_serialNumber
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
js | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
cpp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) serialNumber |
pas | string get_serialNumber( | ): string |
vb | function get_serialNumber( | ) As String |
cs | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
java | String get_serialNumber( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_serialNumber( | ) |
py | get_serialNumber( | ) |
php | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
ts | async get_serialNumber( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_serialNumber( | ) |
dnp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_serialNumber |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFunction.SERIALNUMBER_INVALID.
network→get_subnetMask()
network→subnetMask()network.get_subnetMask()network→get_subnetMask()[network subnetMask]network.get_subnetMask()network.get_subnetMask()network.get_subnetMask()network.get_subnetMask()network.get_subnetMask()network.get_subnetMask()network→get_subnetMask()network.get_subnetMask()network.get_subnetMask()network.get_subnetMask()network.get_subnetMask()YNetwork get_subnetMask
Returns the subnet mask currently used by the device.
js | function get_subnetMask( | ) |
cpp | string get_subnetMask( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) subnetMask |
pas | string get_subnetMask( | ): string |
vb | function get_subnetMask( | ) As String |
cs | string get_subnetMask( | ) |
java | String get_subnetMask( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_subnetMask( | ) |
py | get_subnetMask( | ) |
php | function get_subnetMask( | ) |
ts | async get_subnetMask( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_subnetMask( | ) |
dnp | string get_subnetMask( | ) |
cp | string get_subnetMask( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_subnetMask |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the subnet mask currently used by the device
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.SUBNETMASK_INVALID.
network→get_userData()
network→userData()network.get_userData()network→get_userData()[network userData]network.get_userData()network.get_userData()network.get_userData()network.get_userData()network.get_userData()network→get_userData()network.get_userData()network.get_userData()
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData.
js | function get_userData( | ) |
cpp | void * get_userData( | ) |
m | -(id) userData |
pas | Tobject get_userData( | ): Tobject |
vb | function get_userData( | ) As Object |
cs | object get_userData( | ) |
java | Object get_userData( | ) |
py | get_userData( | ) |
php | function get_userData( | ) |
ts | async get_userData( | ): Promise<object|null> |
es | async get_userData( | ) |
This attribute is never touched directly by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Returns :
the object stored previously by the caller.
network→get_userPassword()
network→userPassword()network.get_userPassword()network→get_userPassword()[network userPassword]network.get_userPassword()network.get_userPassword()network.get_userPassword()network.get_userPassword()network.get_userPassword()network.get_userPassword()network→get_userPassword()network.get_userPassword()network.get_userPassword()network.get_userPassword()network.get_userPassword()YNetwork get_userPassword
Returns a hash string if a password has been set for "user" user, or an empty string otherwise.
js | function get_userPassword( | ) |
cpp | string get_userPassword( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) userPassword |
pas | string get_userPassword( | ): string |
vb | function get_userPassword( | ) As String |
cs | string get_userPassword( | ) |
java | String get_userPassword( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_userPassword( | ) |
py | get_userPassword( | ) |
php | function get_userPassword( | ) |
ts | async get_userPassword( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_userPassword( | ) |
dnp | string get_userPassword( | ) |
cp | string get_userPassword( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_userPassword |
Returns :
a string corresponding to a hash string if a password has been set for "user" user, or an empty string otherwise
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.USERPASSWORD_INVALID.
network→get_wwwWatchdogDelay()
network→wwwWatchdogDelay()network.get_wwwWatchdogDelay()network→get_wwwWatchdogDelay()[network wwwWatchdogDelay]network.get_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.get_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.get_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.get_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.get_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.get_wwwWatchdogDelay()network→get_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.get_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.get_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.get_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.get_wwwWatchdogDelay()YNetwork get_wwwWatchdogDelay
Returns the allowed downtime of the WWW link (in seconds) before triggering an automated reboot to try to recover Internet connectivity.
js | function get_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ) |
cpp | int get_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ) |
m | -(int) wwwWatchdogDelay |
pas | LongInt get_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ) |
java | int get_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ) |
py | get_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ) |
php | function get_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ) |
ts | async get_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ) |
dnp | int get_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ) |
cp | int get_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target get_wwwWatchdogDelay |
A zero value disables automated reboot in case of Internet connectivity loss.
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the allowed downtime of the WWW link (in seconds) before triggering an automated reboot to try to recover Internet connectivity
On failure, throws an exception or returns YNetwork.WWWWATCHDOGDELAY_INVALID.
network→isOnline()network.isOnline()network→isOnline()[network isOnline]network.isOnline()network.isOnline()network.isOnline()network.isOnline()network.isOnline()network→isOnline()network.isOnline()network.isOnline()network.isOnline()network.isOnline()
Checks if the network interface is currently reachable, without raising any error.
js | function isOnline( | ) |
cpp | bool isOnline( | ) |
m | -(BOOL) isOnline |
pas | boolean isOnline( | ): boolean |
vb | function isOnline( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isOnline( | ) |
java | boolean isOnline( | ) |
py | isOnline( | ) |
php | function isOnline( | ) |
ts | async isOnline( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isOnline( | ) |
dnp | bool isOnline( | ) |
cp | bool isOnline( | ) |
If there is a cached value for the network interface in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the network interface.
Returns :
true if the network interface can be reached, and false otherwise
network→isOnline_async()network.isOnline_async()
Checks if the network interface is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version).
js | function isOnline_async( | callback, context) |
If there is a cached value for the network interface in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the requested function.
This asynchronous version exists only in Javascript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the Javascript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the boolean result |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
network→isReadOnly()network→isReadOnly()[network isReadOnly]network.isReadOnly()network.isReadOnly()network.isReadOnly()network.isReadOnly()network.isReadOnly()network.isReadOnly()network→isReadOnly()network.isReadOnly()network.isReadOnly()network.isReadOnly()network.isReadOnly()YNetwork isReadOnly
Test if the function is readOnly.
cpp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
m | -(bool) isReadOnly |
pas | boolean isReadOnly( | ): boolean |
vb | function isReadOnly( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
java | boolean isReadOnly( | ) |
uwp | async Task<bool> isReadOnly( | ) |
py | isReadOnly( | ) |
php | function isReadOnly( | ) |
ts | async isReadOnly( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isReadOnly( | ) |
dnp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target isReadOnly |
Return true if the function is write protected or that the function is not available.
Returns :
true if the function is readOnly or not online.
network→load()network.load()network→load()[network load: ]network.load()network.load()network.load()network.load()network.load()network→load()network.load()network.load()
Preloads the network interface cache with a specified validity duration.
js | function load( | msValidity) |
cpp | YRETCODE load( | int msValidity) |
m | -(YRETCODE) load | : (u64) msValidity |
pas | YRETCODE load( | msValidity: u64): YRETCODE |
vb | function load( | ByVal msValidity As Long) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE load( | ulong msValidity) |
java | int load( | long msValidity) |
py | load( | msValidity) |
php | function load( | $msValidity) |
ts | async load( | msValidity: number): Promise<number> |
es | async load( | msValidity) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity attributed to the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→loadAttribute()network.loadAttribute()network→loadAttribute()[network loadAttribute: ]network.loadAttribute()network.loadAttribute()network.loadAttribute()network.loadAttribute()network.loadAttribute()network.loadAttribute()network→loadAttribute()network.loadAttribute()network.loadAttribute()network.loadAttribute()network.loadAttribute()
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value.
js | function loadAttribute( | attrName) |
cpp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
m | -(NSString*) loadAttribute | : (NSString*) attrName |
pas | string loadAttribute( | attrName: string): string |
vb | function loadAttribute( | ByVal attrName As String) As String |
cs | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
java | String loadAttribute( | String attrName) |
uwp | async Task<string> loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
py | loadAttribute( | attrName) |
php | function loadAttribute( | $attrName) |
ts | async loadAttribute( | attrName: string): Promise<string> |
es | async loadAttribute( | attrName) |
dnp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
cp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
Parameters :
| attrName | the name of the requested attribute |
Returns :
a string with the value of the the attribute
On failure, throws an exception or returns an empty string.
network→load_async()network.load_async()
Preloads the network interface cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version).
js | function load_async( | msValidity, callback, context) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the JavaScript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity of the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the error code (or YAPI.SUCCESS) |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
network→muteValueCallbacks()network.muteValueCallbacks()network→muteValueCallbacks()[network muteValueCallbacks]network.muteValueCallbacks()network.muteValueCallbacks()network.muteValueCallbacks()network.muteValueCallbacks()network.muteValueCallbacks()network.muteValueCallbacks()network→muteValueCallbacks()network.muteValueCallbacks()network.muteValueCallbacks()network.muteValueCallbacks()network.muteValueCallbacks()YNetwork muteValueCallbacks
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) muteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt muteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async muteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target muteValueCallbacks |
You can use this function to save bandwidth and CPU on computers with limited resources, or to prevent unwanted invocations of the HTTP callback. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→nextNetwork()network.nextNetwork()network→nextNetwork()[network nextNetwork]network.nextNetwork()network.nextNetwork()network.nextNetwork()network.nextNetwork()network.nextNetwork()network.nextNetwork()network→nextNetwork()network.nextNetwork()network.nextNetwork()
Continues the enumeration of network interfaces started using yFirstNetwork().
js | function nextNetwork( | ) |
cpp | YNetwork * nextNetwork( | ) |
m | -(nullable YNetwork*) nextNetwork |
pas | TYNetwork nextNetwork( | ): TYNetwork |
vb | function nextNetwork( | ) As YNetwork |
cs | YNetwork nextNetwork( | ) |
java | YNetwork nextNetwork( | ) |
uwp | YNetwork nextNetwork( | ) |
py | nextNetwork( | ) |
php | function nextNetwork( | ) |
ts | nextNetwork( | ): YNetwork | null |
es | nextNetwork( | ) |
Caution: You can't make any assumption about the returned network interfaces order. If you want to find a specific a network interface, use Network.findNetwork() and a hardwareID or a logical name.
Returns :
a pointer to a YNetwork object, corresponding to a network interface currently online, or a null pointer if there are no more network interfaces to enumerate.
network→ping()network.ping()network→ping()[network ping: ]network.ping()network.ping()network.ping()network.ping()network.ping()network.ping()network→ping()network.ping()network.ping()network.ping()network.ping()YNetwork ping
Pings host to test the network connectivity.
js | function ping( | host) |
cpp | string ping( | string host) |
m | -(NSString*) ping | : (NSString*) host |
pas | string ping( | host: string): string |
vb | function ping( | ByVal host As String) As String |
cs | string ping( | string host) |
java | String ping( | String host) |
uwp | async Task<string> ping( | string host) |
py | ping( | host) |
php | function ping( | $host) |
ts | async ping( | host: string): Promise<string> |
es | async ping( | host) |
dnp | string ping( | string host) |
cp | string ping( | string host) |
cmd | YNetwork target ping | host |
Sends four ICMP ECHO_REQUEST requests from the module to the target host. This method returns a string with the result of the 4 ICMP ECHO_REQUEST requests.
Parameters :
| host | the hostname or the IP address of the target |
Returns :
a string with the result of the ping.
network→registerValueCallback()network.registerValueCallback()network→registerValueCallback()[network registerValueCallback: ]network.registerValueCallback()network.registerValueCallback()network.registerValueCallback()network.registerValueCallback()network.registerValueCallback()network.registerValueCallback()network→registerValueCallback()network.registerValueCallback()network.registerValueCallback()
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value.
js | function registerValueCallback( | callback) |
cpp | int registerValueCallback( | YNetworkValueCallback callback) |
m | -(int) registerValueCallback | : (YNetworkValueCallback _Nullable) callback |
pas | LongInt registerValueCallback( | callback: TYNetworkValueCallback): LongInt |
vb | function registerValueCallback( | ByVal callback As YNetworkValueCallback) As Integer |
cs | int registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
java | int registerValueCallback( | UpdateCallback callback) |
uwp | async Task<int> registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
py | registerValueCallback( | callback) |
php | function registerValueCallback( | $callback) |
ts | async registerValueCallback( | callback: YNetworkValueCallback | null): Promise<number> |
es | async registerValueCallback( | callback) |
The callback is invoked only during the execution of ySleep or yHandleEvents. This provides control over the time when the callback is triggered. For good responsiveness, remember to call one of these two functions periodically. To unregister a callback, pass a null pointer as argument.
Parameters :
| callback | the callback function to call, or a null pointer. The callback function should take two arguments: the function object of which the value has changed, and the character string describing the new advertised value. |
network→set_adminPassword()
network→setAdminPassword()network.set_adminPassword()network→set_adminPassword()[network setAdminPassword: ]network.set_adminPassword()network.set_adminPassword()network.set_adminPassword()network.set_adminPassword()network.set_adminPassword()network.set_adminPassword()network→set_adminPassword()network.set_adminPassword()network.set_adminPassword()network.set_adminPassword()network.set_adminPassword()YNetwork set_adminPassword
Changes the password for the "admin" user.
js | function set_adminPassword( | newval) |
cpp | int set_adminPassword( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setAdminPassword | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_adminPassword( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_adminPassword( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_adminPassword( | string newval) |
java | int set_adminPassword( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_adminPassword( | string newval) |
py | set_adminPassword( | newval) |
php | function set_adminPassword( | $newval) |
ts | async set_adminPassword( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_adminPassword( | newval) |
dnp | int set_adminPassword( | string newval) |
cp | int set_adminPassword( | string newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_adminPassword | newval |
This password becomes instantly required to perform any change of the module state. If the specified value is an empty string, a password is not required anymore. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the password for the "admin" user |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_callbackCredentials()
network→setCallbackCredentials()network.set_callbackCredentials()network→set_callbackCredentials()[network setCallbackCredentials: ]network.set_callbackCredentials()network.set_callbackCredentials()network.set_callbackCredentials()network.set_callbackCredentials()network.set_callbackCredentials()network.set_callbackCredentials()network→set_callbackCredentials()network.set_callbackCredentials()network.set_callbackCredentials()network.set_callbackCredentials()network.set_callbackCredentials()YNetwork set_callbackCredentials
Changes the credentials required to connect to the callback address.
js | function set_callbackCredentials( | newval) |
cpp | int set_callbackCredentials( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setCallbackCredentials | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_callbackCredentials( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_callbackCredentials( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_callbackCredentials( | string newval) |
java | int set_callbackCredentials( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_callbackCredentials( | string newval) |
py | set_callbackCredentials( | newval) |
php | function set_callbackCredentials( | $newval) |
ts | async set_callbackCredentials( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_callbackCredentials( | newval) |
dnp | int set_callbackCredentials( | string newval) |
cp | int set_callbackCredentials( | string newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_callbackCredentials | newval |
The credentials must be provided as returned by function get_callbackCredentials, in the form username:hash. The method used to compute the hash varies according to the the authentication scheme implemented by the callback, For Basic authentication, the hash is the MD5 of the string username:password. For Digest authentication, the hash is the MD5 of the string username:realm:password. For a simpler way to configure callback credentials, use function callbackLogin instead. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the credentials required to connect to the callback address |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_callbackEncoding()
network→setCallbackEncoding()network.set_callbackEncoding()network→set_callbackEncoding()[network setCallbackEncoding: ]network.set_callbackEncoding()network.set_callbackEncoding()network.set_callbackEncoding()network.set_callbackEncoding()network.set_callbackEncoding()network.set_callbackEncoding()network→set_callbackEncoding()network.set_callbackEncoding()network.set_callbackEncoding()network.set_callbackEncoding()network.set_callbackEncoding()YNetwork set_callbackEncoding
Changes the encoding standard to use for representing notification values.
js | function set_callbackEncoding( | newval) |
cpp | int set_callbackEncoding( | Y_CALLBACKENCODING_enum newval) |
m | -(int) setCallbackEncoding | : (Y_CALLBACKENCODING_enum) newval |
pas | integer set_callbackEncoding( | newval: Integer): integer |
vb | function set_callbackEncoding( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_callbackEncoding( | int newval) |
java | int set_callbackEncoding( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_callbackEncoding( | int newval) |
py | set_callbackEncoding( | newval) |
php | function set_callbackEncoding( | $newval) |
ts | async set_callbackEncoding( | newval: YNetwork_CallbackEncoding): Promise<number> |
es | async set_callbackEncoding( | newval) |
dnp | int set_callbackEncoding( | int newval) |
cp | int set_callbackEncoding( | int newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_callbackEncoding | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a value among YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_FORM, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_JSON, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_JSON_ARRAY, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_CSV, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_YOCTO_API, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_JSON_NUM, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_EMONCMS, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_AZURE, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_INFLUXDB, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_MQTT, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_YOCTO_API_JZON, YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_PRTG and YNetwork.CALLBACKENCODING_INFLUXDB_V2 corresponding to the encoding standard to use for representing notification values |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_callbackInitialDelay()
network→setCallbackInitialDelay()network.set_callbackInitialDelay()network→set_callbackInitialDelay()[network setCallbackInitialDelay: ]network.set_callbackInitialDelay()network.set_callbackInitialDelay()network.set_callbackInitialDelay()network.set_callbackInitialDelay()network.set_callbackInitialDelay()network.set_callbackInitialDelay()network→set_callbackInitialDelay()network.set_callbackInitialDelay()network.set_callbackInitialDelay()network.set_callbackInitialDelay()network.set_callbackInitialDelay()YNetwork set_callbackInitialDelay
Changes the initial waiting time before first callback notifications, in seconds.
js | function set_callbackInitialDelay( | newval) |
cpp | int set_callbackInitialDelay( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setCallbackInitialDelay | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_callbackInitialDelay( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_callbackInitialDelay( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_callbackInitialDelay( | int newval) |
java | int set_callbackInitialDelay( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_callbackInitialDelay( | int newval) |
py | set_callbackInitialDelay( | newval) |
php | function set_callbackInitialDelay( | $newval) |
ts | async set_callbackInitialDelay( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_callbackInitialDelay( | newval) |
dnp | int set_callbackInitialDelay( | int newval) |
cp | int set_callbackInitialDelay( | int newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_callbackInitialDelay | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the initial waiting time before first callback notifications, in seconds |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_callbackMaxDelay()
network→setCallbackMaxDelay()network.set_callbackMaxDelay()network→set_callbackMaxDelay()[network setCallbackMaxDelay: ]network.set_callbackMaxDelay()network.set_callbackMaxDelay()network.set_callbackMaxDelay()network.set_callbackMaxDelay()network.set_callbackMaxDelay()network.set_callbackMaxDelay()network→set_callbackMaxDelay()network.set_callbackMaxDelay()network.set_callbackMaxDelay()network.set_callbackMaxDelay()network.set_callbackMaxDelay()YNetwork set_callbackMaxDelay
Changes the waiting time between two HTTP callbacks when there is nothing new.
js | function set_callbackMaxDelay( | newval) |
cpp | int set_callbackMaxDelay( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setCallbackMaxDelay | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_callbackMaxDelay( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_callbackMaxDelay( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_callbackMaxDelay( | int newval) |
java | int set_callbackMaxDelay( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_callbackMaxDelay( | int newval) |
py | set_callbackMaxDelay( | newval) |
php | function set_callbackMaxDelay( | $newval) |
ts | async set_callbackMaxDelay( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_callbackMaxDelay( | newval) |
dnp | int set_callbackMaxDelay( | int newval) |
cp | int set_callbackMaxDelay( | int newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_callbackMaxDelay | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the waiting time between two HTTP callbacks when there is nothing new |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_callbackMethod()
network→setCallbackMethod()network.set_callbackMethod()network→set_callbackMethod()[network setCallbackMethod: ]network.set_callbackMethod()network.set_callbackMethod()network.set_callbackMethod()network.set_callbackMethod()network.set_callbackMethod()network.set_callbackMethod()network→set_callbackMethod()network.set_callbackMethod()network.set_callbackMethod()network.set_callbackMethod()network.set_callbackMethod()YNetwork set_callbackMethod
Changes the HTTP method used to notify callbacks for significant state changes.
js | function set_callbackMethod( | newval) |
cpp | int set_callbackMethod( | Y_CALLBACKMETHOD_enum newval) |
m | -(int) setCallbackMethod | : (Y_CALLBACKMETHOD_enum) newval |
pas | integer set_callbackMethod( | newval: Integer): integer |
vb | function set_callbackMethod( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_callbackMethod( | int newval) |
java | int set_callbackMethod( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_callbackMethod( | int newval) |
py | set_callbackMethod( | newval) |
php | function set_callbackMethod( | $newval) |
ts | async set_callbackMethod( | newval: YNetwork_CallbackMethod): Promise<number> |
es | async set_callbackMethod( | newval) |
dnp | int set_callbackMethod( | int newval) |
cp | int set_callbackMethod( | int newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_callbackMethod | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a value among YNetwork.CALLBACKMETHOD_POST, YNetwork.CALLBACKMETHOD_GET and YNetwork.CALLBACKMETHOD_PUT corresponding to the HTTP method used to notify callbacks for significant state changes |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_callbackMinDelay()
network→setCallbackMinDelay()network.set_callbackMinDelay()network→set_callbackMinDelay()[network setCallbackMinDelay: ]network.set_callbackMinDelay()network.set_callbackMinDelay()network.set_callbackMinDelay()network.set_callbackMinDelay()network.set_callbackMinDelay()network.set_callbackMinDelay()network→set_callbackMinDelay()network.set_callbackMinDelay()network.set_callbackMinDelay()network.set_callbackMinDelay()network.set_callbackMinDelay()YNetwork set_callbackMinDelay
Changes the minimum waiting time between two HTTP callbacks, in seconds.
js | function set_callbackMinDelay( | newval) |
cpp | int set_callbackMinDelay( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setCallbackMinDelay | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_callbackMinDelay( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_callbackMinDelay( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_callbackMinDelay( | int newval) |
java | int set_callbackMinDelay( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_callbackMinDelay( | int newval) |
py | set_callbackMinDelay( | newval) |
php | function set_callbackMinDelay( | $newval) |
ts | async set_callbackMinDelay( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_callbackMinDelay( | newval) |
dnp | int set_callbackMinDelay( | int newval) |
cp | int set_callbackMinDelay( | int newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_callbackMinDelay | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the minimum waiting time between two HTTP callbacks, in seconds |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_callbackSchedule()
network→setCallbackSchedule()network.set_callbackSchedule()network→set_callbackSchedule()[network setCallbackSchedule: ]network.set_callbackSchedule()network.set_callbackSchedule()network.set_callbackSchedule()network.set_callbackSchedule()network.set_callbackSchedule()network.set_callbackSchedule()network→set_callbackSchedule()network.set_callbackSchedule()network.set_callbackSchedule()network.set_callbackSchedule()network.set_callbackSchedule()YNetwork set_callbackSchedule
Changes the HTTP callback schedule strategy, as a text string.
js | function set_callbackSchedule( | newval) |
cpp | int set_callbackSchedule( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setCallbackSchedule | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_callbackSchedule( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_callbackSchedule( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_callbackSchedule( | string newval) |
java | int set_callbackSchedule( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_callbackSchedule( | string newval) |
py | set_callbackSchedule( | newval) |
php | function set_callbackSchedule( | $newval) |
ts | async set_callbackSchedule( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_callbackSchedule( | newval) |
dnp | int set_callbackSchedule( | string newval) |
cp | int set_callbackSchedule( | string newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_callbackSchedule | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the HTTP callback schedule strategy, as a text string |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_callbackUrl()
network→setCallbackUrl()network.set_callbackUrl()network→set_callbackUrl()[network setCallbackUrl: ]network.set_callbackUrl()network.set_callbackUrl()network.set_callbackUrl()network.set_callbackUrl()network.set_callbackUrl()network.set_callbackUrl()network→set_callbackUrl()network.set_callbackUrl()network.set_callbackUrl()network.set_callbackUrl()network.set_callbackUrl()YNetwork set_callbackUrl
Changes the callback URL to notify significant state changes.
js | function set_callbackUrl( | newval) |
cpp | int set_callbackUrl( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setCallbackUrl | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_callbackUrl( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_callbackUrl( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_callbackUrl( | string newval) |
java | int set_callbackUrl( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_callbackUrl( | string newval) |
py | set_callbackUrl( | newval) |
php | function set_callbackUrl( | $newval) |
ts | async set_callbackUrl( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_callbackUrl( | newval) |
dnp | int set_callbackUrl( | string newval) |
cp | int set_callbackUrl( | string newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_callbackUrl | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the callback URL to notify significant state changes |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_defaultPage()
network→setDefaultPage()network.set_defaultPage()network→set_defaultPage()[network setDefaultPage: ]network.set_defaultPage()network.set_defaultPage()network.set_defaultPage()network.set_defaultPage()network.set_defaultPage()network.set_defaultPage()network→set_defaultPage()network.set_defaultPage()network.set_defaultPage()network.set_defaultPage()network.set_defaultPage()YNetwork set_defaultPage
Changes the default HTML page returned by the hub.
js | function set_defaultPage( | newval) |
cpp | int set_defaultPage( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setDefaultPage | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_defaultPage( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_defaultPage( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_defaultPage( | string newval) |
java | int set_defaultPage( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_defaultPage( | string newval) |
py | set_defaultPage( | newval) |
php | function set_defaultPage( | $newval) |
ts | async set_defaultPage( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_defaultPage( | newval) |
dnp | int set_defaultPage( | string newval) |
cp | int set_defaultPage( | string newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_defaultPage | newval |
If not value are set the hub return "index.html" which is the web interface of the hub. It is possible to change this page for file that has been uploaded on the hub. The maximum filename size is 15 characters. When you change this parameter, remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the default HTML page returned by the hub |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_discoverable()
network→setDiscoverable()network.set_discoverable()network→set_discoverable()[network setDiscoverable: ]network.set_discoverable()network.set_discoverable()network.set_discoverable()network.set_discoverable()network.set_discoverable()network.set_discoverable()network→set_discoverable()network.set_discoverable()network.set_discoverable()network.set_discoverable()network.set_discoverable()YNetwork set_discoverable
Changes the activation state of the multicast announce protocols to allow easy discovery of the module in the network neighborhood (uPnP/Bonjour protocol).
js | function set_discoverable( | newval) |
cpp | int set_discoverable( | Y_DISCOVERABLE_enum newval) |
m | -(int) setDiscoverable | : (Y_DISCOVERABLE_enum) newval |
pas | integer set_discoverable( | newval: Integer): integer |
vb | function set_discoverable( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_discoverable( | int newval) |
java | int set_discoverable( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_discoverable( | int newval) |
py | set_discoverable( | newval) |
php | function set_discoverable( | $newval) |
ts | async set_discoverable( | newval: YNetwork_Discoverable): Promise<number> |
es | async set_discoverable( | newval) |
dnp | int set_discoverable( | int newval) |
cp | int set_discoverable( | int newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_discoverable | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | either YNetwork.DISCOVERABLE_FALSE or YNetwork.DISCOVERABLE_TRUE, according to the activation state of the multicast announce protocols to allow easy discovery of the module in the network neighborhood (uPnP/Bonjour protocol) |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_httpPort()
network→setHttpPort()network.set_httpPort()network→set_httpPort()[network setHttpPort: ]network.set_httpPort()network.set_httpPort()network.set_httpPort()network.set_httpPort()network.set_httpPort()network.set_httpPort()network→set_httpPort()network.set_httpPort()network.set_httpPort()network.set_httpPort()network.set_httpPort()YNetwork set_httpPort
Changes the the TCP port used to serve the hub web UI.
js | function set_httpPort( | newval) |
cpp | int set_httpPort( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setHttpPort | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_httpPort( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_httpPort( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_httpPort( | int newval) |
java | int set_httpPort( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_httpPort( | int newval) |
py | set_httpPort( | newval) |
php | function set_httpPort( | $newval) |
ts | async set_httpPort( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_httpPort( | newval) |
dnp | int set_httpPort( | int newval) |
cp | int set_httpPort( | int newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_httpPort | newval |
The default value is port 80, which is the default for all Web servers. Regardless of the value set here, the hub will always reply on port 4444, which is used by default by Yoctopuce API library. When you change this parameter, remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the the TCP port used to serve the hub web UI |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_logicalName()
network→setLogicalName()network.set_logicalName()network→set_logicalName()[network setLogicalName: ]network.set_logicalName()network.set_logicalName()network.set_logicalName()network.set_logicalName()network.set_logicalName()network.set_logicalName()network→set_logicalName()network.set_logicalName()network.set_logicalName()network.set_logicalName()network.set_logicalName()YNetwork set_logicalName
Changes the logical name of the network interface.
js | function set_logicalName( | newval) |
cpp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setLogicalName | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_logicalName( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_logicalName( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
java | int set_logicalName( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_logicalName( | string newval) |
py | set_logicalName( | newval) |
php | function set_logicalName( | $newval) |
ts | async set_logicalName( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_logicalName( | newval) |
dnp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_logicalName | newval |
You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the logical name of the network interface. |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_ntpServer()
network→setNtpServer()network.set_ntpServer()network→set_ntpServer()[network setNtpServer: ]network.set_ntpServer()network.set_ntpServer()network.set_ntpServer()network.set_ntpServer()network.set_ntpServer()network.set_ntpServer()network→set_ntpServer()network.set_ntpServer()network.set_ntpServer()network.set_ntpServer()network.set_ntpServer()YNetwork set_ntpServer
Changes the IP address of the NTP server to be used by the module.
js | function set_ntpServer( | newval) |
cpp | int set_ntpServer( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setNtpServer | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_ntpServer( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_ntpServer( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_ntpServer( | string newval) |
java | int set_ntpServer( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_ntpServer( | string newval) |
py | set_ntpServer( | newval) |
php | function set_ntpServer( | $newval) |
ts | async set_ntpServer( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_ntpServer( | newval) |
dnp | int set_ntpServer( | string newval) |
cp | int set_ntpServer( | string newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_ntpServer | newval |
Use an empty string to restore the factory set address. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method and then to reboot the module to apply this setting.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the IP address of the NTP server to be used by the module |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_periodicCallbackSchedule()
network→setPeriodicCallbackSchedule()network.set_periodicCallbackSchedule()network→set_periodicCallbackSchedule()[network setPeriodicCallbackSchedule: ]network.set_periodicCallbackSchedule()network.set_periodicCallbackSchedule()network.set_periodicCallbackSchedule()network.set_periodicCallbackSchedule()network.set_periodicCallbackSchedule()network.set_periodicCallbackSchedule()network→set_periodicCallbackSchedule()network.set_periodicCallbackSchedule()network.set_periodicCallbackSchedule()network.set_periodicCallbackSchedule()network.set_periodicCallbackSchedule()YNetwork set_periodicCallbackSchedule
Setup periodic HTTP callbacks (simplified function).
js | function set_periodicCallbackSchedule( | interval, offset) |
cpp | int set_periodicCallbackSchedule( | string interval, int offset) |
m | -(int) setPeriodicCallbackSchedule | : (NSString*) interval |
| : (int) offset |
pas | LongInt set_periodicCallbackSchedule( | interval: string, |
| offset: LongInt): LongInt |
vb | function set_periodicCallbackSchedule( | ByVal interval As String, |
| ByVal offset As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_periodicCallbackSchedule( | string interval, int offset) |
java | int set_periodicCallbackSchedule( | String interval, int offset) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_periodicCallbackSchedule( | string interval, |
| int offset) |
py | set_periodicCallbackSchedule( | interval, offset) |
php | function set_periodicCallbackSchedule( | $interval, $offset) |
ts | async set_periodicCallbackSchedule( | interval: string, offset: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_periodicCallbackSchedule( | interval, offset) |
dnp | int set_periodicCallbackSchedule( | string interval, int offset) |
cp | int set_periodicCallbackSchedule( | string interval, int offset) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_periodicCallbackSchedule | interval offset |
Parameters :
| interval | a string representing the callback periodicity, expressed in seconds, minutes or hours, eg. "60s", "5m", "1h", "48h". |
| offset | an integer representing the time offset relative to the period when the callback should occur. For instance, if the periodicity is 24h, an offset of 7 will make the callback occur each day at 7AM. |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_primaryDNS()
network→setPrimaryDNS()network.set_primaryDNS()network→set_primaryDNS()[network setPrimaryDNS: ]network.set_primaryDNS()network.set_primaryDNS()network.set_primaryDNS()network.set_primaryDNS()network.set_primaryDNS()network.set_primaryDNS()network→set_primaryDNS()network.set_primaryDNS()network.set_primaryDNS()network.set_primaryDNS()network.set_primaryDNS()YNetwork set_primaryDNS
Changes the IP address of the primary name server to be used by the module.
js | function set_primaryDNS( | newval) |
cpp | int set_primaryDNS( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setPrimaryDNS | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_primaryDNS( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_primaryDNS( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_primaryDNS( | string newval) |
java | int set_primaryDNS( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_primaryDNS( | string newval) |
py | set_primaryDNS( | newval) |
php | function set_primaryDNS( | $newval) |
ts | async set_primaryDNS( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_primaryDNS( | newval) |
dnp | int set_primaryDNS( | string newval) |
cp | int set_primaryDNS( | string newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_primaryDNS | newval |
When using DHCP, if a value is specified, it overrides the value received from the DHCP server. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method and then to reboot the module to apply this setting.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the IP address of the primary name server to be used by the module |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_secondaryDNS()
network→setSecondaryDNS()network.set_secondaryDNS()network→set_secondaryDNS()[network setSecondaryDNS: ]network.set_secondaryDNS()network.set_secondaryDNS()network.set_secondaryDNS()network.set_secondaryDNS()network.set_secondaryDNS()network.set_secondaryDNS()network→set_secondaryDNS()network.set_secondaryDNS()network.set_secondaryDNS()network.set_secondaryDNS()network.set_secondaryDNS()YNetwork set_secondaryDNS
Changes the IP address of the secondary name server to be used by the module.
js | function set_secondaryDNS( | newval) |
cpp | int set_secondaryDNS( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setSecondaryDNS | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_secondaryDNS( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_secondaryDNS( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_secondaryDNS( | string newval) |
java | int set_secondaryDNS( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_secondaryDNS( | string newval) |
py | set_secondaryDNS( | newval) |
php | function set_secondaryDNS( | $newval) |
ts | async set_secondaryDNS( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_secondaryDNS( | newval) |
dnp | int set_secondaryDNS( | string newval) |
cp | int set_secondaryDNS( | string newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_secondaryDNS | newval |
When using DHCP, if a value is specified, it overrides the value received from the DHCP server. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method and then to reboot the module to apply this setting.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the IP address of the secondary name server to be used by the module |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_userData()
network→setUserData()network.set_userData()network→set_userData()[network setUserData: ]network.set_userData()network.set_userData()network.set_userData()network.set_userData()network.set_userData()network→set_userData()network.set_userData()network.set_userData()
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function.
js | function set_userData( | data) |
cpp | void set_userData( | void * data) |
m | -(void) setUserData | : (id) data |
pas | set_userData( | data: Tobject) |
vb | procedure set_userData( | ByVal data As Object) |
cs | void set_userData( | object data) |
java | void set_userData( | Object data) |
py | set_userData( | data) |
php | function set_userData( | $data) |
ts | async set_userData( | data: object|null): Promise<void> |
es | async set_userData( | data) |
This attribute is never touched by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Parameters :
| data | any kind of object to be stored |
network→set_userPassword()
network→setUserPassword()network.set_userPassword()network→set_userPassword()[network setUserPassword: ]network.set_userPassword()network.set_userPassword()network.set_userPassword()network.set_userPassword()network.set_userPassword()network.set_userPassword()network→set_userPassword()network.set_userPassword()network.set_userPassword()network.set_userPassword()network.set_userPassword()YNetwork set_userPassword
Changes the password for the "user" user.
js | function set_userPassword( | newval) |
cpp | int set_userPassword( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setUserPassword | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_userPassword( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_userPassword( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_userPassword( | string newval) |
java | int set_userPassword( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_userPassword( | string newval) |
py | set_userPassword( | newval) |
php | function set_userPassword( | $newval) |
ts | async set_userPassword( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_userPassword( | newval) |
dnp | int set_userPassword( | string newval) |
cp | int set_userPassword( | string newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_userPassword | newval |
This password becomes instantly required to perform any use of the module. If the specified value is an empty string, a password is not required anymore. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the password for the "user" user |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→set_wwwWatchdogDelay()
network→setWwwWatchdogDelay()network.set_wwwWatchdogDelay()network→set_wwwWatchdogDelay()[network setWwwWatchdogDelay: ]network.set_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.set_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.set_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.set_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.set_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.set_wwwWatchdogDelay()network→set_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.set_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.set_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.set_wwwWatchdogDelay()network.set_wwwWatchdogDelay()YNetwork set_wwwWatchdogDelay
Changes the allowed downtime of the WWW link (in seconds) before triggering an automated reboot to try to recover Internet connectivity.
js | function set_wwwWatchdogDelay( | newval) |
cpp | int set_wwwWatchdogDelay( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setWwwWatchdogDelay | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_wwwWatchdogDelay( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_wwwWatchdogDelay( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_wwwWatchdogDelay( | int newval) |
java | int set_wwwWatchdogDelay( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_wwwWatchdogDelay( | int newval) |
py | set_wwwWatchdogDelay( | newval) |
php | function set_wwwWatchdogDelay( | $newval) |
ts | async set_wwwWatchdogDelay( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_wwwWatchdogDelay( | newval) |
dnp | int set_wwwWatchdogDelay( | int newval) |
cp | int set_wwwWatchdogDelay( | int newval) |
cmd | YNetwork target set_wwwWatchdogDelay | newval |
A zero value disables automated reboot in case of Internet connectivity loss. The smallest valid non-zero timeout is 90 seconds. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the allowed downtime of the WWW link (in seconds) before triggering an automated reboot to try to recover Internet connectivity |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→triggerCallback()network.triggerCallback()network→triggerCallback()[network triggerCallback]network.triggerCallback()network.triggerCallback()network.triggerCallback()network.triggerCallback()network.triggerCallback()network.triggerCallback()network→triggerCallback()network.triggerCallback()network.triggerCallback()network.triggerCallback()network.triggerCallback()YNetwork triggerCallback
Trigger an HTTP callback quickly.
js | function triggerCallback( | ) |
cpp | int triggerCallback( | ) |
m | -(int) triggerCallback |
pas | LongInt triggerCallback( | ): LongInt |
vb | function triggerCallback( | ) As Integer |
cs | int triggerCallback( | ) |
java | int triggerCallback( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> triggerCallback( | ) |
py | triggerCallback( | ) |
php | function triggerCallback( | ) |
ts | async triggerCallback( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async triggerCallback( | ) |
dnp | int triggerCallback( | ) |
cp | int triggerCallback( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target triggerCallback |
This function can even be called within an HTTP callback, in which case the next callback will be triggered 5 seconds after the end of the current callback, regardless if the minimum time between callbacks configured in the device.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→unmuteValueCallbacks()network.unmuteValueCallbacks()network→unmuteValueCallbacks()[network unmuteValueCallbacks]network.unmuteValueCallbacks()network.unmuteValueCallbacks()network.unmuteValueCallbacks()network.unmuteValueCallbacks()network.unmuteValueCallbacks()network.unmuteValueCallbacks()network→unmuteValueCallbacks()network.unmuteValueCallbacks()network.unmuteValueCallbacks()network.unmuteValueCallbacks()network.unmuteValueCallbacks()YNetwork unmuteValueCallbacks
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) unmuteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target unmuteValueCallbacks |
This function reverts the effect of a previous call to muteValueCallbacks(). Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→useDHCP()network.useDHCP()network→useDHCP()[network useDHCP: ]network.useDHCP()network.useDHCP()network.useDHCP()network.useDHCP()network.useDHCP()network.useDHCP()network→useDHCP()network.useDHCP()network.useDHCP()network.useDHCP()network.useDHCP()YNetwork useDHCP
Changes the configuration of the network interface to enable the use of an IP address received from a DHCP server.
js | function useDHCP( | fallbackIpAddr, fallbackSubnetMaskLen, fallbackRouter) |
cpp | int useDHCP( | string fallbackIpAddr, |
| int fallbackSubnetMaskLen, | ||
| string fallbackRouter) |
m | -(int) useDHCP | : (NSString*) fallbackIpAddr |
| : (int) fallbackSubnetMaskLen | ||
| : (NSString*) fallbackRouter |
pas | LongInt useDHCP( | fallbackIpAddr: string, |
| fallbackSubnetMaskLen: LongInt, | ||
| fallbackRouter: string): LongInt |
vb | function useDHCP( | ByVal fallbackIpAddr As String, |
| ByVal fallbackSubnetMaskLen As Integer, | ||
| ByVal fallbackRouter As String) As Integer |
cs | int useDHCP( | string fallbackIpAddr, |
| int fallbackSubnetMaskLen, | ||
| string fallbackRouter) |
java | int useDHCP( | String fallbackIpAddr, |
| int fallbackSubnetMaskLen, | ||
| String fallbackRouter) |
uwp | async Task<int> useDHCP( | string fallbackIpAddr, |
| int fallbackSubnetMaskLen, | ||
| string fallbackRouter) |
py | useDHCP( | fallbackIpAddr, fallbackSubnetMaskLen, fallbackRouter) |
php | function useDHCP( | $fallbackIpAddr, $fallbackSubnetMaskLen, $fallbackRouter) |
ts | async useDHCP( | fallbackIpAddr: string, fallbackSubnetMaskLen: number, fallbackRouter: string): Promise<number> |
es | async useDHCP( | fallbackIpAddr, fallbackSubnetMaskLen, fallbackRouter) |
dnp | int useDHCP( | string fallbackIpAddr, |
| int fallbackSubnetMaskLen, | ||
| string fallbackRouter) |
cp | int useDHCP( | string fallbackIpAddr, |
| int fallbackSubnetMaskLen, | ||
| string fallbackRouter) |
cmd | YNetwork target useDHCP | fallbackIpAddr fallbackSubnetMaskLen fallbackRouter |
Until an address is received from a DHCP server, the module uses the IP parameters specified to this function. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method and then to reboot the module to apply this setting.
Parameters :
| fallbackIpAddr | fallback IP address, to be used when no DHCP reply is received |
| fallbackSubnetMaskLen | fallback subnet mask length when no DHCP reply is received, as an integer (e.g. 24 means 255.255.255.0) |
| fallbackRouter | fallback router IP address, to be used when no DHCP reply is received |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→useDHCPauto()network.useDHCPauto()network→useDHCPauto()[network useDHCPauto]network.useDHCPauto()network.useDHCPauto()network.useDHCPauto()network.useDHCPauto()network.useDHCPauto()network.useDHCPauto()network→useDHCPauto()network.useDHCPauto()network.useDHCPauto()network.useDHCPauto()network.useDHCPauto()YNetwork useDHCPauto
Changes the configuration of the network interface to enable the use of an IP address received from a DHCP server.
js | function useDHCPauto( | ) |
cpp | int useDHCPauto( | ) |
m | -(int) useDHCPauto |
pas | LongInt useDHCPauto( | ): LongInt |
vb | function useDHCPauto( | ) As Integer |
cs | int useDHCPauto( | ) |
java | int useDHCPauto( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> useDHCPauto( | ) |
py | useDHCPauto( | ) |
php | function useDHCPauto( | ) |
ts | async useDHCPauto( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async useDHCPauto( | ) |
dnp | int useDHCPauto( | ) |
cp | int useDHCPauto( | ) |
cmd | YNetwork target useDHCPauto |
Until an address is received from a DHCP server, the module uses an IP of the network 169.254.0.0/16 (APIPA). Remember to call the saveToFlash() method and then to reboot the module to apply this setting.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→useStaticIP()network.useStaticIP()network→useStaticIP()[network useStaticIP: ]network.useStaticIP()network.useStaticIP()network.useStaticIP()network.useStaticIP()network.useStaticIP()network.useStaticIP()network→useStaticIP()network.useStaticIP()network.useStaticIP()network.useStaticIP()network.useStaticIP()YNetwork useStaticIP
Changes the configuration of the network interface to use a static IP address.
js | function useStaticIP( | ipAddress, subnetMaskLen, router) |
cpp | int useStaticIP( | string ipAddress, int subnetMaskLen, string router) |
m | -(int) useStaticIP | : (NSString*) ipAddress |
| : (int) subnetMaskLen | ||
| : (NSString*) router |
pas | LongInt useStaticIP( | ipAddress: string, |
| subnetMaskLen: LongInt, | ||
| router: string): LongInt |
vb | function useStaticIP( | ByVal ipAddress As String, |
| ByVal subnetMaskLen As Integer, | ||
| ByVal router As String) As Integer |
cs | int useStaticIP( | string ipAddress, |
| int subnetMaskLen, | ||
| string router) |
java | int useStaticIP( | String ipAddress, |
| int subnetMaskLen, | ||
| String router) |
uwp | async Task<int> useStaticIP( | string ipAddress, |
| int subnetMaskLen, | ||
| string router) |
py | useStaticIP( | ipAddress, subnetMaskLen, router) |
php | function useStaticIP( | $ipAddress, $subnetMaskLen, $router) |
ts | async useStaticIP( | ipAddress: string, subnetMaskLen: number, router: string): Promise<number> |
es | async useStaticIP( | ipAddress, subnetMaskLen, router) |
dnp | int useStaticIP( | string ipAddress, |
| int subnetMaskLen, | ||
| string router) |
cp | int useStaticIP( | string ipAddress, |
| int subnetMaskLen, | ||
| string router) |
cmd | YNetwork target useStaticIP | ipAddress subnetMaskLen router |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method and then to reboot the module to apply this setting.
Parameters :
| ipAddress | device IP address |
| subnetMaskLen | subnet mask length, as an integer (e.g. 24 means 255.255.255.0) |
| router | router IP address (default gateway) |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
network→wait_async()network.wait_async()network.wait_async()network.wait_async()
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function.
js | function wait_async( | callback, context) |
ts | wait_async( | callback: Function, context: object) |
es | wait_async( | callback, context) |
The callback function can therefore freely issue synchronous or asynchronous commands, without risking to block the JavaScript VM.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when all pending commands on the module are completed. The callback function receives two arguments: the caller-specific context object and the receiving function object. |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing.
11.4. Class YFiles
Filesystem control interface, available for instance in the Yocto-Color-V2, the Yocto-Serial, the YoctoHub-Ethernet or the YoctoHub-Wireless-n
The YFiles class is used to access the filesystem embedded on some Yoctopuce devices. This filesystem makes it possible for instance to design a custom web UI (for networked devices) or to add fonts (on display devices).
In order to use the functions described here, you should include:
js | <script type='text/javascript' src='yocto_files.js'></script> |
cpp | #include "yocto_files.h" |
m | #import "yocto_files.h" |
pas | uses yocto_files; |
vb | yocto_files.vb |
cs | yocto_files.cs |
java | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YFiles; |
uwp | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YFiles; |
py | from yocto_files import * |
php | require_once('yocto_files.php'); |
ts | in HTML: import { YFiles } from '../../dist/esm/yocto_files.js'; in Node.js: import { YFiles } from 'yoctolib-cjs/yocto_files.js'; |
es | in HTML: <script src="../../lib/yocto_files.js"></script> in node.js: require('yoctolib-es2017/yocto_files.js'); |
dnp | import YoctoProxyAPI.YFilesProxy |
cp | #include "yocto_files_proxy.h" |
vi | YFiles.vi |
ml | import YoctoProxyAPI.YFilesProxy |
| Global functions |
|---|
| YFiles.FindFiles(func) |
Retrieves a filesystem for a given identifier. |
| YFiles.FindFilesInContext(yctx, func) |
Retrieves a filesystem for a given identifier in a YAPI context. |
| YFiles.FirstFiles() |
Starts the enumeration of filesystems currently accessible. |
| YFiles.FirstFilesInContext(yctx) |
Starts the enumeration of filesystems currently accessible. |
| YFiles.GetSimilarFunctions() |
Enumerates all functions of type Files available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID. |
| YFiles properties |
| files→AdvertisedValue [read-only] |
Short string representing the current state of the function. |
| files→FilesCount [read-only] |
Number of files currently loaded in the filesystem. |
| files→FriendlyName [read-only] |
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| files→FunctionId [read-only] |
Hardware identifier of the filesystem, without reference to the module. |
| files→HardwareId [read-only] |
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| files→IsOnline [read-only] |
Checks if the function is currently reachable. |
| files→LogicalName [writable] |
Logical name of the function. |
| files→SerialNumber [read-only] |
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| YFiles methods |
| files→clearCache() |
Invalidates the cache. |
| files→describe() |
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the filesystem in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| files→download(pathname) |
Downloads the requested file and returns a binary buffer with its content. |
| files→download_async(pathname, callback, context) |
Downloads the requested file and returns a binary buffer with its content. |
| files→fileExist(filename) |
Test if a file exist on the filesystem of the module. |
| files→format_fs() |
Reinitialize the filesystem to its clean, unfragmented, empty state. |
| files→get_advertisedValue() |
Returns the current value of the filesystem (no more than 6 characters). |
| files→get_errorMessage() |
Returns the error message of the latest error with the filesystem. |
| files→get_errorType() |
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the filesystem. |
| files→get_filesCount() |
Returns the number of files currently loaded in the filesystem. |
| files→get_freeSpace() |
Returns the free space for uploading new files to the filesystem, in bytes. |
| files→get_friendlyName() |
Returns a global identifier of the filesystem in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| files→get_functionDescriptor() |
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function. |
| files→get_functionId() |
Returns the hardware identifier of the filesystem, without reference to the module. |
| files→get_hardwareId() |
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the filesystem in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| files→get_list(pattern) |
Returns a list of YFileRecord objects that describe files currently loaded in the filesystem. |
| files→get_logicalName() |
Returns the logical name of the filesystem. |
| files→get_module() |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located. |
| files→get_module_async(callback, context) |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version). |
| files→get_serialNumber() |
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| files→get_userData() |
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData. |
| files→isOnline() |
Checks if the filesystem is currently reachable, without raising any error. |
| files→isOnline_async(callback, context) |
Checks if the filesystem is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version). |
| files→isReadOnly() |
Test if the function is readOnly. |
| files→load(msValidity) |
Preloads the filesystem cache with a specified validity duration. |
| files→loadAttribute(attrName) |
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value. |
| files→load_async(msValidity, callback, context) |
Preloads the filesystem cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version). |
| files→muteValueCallbacks() |
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| files→nextFiles() |
Continues the enumeration of filesystems started using yFirstFiles(). |
| files→registerValueCallback(callback) |
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value. |
| files→remove(pathname) |
Deletes a file, given by its full path name, from the filesystem. |
| files→set_logicalName(newval) |
Changes the logical name of the filesystem. |
| files→set_userData(data) |
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function. |
| files→unmuteValueCallbacks() |
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| files→upload(pathname, content) |
Uploads a file to the filesystem, to the specified full path name. |
| files→wait_async(callback, context) |
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function. |
YFiles.FindFiles()
YFiles.FindFiles()yFindFiles()YFiles::FindFiles()[YFiles FindFiles: ]yFindFiles()YFiles.FindFiles()YFiles.FindFiles()YFiles.FindFiles()YFiles.FindFiles()YFiles.FindFiles()YFiles::FindFiles()YFiles.FindFiles()YFiles.FindFiles()YFiles.FindFiles()YFiles.FindFiles()
Retrieves a filesystem for a given identifier.
js | function yFindFiles( | func) |
cpp | YFiles* FindFiles( | string func) |
m | +(YFiles*) FindFiles | : (NSString*) func |
pas | TYFiles yFindFiles( | func: string): TYFiles |
vb | function FindFiles( | ByVal func As String) As YFiles |
cs | static YFiles FindFiles( | string func) |
java | static YFiles FindFiles( | String func) |
uwp | static YFiles FindFiles( | string func) |
py | FindFiles( | func) |
php | function FindFiles( | $func) |
ts | static FindFiles( | func: string): YFiles |
es | static FindFiles( | func) |
dnp | static YFilesProxy FindFiles( | string func) |
cp | static YFilesProxy * FindFiles( | string func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the filesystem is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YFiles.isOnline() to test if the filesystem is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a filesystem by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
If a call to this object's is_online() method returns FALSE although you are certain that the matching device is plugged, make sure that you did call registerHub() at application initialization time.
Parameters :
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the filesystem, for instance YRGBLED2.files. |
Returns :
a YFiles object allowing you to drive the filesystem.
YFiles.FindFilesInContext()
YFiles.FindFilesInContext()YFiles.FindFilesInContext()YFiles.FindFilesInContext()YFiles.FindFilesInContext()YFiles.FindFilesInContext()
Retrieves a filesystem for a given identifier in a YAPI context.
java | static YFiles FindFilesInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, String func) |
uwp | static YFiles FindFilesInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, string func) |
ts | static FindFilesInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext, func: string): YFiles |
es | static FindFilesInContext( | yctx, func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the filesystem is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YFiles.isOnline() to test if the filesystem is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a filesystem by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context |
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the filesystem, for instance YRGBLED2.files. |
Returns :
a YFiles object allowing you to drive the filesystem.
YFiles.FirstFiles()
YFiles.FirstFiles()yFirstFiles()YFiles::FirstFiles()[YFiles FirstFiles]yFirstFiles()YFiles.FirstFiles()YFiles.FirstFiles()YFiles.FirstFiles()YFiles.FirstFiles()YFiles.FirstFiles()YFiles::FirstFiles()YFiles.FirstFiles()YFiles.FirstFiles()
Starts the enumeration of filesystems currently accessible.
js | function yFirstFiles( | ) |
cpp | YFiles * FirstFiles( | ) |
m | +(YFiles*) FirstFiles |
pas | TYFiles yFirstFiles( | ): TYFiles |
vb | function FirstFiles( | ) As YFiles |
cs | static YFiles FirstFiles( | ) |
java | static YFiles FirstFiles( | ) |
uwp | static YFiles FirstFiles( | ) |
py | FirstFiles( | ) |
php | function FirstFiles( | ) |
ts | static FirstFiles( | ): YFiles | null |
es | static FirstFiles( | ) |
Use the method YFiles.nextFiles() to iterate on next filesystems.
Returns :
a pointer to a YFiles object, corresponding to the first filesystem currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YFiles.FirstFilesInContext()
YFiles.FirstFilesInContext()YFiles.FirstFilesInContext()YFiles.FirstFilesInContext()YFiles.FirstFilesInContext()YFiles.FirstFilesInContext()
Starts the enumeration of filesystems currently accessible.
java | static YFiles FirstFilesInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
uwp | static YFiles FirstFilesInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
ts | static FirstFilesInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext): YFiles | null |
es | static FirstFilesInContext( | yctx) |
Use the method YFiles.nextFiles() to iterate on next filesystems.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context. |
Returns :
a pointer to a YFiles object, corresponding to the first filesystem currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YFiles.GetSimilarFunctions()
YFiles.GetSimilarFunctions()YFiles.GetSimilarFunctions()YFiles.GetSimilarFunctions()
Enumerates all functions of type Files available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID.
dnp | static new string[] GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
cp | static vector<string> GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
Each of these IDs can be provided as argument to the method YFiles.FindFiles to obtain an object that can control the corresponding device.
Returns :
an array of strings, each string containing the unique hardwareId of a device function currently connected.
files→AdvertisedValuefiles.AdvertisedValue
Short string representing the current state of the function.
dnp | string AdvertisedValue |
files→FilesCountfiles.FilesCount
Number of files currently loaded in the filesystem.
dnp | int FilesCount |
files→FriendlyNamefiles.FriendlyName
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
dnp | string FriendlyName |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the function if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the function (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
files→FunctionIdfiles.FunctionId
Hardware identifier of the filesystem, without reference to the module.
dnp | string FunctionId |
For example relay1
files→HardwareIdfiles.HardwareId
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
dnp | string HardwareId |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the function (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
files→IsOnlinefiles.IsOnline
Checks if the function is currently reachable.
dnp | bool IsOnline |
If there is a cached value for the function in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the function.
files→LogicalNamefiles.LogicalName
Logical name of the function.
dnp | string LogicalName |
Writable. You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
files→SerialNumberfiles.SerialNumber
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
dnp | string SerialNumber |
files→clearCache()files.clearCache()files→clearCache()[files clearCache]files.clearCache()files.clearCache()files.clearCache()files.clearCache()files.clearCache()files→clearCache()files.clearCache()files.clearCache()
Invalidates the cache.
js | function clearCache( | ) |
cpp | void clearCache( | ) |
m | -(void) clearCache |
pas | clearCache( | ) |
vb | procedure clearCache( | ) |
cs | void clearCache( | ) |
java | void clearCache( | ) |
py | clearCache( | ) |
php | function clearCache( | ) |
ts | async clearCache( | ): Promise<void> |
es | async clearCache( | ) |
Invalidates the cache of the filesystem attributes. Forces the next call to get_xxx() or loadxxx() to use values that come from the device.
files→describe()files.describe()files→describe()[files describe]files.describe()files.describe()files.describe()files.describe()files.describe()files→describe()files.describe()files.describe()
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the filesystem in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function describe( | ) |
cpp | string describe( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) describe |
pas | string describe( | ): string |
vb | function describe( | ) As String |
cs | string describe( | ) |
java | String describe( | ) |
py | describe( | ) |
php | function describe( | ) |
ts | async describe( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async describe( | ) |
More precisely, TYPE is the type of the function, NAME it the name used for the first access to the function, SERIAL is the serial number of the module if the module is connected or "unresolved", and FUNCTIONID is the hardware identifier of the function if the module is connected. For example, this method returns Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1 if the module is already connected or Relay(BadCustomeName.relay1)=unresolved if the module has not yet been connected. This method does not trigger any USB or TCP transaction and can therefore be used in a debugger.
Returns :
a string that describes the filesystem (ex: Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
files→download()files.download()files→download()[files download: ]files.download()files.download()files.download()files.download()files.download()files.download()files→download()files.download()files.download()files.download()files.download()YFiles download
Downloads the requested file and returns a binary buffer with its content.
js | function download( | pathname) |
cpp | string download( | string pathname) |
m | -(NSMutableData*) download | : (NSString*) pathname |
pas | TByteArray download( | pathname: string): TByteArray |
vb | function download( | ByVal pathname As String) As Byte |
cs | byte[] download( | string pathname) |
java | byte[] download( | String pathname) |
uwp | async Task<byte[]> download( | string pathname) |
py | download( | pathname) |
php | function download( | $pathname) |
ts | async download( | pathname: string): Promise<Uint8Array> |
es | async download( | pathname) |
dnp | byte[] download( | string pathname) |
cp | string download( | string pathname) |
cmd | YFiles target download | pathname |
Parameters :
| pathname | path and name of the file to download |
Returns :
a binary buffer with the file content
On failure, throws an exception or returns an empty content.
files→download_async()files.download_async()
Downloads the requested file and returns a binary buffer with its content.
js | function download_async( | pathname, callback, context) |
This is the asynchronous version that uses a callback to pass the result when the download is completed.
Parameters :
| pathname | path and name of the new file to load |
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the w The callback function receives three arguments: - the user-specific context object - the YFiles object whose download_async was invoked - a binary buffer with the file content |
| context | user-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing.
files→fileExist()files.fileExist()files→fileExist()[files fileExist: ]files.fileExist()files.fileExist()files.fileExist()files.fileExist()files.fileExist()files.fileExist()files→fileExist()files.fileExist()files.fileExist()files.fileExist()files.fileExist()YFiles fileExist
Test if a file exist on the filesystem of the module.
js | function fileExist( | filename) |
cpp | bool fileExist( | string filename) |
m | -(bool) fileExist | : (NSString*) filename |
pas | boolean fileExist( | filename: string): boolean |
vb | function fileExist( | ByVal filename As String) As Boolean |
cs | bool fileExist( | string filename) |
java | boolean fileExist( | String filename) |
uwp | async Task<bool> fileExist( | string filename) |
py | fileExist( | filename) |
php | function fileExist( | $filename) |
ts | async fileExist( | filename: string): Promise<boolean> |
es | async fileExist( | filename) |
dnp | bool fileExist( | string filename) |
cp | bool fileExist( | string filename) |
cmd | YFiles target fileExist | filename |
Parameters :
| filename | the file name to test. |
Returns :
a true if the file exist, false otherwise.
On failure, throws an exception.
files→format_fs()files.format_fs()files→format_fs()[files format_fs]files.format_fs()files.format_fs()files.format_fs()files.format_fs()files.format_fs()files.format_fs()files→format_fs()files.format_fs()files.format_fs()files.format_fs()files.format_fs()YFiles format_fs
Reinitialize the filesystem to its clean, unfragmented, empty state.
js | function format_fs( | ) |
cpp | int format_fs( | ) |
m | -(int) format_fs |
pas | LongInt format_fs( | ): LongInt |
vb | function format_fs( | ) As Integer |
cs | int format_fs( | ) |
java | int format_fs( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> format_fs( | ) |
py | format_fs( | ) |
php | function format_fs( | ) |
ts | async format_fs( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async format_fs( | ) |
dnp | int format_fs( | ) |
cp | int format_fs( | ) |
cmd | YFiles target format_fs |
All files previously uploaded are permanently lost.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
files→get_advertisedValue()
files→advertisedValue()files.get_advertisedValue()files→get_advertisedValue()[files advertisedValue]files.get_advertisedValue()files.get_advertisedValue()files.get_advertisedValue()files.get_advertisedValue()files.get_advertisedValue()files.get_advertisedValue()files→get_advertisedValue()files.get_advertisedValue()files.get_advertisedValue()files.get_advertisedValue()files.get_advertisedValue()YFiles get_advertisedValue
Returns the current value of the filesystem (no more than 6 characters).
js | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cpp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) advertisedValue |
pas | string get_advertisedValue( | ): string |
vb | function get_advertisedValue( | ) As String |
cs | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
java | String get_advertisedValue( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_advertisedValue( | ) |
py | get_advertisedValue( | ) |
php | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
ts | async get_advertisedValue( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_advertisedValue( | ) |
dnp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cmd | YFiles target get_advertisedValue |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the current value of the filesystem (no more than 6 characters).
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFiles.ADVERTISEDVALUE_INVALID.
files→get_errorMessage()
files→errorMessage()files.get_errorMessage()files→get_errorMessage()[files errorMessage]files.get_errorMessage()files.get_errorMessage()files.get_errorMessage()files.get_errorMessage()files.get_errorMessage()files→get_errorMessage()files.get_errorMessage()files.get_errorMessage()
Returns the error message of the latest error with the filesystem.
js | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
cpp | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) errorMessage |
pas | string get_errorMessage( | ): string |
vb | function get_errorMessage( | ) As String |
cs | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
java | String get_errorMessage( | ) |
py | get_errorMessage( | ) |
php | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
ts | get_errorMessage( | ): string |
es | get_errorMessage( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a string corresponding to the latest error message that occured while using the filesystem object
files→get_errorType()
files→errorType()files.get_errorType()files→get_errorType()[files errorType]files.get_errorType()files.get_errorType()files.get_errorType()files.get_errorType()files.get_errorType()files→get_errorType()files.get_errorType()files.get_errorType()
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the filesystem.
js | function get_errorType( | ) |
cpp | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
m | -(YRETCODE) errorType |
pas | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ): YRETCODE |
vb | function get_errorType( | ) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
java | int get_errorType( | ) |
py | get_errorType( | ) |
php | function get_errorType( | ) |
ts | get_errorType( | ): number |
es | get_errorType( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a number corresponding to the code of the latest error that occurred while using the filesystem object
files→get_filesCount()
files→filesCount()files.get_filesCount()files→get_filesCount()[files filesCount]files.get_filesCount()files.get_filesCount()files.get_filesCount()files.get_filesCount()files.get_filesCount()files.get_filesCount()files→get_filesCount()files.get_filesCount()files.get_filesCount()files.get_filesCount()files.get_filesCount()YFiles get_filesCount
Returns the number of files currently loaded in the filesystem.
js | function get_filesCount( | ) |
cpp | int get_filesCount( | ) |
m | -(int) filesCount |
pas | LongInt get_filesCount( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_filesCount( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_filesCount( | ) |
java | int get_filesCount( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_filesCount( | ) |
py | get_filesCount( | ) |
php | function get_filesCount( | ) |
ts | async get_filesCount( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_filesCount( | ) |
dnp | int get_filesCount( | ) |
cp | int get_filesCount( | ) |
cmd | YFiles target get_filesCount |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the number of files currently loaded in the filesystem
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFiles.FILESCOUNT_INVALID.
files→get_freeSpace()
files→freeSpace()files.get_freeSpace()files→get_freeSpace()[files freeSpace]files.get_freeSpace()files.get_freeSpace()files.get_freeSpace()files.get_freeSpace()files.get_freeSpace()files.get_freeSpace()files→get_freeSpace()files.get_freeSpace()files.get_freeSpace()files.get_freeSpace()files.get_freeSpace()YFiles get_freeSpace
Returns the free space for uploading new files to the filesystem, in bytes.
js | function get_freeSpace( | ) |
cpp | int get_freeSpace( | ) |
m | -(int) freeSpace |
pas | LongInt get_freeSpace( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_freeSpace( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_freeSpace( | ) |
java | int get_freeSpace( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_freeSpace( | ) |
py | get_freeSpace( | ) |
php | function get_freeSpace( | ) |
ts | async get_freeSpace( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_freeSpace( | ) |
dnp | int get_freeSpace( | ) |
cp | int get_freeSpace( | ) |
cmd | YFiles target get_freeSpace |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the free space for uploading new files to the filesystem, in bytes
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFiles.FREESPACE_INVALID.
files→get_friendlyName()
files→friendlyName()files.get_friendlyName()files→get_friendlyName()[files friendlyName]files.get_friendlyName()files.get_friendlyName()files.get_friendlyName()files→get_friendlyName()files.get_friendlyName()files.get_friendlyName()files.get_friendlyName()files.get_friendlyName()
Returns a global identifier of the filesystem in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
js | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
cpp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) friendlyName |
cs | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
java | String get_friendlyName( | ) |
py | get_friendlyName( | ) |
php | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
ts | async get_friendlyName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_friendlyName( | ) |
dnp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
cp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the filesystem if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the filesystem (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the filesystem using logical names (ex: MyCustomName.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFiles.FRIENDLYNAME_INVALID.
files→get_functionDescriptor()
files→functionDescriptor()files.get_functionDescriptor()files→get_functionDescriptor()[files functionDescriptor]files.get_functionDescriptor()files.get_functionDescriptor()files.get_functionDescriptor()files.get_functionDescriptor()files.get_functionDescriptor()files→get_functionDescriptor()files.get_functionDescriptor()files.get_functionDescriptor()
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function.
js | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
cpp | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
m | -(YFUN_DESCR) functionDescriptor |
pas | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ): YFUN_DESCR |
vb | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) As YFUN_DESCR |
cs | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
java | String get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
py | get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
php | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
ts | async get_functionDescriptor( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
This identifier can be used to test if two instances of YFunction reference the same physical function on the same physical device.
Returns :
an identifier of type YFUN_DESCR.
If the function has never been contacted, the returned value is Y$CLASSNAME$.FUNCTIONDESCRIPTOR_INVALID.
files→get_functionId()
files→functionId()files.get_functionId()files→get_functionId()[files functionId]files.get_functionId()files.get_functionId()files.get_functionId()files.get_functionId()files→get_functionId()files.get_functionId()files.get_functionId()files.get_functionId()files.get_functionId()
Returns the hardware identifier of the filesystem, without reference to the module.
js | function get_functionId( | ) |
cpp | string get_functionId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) functionId |
vb | function get_functionId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_functionId( | ) |
java | String get_functionId( | ) |
py | get_functionId( | ) |
php | function get_functionId( | ) |
ts | async get_functionId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionId( | ) |
dnp | string get_functionId( | ) |
cp | string get_functionId( | ) |
For example relay1
Returns :
a string that identifies the filesystem (ex: relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFiles.FUNCTIONID_INVALID.
files→get_hardwareId()
files→hardwareId()files.get_hardwareId()files→get_hardwareId()[files hardwareId]files.get_hardwareId()files.get_hardwareId()files.get_hardwareId()files.get_hardwareId()files→get_hardwareId()files.get_hardwareId()files.get_hardwareId()files.get_hardwareId()files.get_hardwareId()
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the filesystem in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
cpp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) hardwareId |
vb | function get_hardwareId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
java | String get_hardwareId( | ) |
py | get_hardwareId( | ) |
php | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
ts | async get_hardwareId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_hardwareId( | ) |
dnp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
cp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the filesystem (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the filesystem (ex: RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFiles.HARDWAREID_INVALID.
files→get_list()
files→list()files.get_list()files→get_list()[files list: ]files.get_list()files.get_list()files.get_list()files.get_list()files.get_list()files.get_list()files→get_list()files.get_list()files.get_list()files.get_list()files.get_list()YFiles get_list
Returns a list of YFileRecord objects that describe files currently loaded in the filesystem.
js | function get_list( | pattern) |
cpp | vector<YFileRecord> get_list( | string pattern) |
m | -(NSMutableArray*) list | : (NSString*) pattern |
pas | TYFileRecordArray get_list( | pattern: string): TYFileRecordArray |
vb | function get_list( | ByVal pattern As String) As List |
cs | List<YFileRecord> get_list( | string pattern) |
java | ArrayList<YFileRecord> get_list( | String pattern) |
uwp | async Task<List<YFileRecord>> get_list( | string pattern) |
py | get_list( | pattern) |
php | function get_list( | $pattern) |
ts | async get_list( | pattern: string): Promise<YFileRecord[] |
es | async get_list( | pattern) |
dnp | YFileRecordProxy[] get_list( | string pattern) |
cp | vector<YFileRecordProxy> get_list( | string pattern) |
cmd | YFiles target get_list | pattern |
Parameters :
| pattern | an optional filter pattern, using star and question marks as wild cards. When an empty pattern is provided, all file records are returned. |
Returns :
a list of YFileRecord objects, containing the file path and name, byte size and 32-bit CRC of the file content.
On failure, throws an exception or returns an empty list.
files→get_logicalName()
files→logicalName()files.get_logicalName()files→get_logicalName()[files logicalName]files.get_logicalName()files.get_logicalName()files.get_logicalName()files.get_logicalName()files.get_logicalName()files.get_logicalName()files→get_logicalName()files.get_logicalName()files.get_logicalName()files.get_logicalName()files.get_logicalName()YFiles get_logicalName
Returns the logical name of the filesystem.
js | function get_logicalName( | ) |
cpp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) logicalName |
pas | string get_logicalName( | ): string |
vb | function get_logicalName( | ) As String |
cs | string get_logicalName( | ) |
java | String get_logicalName( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_logicalName( | ) |
py | get_logicalName( | ) |
php | function get_logicalName( | ) |
ts | async get_logicalName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_logicalName( | ) |
dnp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cmd | YFiles target get_logicalName |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the logical name of the filesystem.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFiles.LOGICALNAME_INVALID.
files→get_module()
files→module()files.get_module()files→get_module()[files module]files.get_module()files.get_module()files.get_module()files.get_module()files.get_module()files→get_module()files.get_module()files.get_module()files.get_module()files.get_module()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located.
js | function get_module( | ) |
cpp | YModule * get_module( | ) |
m | -(YModule*) module |
pas | TYModule get_module( | ): TYModule |
vb | function get_module( | ) As YModule |
cs | YModule get_module( | ) |
java | YModule get_module( | ) |
py | get_module( | ) |
php | function get_module( | ) |
ts | async get_module( | ): Promise<YModule> |
es | async get_module( | ) |
dnp | YModuleProxy get_module( | ) |
cp | YModuleProxy * get_module( | ) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned instance of YModule is not shown as on-line.
Returns :
an instance of YModule
files→get_module_async()
files→module_async()files.get_module_async()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version).
js | function get_module_async( | callback, context) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned YModule object does not show as on-line.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking Firefox JavaScript VM that does not implement context switching during blocking I/O calls. See the documentation section on asynchronous JavasSript calls for more details.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the requested YModule object |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
files→get_serialNumber()
files→serialNumber()files.get_serialNumber()files→get_serialNumber()[files serialNumber]files.get_serialNumber()files.get_serialNumber()files.get_serialNumber()files.get_serialNumber()files.get_serialNumber()files.get_serialNumber()files→get_serialNumber()files.get_serialNumber()files.get_serialNumber()files.get_serialNumber()files.get_serialNumber()YFiles get_serialNumber
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
js | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
cpp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) serialNumber |
pas | string get_serialNumber( | ): string |
vb | function get_serialNumber( | ) As String |
cs | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
java | String get_serialNumber( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_serialNumber( | ) |
py | get_serialNumber( | ) |
php | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
ts | async get_serialNumber( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_serialNumber( | ) |
dnp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cmd | YFiles target get_serialNumber |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFunction.SERIALNUMBER_INVALID.
files→get_userData()
files→userData()files.get_userData()files→get_userData()[files userData]files.get_userData()files.get_userData()files.get_userData()files.get_userData()files.get_userData()files→get_userData()files.get_userData()files.get_userData()
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData.
js | function get_userData( | ) |
cpp | void * get_userData( | ) |
m | -(id) userData |
pas | Tobject get_userData( | ): Tobject |
vb | function get_userData( | ) As Object |
cs | object get_userData( | ) |
java | Object get_userData( | ) |
py | get_userData( | ) |
php | function get_userData( | ) |
ts | async get_userData( | ): Promise<object|null> |
es | async get_userData( | ) |
This attribute is never touched directly by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Returns :
the object stored previously by the caller.
files→isOnline()files.isOnline()files→isOnline()[files isOnline]files.isOnline()files.isOnline()files.isOnline()files.isOnline()files.isOnline()files→isOnline()files.isOnline()files.isOnline()files.isOnline()files.isOnline()
Checks if the filesystem is currently reachable, without raising any error.
js | function isOnline( | ) |
cpp | bool isOnline( | ) |
m | -(BOOL) isOnline |
pas | boolean isOnline( | ): boolean |
vb | function isOnline( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isOnline( | ) |
java | boolean isOnline( | ) |
py | isOnline( | ) |
php | function isOnline( | ) |
ts | async isOnline( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isOnline( | ) |
dnp | bool isOnline( | ) |
cp | bool isOnline( | ) |
If there is a cached value for the filesystem in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the filesystem.
Returns :
true if the filesystem can be reached, and false otherwise
files→isOnline_async()files.isOnline_async()
Checks if the filesystem is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version).
js | function isOnline_async( | callback, context) |
If there is a cached value for the filesystem in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the requested function.
This asynchronous version exists only in Javascript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the Javascript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the boolean result |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
files→isReadOnly()files→isReadOnly()[files isReadOnly]files.isReadOnly()files.isReadOnly()files.isReadOnly()files.isReadOnly()files.isReadOnly()files.isReadOnly()files→isReadOnly()files.isReadOnly()files.isReadOnly()files.isReadOnly()files.isReadOnly()YFiles isReadOnly
Test if the function is readOnly.
cpp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
m | -(bool) isReadOnly |
pas | boolean isReadOnly( | ): boolean |
vb | function isReadOnly( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
java | boolean isReadOnly( | ) |
uwp | async Task<bool> isReadOnly( | ) |
py | isReadOnly( | ) |
php | function isReadOnly( | ) |
ts | async isReadOnly( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isReadOnly( | ) |
dnp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cmd | YFiles target isReadOnly |
Return true if the function is write protected or that the function is not available.
Returns :
true if the function is readOnly or not online.
files→load()files.load()files→load()[files load: ]files.load()files.load()files.load()files.load()files.load()files→load()files.load()files.load()
Preloads the filesystem cache with a specified validity duration.
js | function load( | msValidity) |
cpp | YRETCODE load( | int msValidity) |
m | -(YRETCODE) load | : (u64) msValidity |
pas | YRETCODE load( | msValidity: u64): YRETCODE |
vb | function load( | ByVal msValidity As Long) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE load( | ulong msValidity) |
java | int load( | long msValidity) |
py | load( | msValidity) |
php | function load( | $msValidity) |
ts | async load( | msValidity: number): Promise<number> |
es | async load( | msValidity) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity attributed to the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
files→loadAttribute()files.loadAttribute()files→loadAttribute()[files loadAttribute: ]files.loadAttribute()files.loadAttribute()files.loadAttribute()files.loadAttribute()files.loadAttribute()files.loadAttribute()files→loadAttribute()files.loadAttribute()files.loadAttribute()files.loadAttribute()files.loadAttribute()
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value.
js | function loadAttribute( | attrName) |
cpp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
m | -(NSString*) loadAttribute | : (NSString*) attrName |
pas | string loadAttribute( | attrName: string): string |
vb | function loadAttribute( | ByVal attrName As String) As String |
cs | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
java | String loadAttribute( | String attrName) |
uwp | async Task<string> loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
py | loadAttribute( | attrName) |
php | function loadAttribute( | $attrName) |
ts | async loadAttribute( | attrName: string): Promise<string> |
es | async loadAttribute( | attrName) |
dnp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
cp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
Parameters :
| attrName | the name of the requested attribute |
Returns :
a string with the value of the the attribute
On failure, throws an exception or returns an empty string.
files→load_async()files.load_async()
Preloads the filesystem cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version).
js | function load_async( | msValidity, callback, context) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the JavaScript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity of the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the error code (or YAPI.SUCCESS) |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
files→muteValueCallbacks()files.muteValueCallbacks()files→muteValueCallbacks()[files muteValueCallbacks]files.muteValueCallbacks()files.muteValueCallbacks()files.muteValueCallbacks()files.muteValueCallbacks()files.muteValueCallbacks()files.muteValueCallbacks()files→muteValueCallbacks()files.muteValueCallbacks()files.muteValueCallbacks()files.muteValueCallbacks()files.muteValueCallbacks()YFiles muteValueCallbacks
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) muteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt muteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async muteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YFiles target muteValueCallbacks |
You can use this function to save bandwidth and CPU on computers with limited resources, or to prevent unwanted invocations of the HTTP callback. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
files→nextFiles()files.nextFiles()files→nextFiles()[files nextFiles]files.nextFiles()files.nextFiles()files.nextFiles()files.nextFiles()files.nextFiles()files.nextFiles()files→nextFiles()files.nextFiles()files.nextFiles()
Continues the enumeration of filesystems started using yFirstFiles().
js | function nextFiles( | ) |
cpp | YFiles * nextFiles( | ) |
m | -(nullable YFiles*) nextFiles |
pas | TYFiles nextFiles( | ): TYFiles |
vb | function nextFiles( | ) As YFiles |
cs | YFiles nextFiles( | ) |
java | YFiles nextFiles( | ) |
uwp | YFiles nextFiles( | ) |
py | nextFiles( | ) |
php | function nextFiles( | ) |
ts | nextFiles( | ): YFiles | null |
es | nextFiles( | ) |
Caution: You can't make any assumption about the returned filesystems order. If you want to find a specific a filesystem, use Files.findFiles() and a hardwareID or a logical name.
Returns :
a pointer to a YFiles object, corresponding to a filesystem currently online, or a null pointer if there are no more filesystems to enumerate.
files→registerValueCallback()files.registerValueCallback()files→registerValueCallback()[files registerValueCallback: ]files.registerValueCallback()files.registerValueCallback()files.registerValueCallback()files.registerValueCallback()files.registerValueCallback()files.registerValueCallback()files→registerValueCallback()files.registerValueCallback()files.registerValueCallback()
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value.
js | function registerValueCallback( | callback) |
cpp | int registerValueCallback( | YFilesValueCallback callback) |
m | -(int) registerValueCallback | : (YFilesValueCallback _Nullable) callback |
pas | LongInt registerValueCallback( | callback: TYFilesValueCallback): LongInt |
vb | function registerValueCallback( | ByVal callback As YFilesValueCallback) As Integer |
cs | int registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
java | int registerValueCallback( | UpdateCallback callback) |
uwp | async Task<int> registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
py | registerValueCallback( | callback) |
php | function registerValueCallback( | $callback) |
ts | async registerValueCallback( | callback: YFilesValueCallback | null): Promise<number> |
es | async registerValueCallback( | callback) |
The callback is invoked only during the execution of ySleep or yHandleEvents. This provides control over the time when the callback is triggered. For good responsiveness, remember to call one of these two functions periodically. To unregister a callback, pass a null pointer as argument.
Parameters :
| callback | the callback function to call, or a null pointer. The callback function should take two arguments: the function object of which the value has changed, and the character string describing the new advertised value. |
files→remove()files.remove()files→remove()[files remove: ]files.remove()files.remove()files.remove()files.remove()files.remove()files.remove()files→remove()files.remove()files.remove()files.remove()files.remove()YFiles remove
Deletes a file, given by its full path name, from the filesystem.
js | function remove( | pathname) |
cpp | int remove( | string pathname) |
m | -(int) remove | : (NSString*) pathname |
pas | LongInt remove( | pathname: string): LongInt |
vb | function remove( | ByVal pathname As String) As Integer |
cs | int remove( | string pathname) |
java | int remove( | String pathname) |
uwp | async Task<int> remove( | string pathname) |
py | remove( | pathname) |
php | function remove( | $pathname) |
ts | async remove( | pathname: string): Promise<number> |
es | async remove( | pathname) |
dnp | int remove( | string pathname) |
cp | int remove( | string pathname) |
cmd | YFiles target remove | pathname |
Because of filesystem fragmentation, deleting a file may not always free up the whole space used by the file. However, rewriting a file with the same path name will always reuse any space not freed previously. If you need to ensure that no space is taken by previously deleted files, you can use format_fs to fully reinitialize the filesystem.
Parameters :
| pathname | path and name of the file to remove. |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
files→set_logicalName()
files→setLogicalName()files.set_logicalName()files→set_logicalName()[files setLogicalName: ]files.set_logicalName()files.set_logicalName()files.set_logicalName()files.set_logicalName()files.set_logicalName()files.set_logicalName()files→set_logicalName()files.set_logicalName()files.set_logicalName()files.set_logicalName()files.set_logicalName()YFiles set_logicalName
Changes the logical name of the filesystem.
js | function set_logicalName( | newval) |
cpp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setLogicalName | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_logicalName( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_logicalName( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
java | int set_logicalName( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_logicalName( | string newval) |
py | set_logicalName( | newval) |
php | function set_logicalName( | $newval) |
ts | async set_logicalName( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_logicalName( | newval) |
dnp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cmd | YFiles target set_logicalName | newval |
You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the logical name of the filesystem. |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
files→set_userData()
files→setUserData()files.set_userData()files→set_userData()[files setUserData: ]files.set_userData()files.set_userData()files.set_userData()files.set_userData()files.set_userData()files→set_userData()files.set_userData()files.set_userData()
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function.
js | function set_userData( | data) |
cpp | void set_userData( | void * data) |
m | -(void) setUserData | : (id) data |
pas | set_userData( | data: Tobject) |
vb | procedure set_userData( | ByVal data As Object) |
cs | void set_userData( | object data) |
java | void set_userData( | Object data) |
py | set_userData( | data) |
php | function set_userData( | $data) |
ts | async set_userData( | data: object|null): Promise<void> |
es | async set_userData( | data) |
This attribute is never touched by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Parameters :
| data | any kind of object to be stored |
files→unmuteValueCallbacks()files.unmuteValueCallbacks()files→unmuteValueCallbacks()[files unmuteValueCallbacks]files.unmuteValueCallbacks()files.unmuteValueCallbacks()files.unmuteValueCallbacks()files.unmuteValueCallbacks()files.unmuteValueCallbacks()files.unmuteValueCallbacks()files→unmuteValueCallbacks()files.unmuteValueCallbacks()files.unmuteValueCallbacks()files.unmuteValueCallbacks()files.unmuteValueCallbacks()YFiles unmuteValueCallbacks
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) unmuteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YFiles target unmuteValueCallbacks |
This function reverts the effect of a previous call to muteValueCallbacks(). Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
files→upload()files.upload()files→upload()[files upload: ]files.upload()files.upload()files.upload()files.upload()files.upload()files.upload()files→upload()files.upload()files.upload()files.upload()files.upload()YFiles upload
Uploads a file to the filesystem, to the specified full path name.
js | function upload( | pathname, content) |
cpp | int upload( | string pathname, string content) |
m | -(int) upload | : (NSString*) pathname |
| : (NSData*) content |
pas | LongInt upload( | pathname: string, content: TByteArray): LongInt |
vb | procedure upload( | ByVal pathname As String, ByVal content As Byte() |
cs | int upload( | string pathname, byte[] content) |
java | int upload( | String pathname, byte[] content) |
uwp | async Task<int> upload( | string pathname, byte[] content) |
py | upload( | pathname, content) |
php | function upload( | $pathname, $content) |
ts | async upload( | pathname: string, content: Uint8Array): Promise<number> |
es | async upload( | pathname, content) |
dnp | int upload( | string pathname, byte[] content) |
cp | int upload( | string pathname, string content) |
cmd | YFiles target upload | pathname content |
If a file already exists with the same path name, its content is overwritten.
Parameters :
| pathname | path and name of the new file to create |
| content | binary buffer with the content to set |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
files→wait_async()files.wait_async()files.wait_async()files.wait_async()
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function.
js | function wait_async( | callback, context) |
ts | wait_async( | callback: Function, context: object) |
es | wait_async( | callback, context) |
The callback function can therefore freely issue synchronous or asynchronous commands, without risking to block the JavaScript VM.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when all pending commands on the module are completed. The callback function receives two arguments: the caller-specific context object and the receiving function object. |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing.
11.5. Class YRealTimeClock
Real-time clock control interface, available for instance in the YoctoHub-GSM-3G-EU, the YoctoHub-GSM-3G-NA, the YoctoHub-GSM-4G or the YoctoHub-Wireless-n
The YRealTimeClock class provide access to the embedded real-time clock available on some Yoctopuce devices. It can provide current date and time, even after a power outage lasting several days. It is the base for automated wake-up functions provided by the WakeUpScheduler. The current time may represent a local time as well as an UTC time, but no automatic time change will occur to account for daylight saving time.
In order to use the functions described here, you should include:
es | in HTML: <script src="../../lib/yocto_realtimeclock.js"></script> in node.js: require('yoctolib-es2017/yocto_realtimeclock.js'); |
js | <script type='text/javascript' src='yocto_realtimeclock.js'></script> |
cpp | #include "yocto_realtimeclock.h" |
m | #import "yocto_realtimeclock.h" |
pas | uses yocto_realtimeclock; |
vb | yocto_realtimeclock.vb |
cs | yocto_realtimeclock.cs |
java | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YRealTimeClock; |
uwp | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YRealTimeClock; |
py | from yocto_realtimeclock import * |
php | require_once('yocto_realtimeclock.php'); |
ts | in HTML: import { YRealTimeClock } from '../../dist/esm/yocto_realtimeclock.js'; in Node.js: import { YRealTimeClock } from 'yoctolib-cjs/yocto_realtimeclock.js'; |
dnp | import YoctoProxyAPI.YRealTimeClockProxy |
cp | #include "yocto_realtimeclock_proxy.h" |
vi | YRealTimeClock.vi |
ml | import YoctoProxyAPI.YRealTimeClockProxy |
| Global functions |
|---|
| YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClock(func) |
Retrieves a real-time clock for a given identifier. |
| YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClockInContext(yctx, func) |
Retrieves a real-time clock for a given identifier in a YAPI context. |
| YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClock() |
Starts the enumeration of real-time clocks currently accessible. |
| YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClockInContext(yctx) |
Starts the enumeration of real-time clocks currently accessible. |
| YRealTimeClock.GetSimilarFunctions() |
Enumerates all functions of type RealTimeClock available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID. |
| YRealTimeClock properties |
| realtimeclock→AdvertisedValue [read-only] |
Short string representing the current state of the function. |
| realtimeclock→FriendlyName [read-only] |
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| realtimeclock→FunctionId [read-only] |
Hardware identifier of the real-time clock, without reference to the module. |
| realtimeclock→HardwareId [read-only] |
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| realtimeclock→IsOnline [read-only] |
Checks if the function is currently reachable. |
| realtimeclock→LogicalName [writable] |
Logical name of the function. |
| realtimeclock→SerialNumber [read-only] |
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| realtimeclock→UtcOffset [writable] |
Number of seconds between current time and UTC time (time zone). |
| YRealTimeClock methods |
| realtimeclock→clearCache() |
Invalidates the cache. |
| realtimeclock→describe() |
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the real-time clock in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| realtimeclock→get_advertisedValue() |
Returns the current value of the real-time clock (no more than 6 characters). |
| realtimeclock→get_dateTime() |
Returns the current time in the form "YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss". |
| realtimeclock→get_errorMessage() |
Returns the error message of the latest error with the real-time clock. |
| realtimeclock→get_errorType() |
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the real-time clock. |
| realtimeclock→get_friendlyName() |
Returns a global identifier of the real-time clock in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| realtimeclock→get_functionDescriptor() |
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function. |
| realtimeclock→get_functionId() |
Returns the hardware identifier of the real-time clock, without reference to the module. |
| realtimeclock→get_hardwareId() |
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the real-time clock in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| realtimeclock→get_logicalName() |
Returns the logical name of the real-time clock. |
| realtimeclock→get_module() |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located. |
| realtimeclock→get_module_async(callback, context) |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version). |
| realtimeclock→get_serialNumber() |
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| realtimeclock→get_timeSet() |
Returns true if the clock has been set, and false otherwise. |
| realtimeclock→get_unixTime() |
Returns the current time in Unix format (number of elapsed seconds since Jan 1st, 1970). |
| realtimeclock→get_userData() |
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData. |
| realtimeclock→get_utcOffset() |
Returns the number of seconds between current time and UTC time (time zone). |
| realtimeclock→isOnline() |
Checks if the real-time clock is currently reachable, without raising any error. |
| realtimeclock→isOnline_async(callback, context) |
Checks if the real-time clock is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version). |
| realtimeclock→isReadOnly() |
Test if the function is readOnly. |
| realtimeclock→load(msValidity) |
Preloads the real-time clock cache with a specified validity duration. |
| realtimeclock→loadAttribute(attrName) |
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value. |
| realtimeclock→load_async(msValidity, callback, context) |
Preloads the real-time clock cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version). |
| realtimeclock→muteValueCallbacks() |
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| realtimeclock→nextRealTimeClock() |
Continues the enumeration of real-time clocks started using yFirstRealTimeClock(). |
| realtimeclock→registerValueCallback(callback) |
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value. |
| realtimeclock→set_logicalName(newval) |
Changes the logical name of the real-time clock. |
| realtimeclock→set_unixTime(newval) |
Changes the current time. |
| realtimeclock→set_userData(data) |
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function. |
| realtimeclock→set_utcOffset(newval) |
Changes the number of seconds between current time and UTC time (time zone). |
| realtimeclock→unmuteValueCallbacks() |
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| realtimeclock→wait_async(callback, context) |
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function. |
YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClock()
YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClock()yFindRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock::FindRealTimeClock()[YRealTimeClock FindRealTimeClock: ]yFindRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock::FindRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClock()
Retrieves a real-time clock for a given identifier.
js | function yFindRealTimeClock( | func) |
cpp | YRealTimeClock* FindRealTimeClock( | string func) |
m | +(YRealTimeClock*) FindRealTimeClock | : (NSString*) func |
pas | TYRealTimeClock yFindRealTimeClock( | func: string): TYRealTimeClock |
vb | function FindRealTimeClock( | ByVal func As String) As YRealTimeClock |
cs | static YRealTimeClock FindRealTimeClock( | string func) |
java | static YRealTimeClock FindRealTimeClock( | String func) |
uwp | static YRealTimeClock FindRealTimeClock( | string func) |
py | FindRealTimeClock( | func) |
php | function FindRealTimeClock( | $func) |
ts | static FindRealTimeClock( | func: string): YRealTimeClock |
es | static FindRealTimeClock( | func) |
dnp | static YRealTimeClockProxy FindRealTimeClock( | string func) |
cp | static YRealTimeClockProxy * FindRealTimeClock( | string func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the real-time clock is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YRealTimeClock.isOnline() to test if the real-time clock is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a real-time clock by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
If a call to this object's is_online() method returns FALSE although you are certain that the matching device is plugged, make sure that you did call registerHub() at application initialization time.
Parameters :
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the real-time clock, for instance YHUBGSM3.realTimeClock. |
Returns :
a YRealTimeClock object allowing you to drive the real-time clock.
YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClockInContext()
YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClockInContext()YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClockInContext()YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClockInContext()YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClockInContext()YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClockInContext()
Retrieves a real-time clock for a given identifier in a YAPI context.
java | static YRealTimeClock FindRealTimeClockInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, |
| String func) |
uwp | static YRealTimeClock FindRealTimeClockInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, |
| string func) |
ts | static FindRealTimeClockInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext, func: string): YRealTimeClock |
es | static FindRealTimeClockInContext( | yctx, func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the real-time clock is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YRealTimeClock.isOnline() to test if the real-time clock is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a real-time clock by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context |
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the real-time clock, for instance YHUBGSM3.realTimeClock. |
Returns :
a YRealTimeClock object allowing you to drive the real-time clock.
YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClock()
YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClock()yFirstRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock::FirstRealTimeClock()[YRealTimeClock FirstRealTimeClock]yFirstRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock::FirstRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClock()YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClock()
Starts the enumeration of real-time clocks currently accessible.
js | function yFirstRealTimeClock( | ) |
cpp | YRealTimeClock * FirstRealTimeClock( | ) |
m | +(YRealTimeClock*) FirstRealTimeClock |
pas | TYRealTimeClock yFirstRealTimeClock( | ): TYRealTimeClock |
vb | function FirstRealTimeClock( | ) As YRealTimeClock |
cs | static YRealTimeClock FirstRealTimeClock( | ) |
java | static YRealTimeClock FirstRealTimeClock( | ) |
uwp | static YRealTimeClock FirstRealTimeClock( | ) |
py | FirstRealTimeClock( | ) |
php | function FirstRealTimeClock( | ) |
ts | static FirstRealTimeClock( | ): YRealTimeClock | null |
es | static FirstRealTimeClock( | ) |
Use the method YRealTimeClock.nextRealTimeClock() to iterate on next real-time clocks.
Returns :
a pointer to a YRealTimeClock object, corresponding to the first real-time clock currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClockInContext()
YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClockInContext()YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClockInContext()YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClockInContext()YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClockInContext()YRealTimeClock.FirstRealTimeClockInContext()
Starts the enumeration of real-time clocks currently accessible.
java | static YRealTimeClock FirstRealTimeClockInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
uwp | static YRealTimeClock FirstRealTimeClockInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
ts | static FirstRealTimeClockInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext): YRealTimeClock | null |
es | static FirstRealTimeClockInContext( | yctx) |
Use the method YRealTimeClock.nextRealTimeClock() to iterate on next real-time clocks.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context. |
Returns :
a pointer to a YRealTimeClock object, corresponding to the first real-time clock currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YRealTimeClock.GetSimilarFunctions()
YRealTimeClock.GetSimilarFunctions()YRealTimeClock.GetSimilarFunctions()YRealTimeClock.GetSimilarFunctions()
Enumerates all functions of type RealTimeClock available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID.
dnp | static new string[] GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
cp | static vector<string> GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
Each of these IDs can be provided as argument to the method YRealTimeClock.FindRealTimeClock to obtain an object that can control the corresponding device.
Returns :
an array of strings, each string containing the unique hardwareId of a device function currently connected.
realtimeclock→AdvertisedValuerealtimeclock.AdvertisedValue
Short string representing the current state of the function.
dnp | string AdvertisedValue |
realtimeclock→FriendlyNamerealtimeclock.FriendlyName
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
dnp | string FriendlyName |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the function if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the function (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
realtimeclock→FunctionIdrealtimeclock.FunctionId
Hardware identifier of the real-time clock, without reference to the module.
dnp | string FunctionId |
For example relay1
realtimeclock→HardwareIdrealtimeclock.HardwareId
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
dnp | string HardwareId |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the function (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
realtimeclock→IsOnlinerealtimeclock.IsOnline
Checks if the function is currently reachable.
dnp | bool IsOnline |
If there is a cached value for the function in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the function.
realtimeclock→LogicalNamerealtimeclock.LogicalName
Logical name of the function.
dnp | string LogicalName |
Writable. You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
realtimeclock→SerialNumberrealtimeclock.SerialNumber
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
dnp | string SerialNumber |
realtimeclock→UtcOffsetrealtimeclock.UtcOffset
Number of seconds between current time and UTC time (time zone).
dnp | int UtcOffset |
Writable. The timezone is automatically rounded to the nearest multiple of 15 minutes. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
realtimeclock→clearCache()realtimeclock.clearCache()realtimeclock→clearCache()[realtimeclock clearCache]realtimeclock.clearCache()realtimeclock.clearCache()realtimeclock.clearCache()realtimeclock.clearCache()realtimeclock.clearCache()realtimeclock→clearCache()realtimeclock.clearCache()realtimeclock.clearCache()
Invalidates the cache.
js | function clearCache( | ) |
cpp | void clearCache( | ) |
m | -(void) clearCache |
pas | clearCache( | ) |
vb | procedure clearCache( | ) |
cs | void clearCache( | ) |
java | void clearCache( | ) |
py | clearCache( | ) |
php | function clearCache( | ) |
ts | async clearCache( | ): Promise<void> |
es | async clearCache( | ) |
Invalidates the cache of the real-time clock attributes. Forces the next call to get_xxx() or loadxxx() to use values that come from the device.
realtimeclock→describe()realtimeclock.describe()realtimeclock→describe()[realtimeclock describe]realtimeclock.describe()realtimeclock.describe()realtimeclock.describe()realtimeclock.describe()realtimeclock.describe()realtimeclock→describe()realtimeclock.describe()realtimeclock.describe()
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the real-time clock in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function describe( | ) |
cpp | string describe( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) describe |
pas | string describe( | ): string |
vb | function describe( | ) As String |
cs | string describe( | ) |
java | String describe( | ) |
py | describe( | ) |
php | function describe( | ) |
ts | async describe( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async describe( | ) |
More precisely, TYPE is the type of the function, NAME it the name used for the first access to the function, SERIAL is the serial number of the module if the module is connected or "unresolved", and FUNCTIONID is the hardware identifier of the function if the module is connected. For example, this method returns Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1 if the module is already connected or Relay(BadCustomeName.relay1)=unresolved if the module has not yet been connected. This method does not trigger any USB or TCP transaction and can therefore be used in a debugger.
Returns :
a string that describes the real-time clock (ex: Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
realtimeclock→get_advertisedValue()
realtimeclock→advertisedValue()realtimeclock.get_advertisedValue()realtimeclock→get_advertisedValue()[realtimeclock advertisedValue]realtimeclock.get_advertisedValue()realtimeclock.get_advertisedValue()realtimeclock.get_advertisedValue()realtimeclock.get_advertisedValue()realtimeclock.get_advertisedValue()realtimeclock.get_advertisedValue()realtimeclock→get_advertisedValue()realtimeclock.get_advertisedValue()realtimeclock.get_advertisedValue()realtimeclock.get_advertisedValue()realtimeclock.get_advertisedValue()YRealTimeClock get_advertisedValue
Returns the current value of the real-time clock (no more than 6 characters).
js | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cpp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) advertisedValue |
pas | string get_advertisedValue( | ): string |
vb | function get_advertisedValue( | ) As String |
cs | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
java | String get_advertisedValue( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_advertisedValue( | ) |
py | get_advertisedValue( | ) |
php | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
ts | async get_advertisedValue( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_advertisedValue( | ) |
dnp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cmd | YRealTimeClock target get_advertisedValue |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the current value of the real-time clock (no more than 6 characters).
On failure, throws an exception or returns YRealTimeClock.ADVERTISEDVALUE_INVALID.
realtimeclock→get_dateTime()
realtimeclock→dateTime()realtimeclock.get_dateTime()realtimeclock→get_dateTime()[realtimeclock dateTime]realtimeclock.get_dateTime()realtimeclock.get_dateTime()realtimeclock.get_dateTime()realtimeclock.get_dateTime()realtimeclock.get_dateTime()realtimeclock.get_dateTime()realtimeclock→get_dateTime()realtimeclock.get_dateTime()realtimeclock.get_dateTime()realtimeclock.get_dateTime()realtimeclock.get_dateTime()YRealTimeClock get_dateTime
Returns the current time in the form "YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss".
js | function get_dateTime( | ) |
cpp | string get_dateTime( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) dateTime |
pas | string get_dateTime( | ): string |
vb | function get_dateTime( | ) As String |
cs | string get_dateTime( | ) |
java | String get_dateTime( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_dateTime( | ) |
py | get_dateTime( | ) |
php | function get_dateTime( | ) |
ts | async get_dateTime( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_dateTime( | ) |
dnp | string get_dateTime( | ) |
cp | string get_dateTime( | ) |
cmd | YRealTimeClock target get_dateTime |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the current time in the form "YYYY/MM/DD hh:mm:ss"
On failure, throws an exception or returns YRealTimeClock.DATETIME_INVALID.
realtimeclock→get_errorMessage()
realtimeclock→errorMessage()realtimeclock.get_errorMessage()realtimeclock→get_errorMessage()[realtimeclock errorMessage]realtimeclock.get_errorMessage()realtimeclock.get_errorMessage()realtimeclock.get_errorMessage()realtimeclock.get_errorMessage()realtimeclock.get_errorMessage()realtimeclock→get_errorMessage()realtimeclock.get_errorMessage()realtimeclock.get_errorMessage()
Returns the error message of the latest error with the real-time clock.
js | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
cpp | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) errorMessage |
pas | string get_errorMessage( | ): string |
vb | function get_errorMessage( | ) As String |
cs | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
java | String get_errorMessage( | ) |
py | get_errorMessage( | ) |
php | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
ts | get_errorMessage( | ): string |
es | get_errorMessage( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a string corresponding to the latest error message that occured while using the real-time clock object
realtimeclock→get_errorType()
realtimeclock→errorType()realtimeclock.get_errorType()realtimeclock→get_errorType()[realtimeclock errorType]realtimeclock.get_errorType()realtimeclock.get_errorType()realtimeclock.get_errorType()realtimeclock.get_errorType()realtimeclock.get_errorType()realtimeclock→get_errorType()realtimeclock.get_errorType()realtimeclock.get_errorType()
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the real-time clock.
js | function get_errorType( | ) |
cpp | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
m | -(YRETCODE) errorType |
pas | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ): YRETCODE |
vb | function get_errorType( | ) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
java | int get_errorType( | ) |
py | get_errorType( | ) |
php | function get_errorType( | ) |
ts | get_errorType( | ): number |
es | get_errorType( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a number corresponding to the code of the latest error that occurred while using the real-time clock object
realtimeclock→get_friendlyName()
realtimeclock→friendlyName()realtimeclock.get_friendlyName()realtimeclock→get_friendlyName()[realtimeclock friendlyName]realtimeclock.get_friendlyName()realtimeclock.get_friendlyName()realtimeclock.get_friendlyName()realtimeclock→get_friendlyName()realtimeclock.get_friendlyName()realtimeclock.get_friendlyName()realtimeclock.get_friendlyName()realtimeclock.get_friendlyName()
Returns a global identifier of the real-time clock in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
js | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
cpp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) friendlyName |
cs | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
java | String get_friendlyName( | ) |
py | get_friendlyName( | ) |
php | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
ts | async get_friendlyName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_friendlyName( | ) |
dnp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
cp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the real-time clock if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the real-time clock (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the real-time clock using logical names (ex: MyCustomName.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YRealTimeClock.FRIENDLYNAME_INVALID.
realtimeclock→get_functionDescriptor()
realtimeclock→functionDescriptor()realtimeclock.get_functionDescriptor()realtimeclock→get_functionDescriptor()[realtimeclock functionDescriptor]realtimeclock.get_functionDescriptor()realtimeclock.get_functionDescriptor()realtimeclock.get_functionDescriptor()realtimeclock.get_functionDescriptor()realtimeclock.get_functionDescriptor()realtimeclock→get_functionDescriptor()realtimeclock.get_functionDescriptor()realtimeclock.get_functionDescriptor()
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function.
js | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
cpp | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
m | -(YFUN_DESCR) functionDescriptor |
pas | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ): YFUN_DESCR |
vb | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) As YFUN_DESCR |
cs | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
java | String get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
py | get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
php | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
ts | async get_functionDescriptor( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
This identifier can be used to test if two instances of YFunction reference the same physical function on the same physical device.
Returns :
an identifier of type YFUN_DESCR.
If the function has never been contacted, the returned value is Y$CLASSNAME$.FUNCTIONDESCRIPTOR_INVALID.
realtimeclock→get_functionId()
realtimeclock→functionId()realtimeclock.get_functionId()realtimeclock→get_functionId()[realtimeclock functionId]realtimeclock.get_functionId()realtimeclock.get_functionId()realtimeclock.get_functionId()realtimeclock.get_functionId()realtimeclock→get_functionId()realtimeclock.get_functionId()realtimeclock.get_functionId()realtimeclock.get_functionId()realtimeclock.get_functionId()
Returns the hardware identifier of the real-time clock, without reference to the module.
js | function get_functionId( | ) |
cpp | string get_functionId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) functionId |
vb | function get_functionId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_functionId( | ) |
java | String get_functionId( | ) |
py | get_functionId( | ) |
php | function get_functionId( | ) |
ts | async get_functionId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionId( | ) |
dnp | string get_functionId( | ) |
cp | string get_functionId( | ) |
For example relay1
Returns :
a string that identifies the real-time clock (ex: relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YRealTimeClock.FUNCTIONID_INVALID.
realtimeclock→get_hardwareId()
realtimeclock→hardwareId()realtimeclock.get_hardwareId()realtimeclock→get_hardwareId()[realtimeclock hardwareId]realtimeclock.get_hardwareId()realtimeclock.get_hardwareId()realtimeclock.get_hardwareId()realtimeclock.get_hardwareId()realtimeclock→get_hardwareId()realtimeclock.get_hardwareId()realtimeclock.get_hardwareId()realtimeclock.get_hardwareId()realtimeclock.get_hardwareId()
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the real-time clock in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
cpp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) hardwareId |
vb | function get_hardwareId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
java | String get_hardwareId( | ) |
py | get_hardwareId( | ) |
php | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
ts | async get_hardwareId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_hardwareId( | ) |
dnp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
cp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the real-time clock (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the real-time clock (ex: RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YRealTimeClock.HARDWAREID_INVALID.
realtimeclock→get_logicalName()
realtimeclock→logicalName()realtimeclock.get_logicalName()realtimeclock→get_logicalName()[realtimeclock logicalName]realtimeclock.get_logicalName()realtimeclock.get_logicalName()realtimeclock.get_logicalName()realtimeclock.get_logicalName()realtimeclock.get_logicalName()realtimeclock.get_logicalName()realtimeclock→get_logicalName()realtimeclock.get_logicalName()realtimeclock.get_logicalName()realtimeclock.get_logicalName()realtimeclock.get_logicalName()YRealTimeClock get_logicalName
Returns the logical name of the real-time clock.
js | function get_logicalName( | ) |
cpp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) logicalName |
pas | string get_logicalName( | ): string |
vb | function get_logicalName( | ) As String |
cs | string get_logicalName( | ) |
java | String get_logicalName( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_logicalName( | ) |
py | get_logicalName( | ) |
php | function get_logicalName( | ) |
ts | async get_logicalName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_logicalName( | ) |
dnp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cmd | YRealTimeClock target get_logicalName |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the logical name of the real-time clock.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YRealTimeClock.LOGICALNAME_INVALID.
realtimeclock→get_module()
realtimeclock→module()realtimeclock.get_module()realtimeclock→get_module()[realtimeclock module]realtimeclock.get_module()realtimeclock.get_module()realtimeclock.get_module()realtimeclock.get_module()realtimeclock.get_module()realtimeclock→get_module()realtimeclock.get_module()realtimeclock.get_module()realtimeclock.get_module()realtimeclock.get_module()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located.
js | function get_module( | ) |
cpp | YModule * get_module( | ) |
m | -(YModule*) module |
pas | TYModule get_module( | ): TYModule |
vb | function get_module( | ) As YModule |
cs | YModule get_module( | ) |
java | YModule get_module( | ) |
py | get_module( | ) |
php | function get_module( | ) |
ts | async get_module( | ): Promise<YModule> |
es | async get_module( | ) |
dnp | YModuleProxy get_module( | ) |
cp | YModuleProxy * get_module( | ) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned instance of YModule is not shown as on-line.
Returns :
an instance of YModule
realtimeclock→get_module_async()
realtimeclock→module_async()realtimeclock.get_module_async()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version).
js | function get_module_async( | callback, context) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned YModule object does not show as on-line.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking Firefox JavaScript VM that does not implement context switching during blocking I/O calls. See the documentation section on asynchronous JavasSript calls for more details.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the requested YModule object |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
realtimeclock→get_serialNumber()
realtimeclock→serialNumber()realtimeclock.get_serialNumber()realtimeclock→get_serialNumber()[realtimeclock serialNumber]realtimeclock.get_serialNumber()realtimeclock.get_serialNumber()realtimeclock.get_serialNumber()realtimeclock.get_serialNumber()realtimeclock.get_serialNumber()realtimeclock.get_serialNumber()realtimeclock→get_serialNumber()realtimeclock.get_serialNumber()realtimeclock.get_serialNumber()realtimeclock.get_serialNumber()realtimeclock.get_serialNumber()YRealTimeClock get_serialNumber
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
js | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
cpp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) serialNumber |
pas | string get_serialNumber( | ): string |
vb | function get_serialNumber( | ) As String |
cs | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
java | String get_serialNumber( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_serialNumber( | ) |
py | get_serialNumber( | ) |
php | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
ts | async get_serialNumber( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_serialNumber( | ) |
dnp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cmd | YRealTimeClock target get_serialNumber |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFunction.SERIALNUMBER_INVALID.
realtimeclock→get_timeSet()
realtimeclock→timeSet()realtimeclock.get_timeSet()realtimeclock→get_timeSet()[realtimeclock timeSet]realtimeclock.get_timeSet()realtimeclock.get_timeSet()realtimeclock.get_timeSet()realtimeclock.get_timeSet()realtimeclock.get_timeSet()realtimeclock.get_timeSet()realtimeclock→get_timeSet()realtimeclock.get_timeSet()realtimeclock.get_timeSet()realtimeclock.get_timeSet()realtimeclock.get_timeSet()YRealTimeClock get_timeSet
Returns true if the clock has been set, and false otherwise.
js | function get_timeSet( | ) |
cpp | Y_TIMESET_enum get_timeSet( | ) |
m | -(Y_TIMESET_enum) timeSet |
pas | Integer get_timeSet( | ): Integer |
vb | function get_timeSet( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_timeSet( | ) |
java | int get_timeSet( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_timeSet( | ) |
py | get_timeSet( | ) |
php | function get_timeSet( | ) |
ts | async get_timeSet( | ): Promise<YRealTimeClock_TimeSet> |
es | async get_timeSet( | ) |
dnp | int get_timeSet( | ) |
cp | int get_timeSet( | ) |
cmd | YRealTimeClock target get_timeSet |
Returns :
either YRealTimeClock.TIMESET_FALSE or YRealTimeClock.TIMESET_TRUE, according to true if the clock has been set, and false otherwise
On failure, throws an exception or returns YRealTimeClock.TIMESET_INVALID.
realtimeclock→get_unixTime()
realtimeclock→unixTime()realtimeclock.get_unixTime()realtimeclock→get_unixTime()[realtimeclock unixTime]realtimeclock.get_unixTime()realtimeclock.get_unixTime()realtimeclock.get_unixTime()realtimeclock.get_unixTime()realtimeclock.get_unixTime()realtimeclock.get_unixTime()realtimeclock→get_unixTime()realtimeclock.get_unixTime()realtimeclock.get_unixTime()realtimeclock.get_unixTime()realtimeclock.get_unixTime()YRealTimeClock get_unixTime
Returns the current time in Unix format (number of elapsed seconds since Jan 1st, 1970).
js | function get_unixTime( | ) |
cpp | s64 get_unixTime( | ) |
m | -(s64) unixTime |
pas | int64 get_unixTime( | ): int64 |
vb | function get_unixTime( | ) As Long |
cs | long get_unixTime( | ) |
java | long get_unixTime( | ) |
uwp | async Task<long> get_unixTime( | ) |
py | get_unixTime( | ) |
php | function get_unixTime( | ) |
ts | async get_unixTime( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_unixTime( | ) |
dnp | long get_unixTime( | ) |
cp | s64 get_unixTime( | ) |
cmd | YRealTimeClock target get_unixTime |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the current time in Unix format (number of elapsed seconds since Jan 1st, 1970)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YRealTimeClock.UNIXTIME_INVALID.
realtimeclock→get_userData()
realtimeclock→userData()realtimeclock.get_userData()realtimeclock→get_userData()[realtimeclock userData]realtimeclock.get_userData()realtimeclock.get_userData()realtimeclock.get_userData()realtimeclock.get_userData()realtimeclock.get_userData()realtimeclock→get_userData()realtimeclock.get_userData()realtimeclock.get_userData()
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData.
js | function get_userData( | ) |
cpp | void * get_userData( | ) |
m | -(id) userData |
pas | Tobject get_userData( | ): Tobject |
vb | function get_userData( | ) As Object |
cs | object get_userData( | ) |
java | Object get_userData( | ) |
py | get_userData( | ) |
php | function get_userData( | ) |
ts | async get_userData( | ): Promise<object|null> |
es | async get_userData( | ) |
This attribute is never touched directly by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Returns :
the object stored previously by the caller.
realtimeclock→get_utcOffset()
realtimeclock→utcOffset()realtimeclock.get_utcOffset()realtimeclock→get_utcOffset()[realtimeclock utcOffset]realtimeclock.get_utcOffset()realtimeclock.get_utcOffset()realtimeclock.get_utcOffset()realtimeclock.get_utcOffset()realtimeclock.get_utcOffset()realtimeclock.get_utcOffset()realtimeclock→get_utcOffset()realtimeclock.get_utcOffset()realtimeclock.get_utcOffset()realtimeclock.get_utcOffset()realtimeclock.get_utcOffset()YRealTimeClock get_utcOffset
Returns the number of seconds between current time and UTC time (time zone).
js | function get_utcOffset( | ) |
cpp | int get_utcOffset( | ) |
m | -(int) utcOffset |
pas | LongInt get_utcOffset( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_utcOffset( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_utcOffset( | ) |
java | int get_utcOffset( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_utcOffset( | ) |
py | get_utcOffset( | ) |
php | function get_utcOffset( | ) |
ts | async get_utcOffset( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_utcOffset( | ) |
dnp | int get_utcOffset( | ) |
cp | int get_utcOffset( | ) |
cmd | YRealTimeClock target get_utcOffset |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the number of seconds between current time and UTC time (time zone)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YRealTimeClock.UTCOFFSET_INVALID.
realtimeclock→isOnline()realtimeclock.isOnline()realtimeclock→isOnline()[realtimeclock isOnline]realtimeclock.isOnline()realtimeclock.isOnline()realtimeclock.isOnline()realtimeclock.isOnline()realtimeclock.isOnline()realtimeclock→isOnline()realtimeclock.isOnline()realtimeclock.isOnline()realtimeclock.isOnline()realtimeclock.isOnline()
Checks if the real-time clock is currently reachable, without raising any error.
js | function isOnline( | ) |
cpp | bool isOnline( | ) |
m | -(BOOL) isOnline |
pas | boolean isOnline( | ): boolean |
vb | function isOnline( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isOnline( | ) |
java | boolean isOnline( | ) |
py | isOnline( | ) |
php | function isOnline( | ) |
ts | async isOnline( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isOnline( | ) |
dnp | bool isOnline( | ) |
cp | bool isOnline( | ) |
If there is a cached value for the real-time clock in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the real-time clock.
Returns :
true if the real-time clock can be reached, and false otherwise
realtimeclock→isOnline_async()realtimeclock.isOnline_async()
Checks if the real-time clock is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version).
js | function isOnline_async( | callback, context) |
If there is a cached value for the real-time clock in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the requested function.
This asynchronous version exists only in Javascript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the Javascript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the boolean result |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
realtimeclock→isReadOnly()realtimeclock→isReadOnly()[realtimeclock isReadOnly]realtimeclock.isReadOnly()realtimeclock.isReadOnly()realtimeclock.isReadOnly()realtimeclock.isReadOnly()realtimeclock.isReadOnly()realtimeclock.isReadOnly()realtimeclock→isReadOnly()realtimeclock.isReadOnly()realtimeclock.isReadOnly()realtimeclock.isReadOnly()realtimeclock.isReadOnly()YRealTimeClock isReadOnly
Test if the function is readOnly.
cpp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
m | -(bool) isReadOnly |
pas | boolean isReadOnly( | ): boolean |
vb | function isReadOnly( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
java | boolean isReadOnly( | ) |
uwp | async Task<bool> isReadOnly( | ) |
py | isReadOnly( | ) |
php | function isReadOnly( | ) |
ts | async isReadOnly( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isReadOnly( | ) |
dnp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cmd | YRealTimeClock target isReadOnly |
Return true if the function is write protected or that the function is not available.
Returns :
true if the function is readOnly or not online.
realtimeclock→load()realtimeclock.load()realtimeclock→load()[realtimeclock load: ]realtimeclock.load()realtimeclock.load()realtimeclock.load()realtimeclock.load()realtimeclock.load()realtimeclock→load()realtimeclock.load()realtimeclock.load()
Preloads the real-time clock cache with a specified validity duration.
js | function load( | msValidity) |
cpp | YRETCODE load( | int msValidity) |
m | -(YRETCODE) load | : (u64) msValidity |
pas | YRETCODE load( | msValidity: u64): YRETCODE |
vb | function load( | ByVal msValidity As Long) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE load( | ulong msValidity) |
java | int load( | long msValidity) |
py | load( | msValidity) |
php | function load( | $msValidity) |
ts | async load( | msValidity: number): Promise<number> |
es | async load( | msValidity) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity attributed to the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
realtimeclock→loadAttribute()realtimeclock.loadAttribute()realtimeclock→loadAttribute()[realtimeclock loadAttribute: ]realtimeclock.loadAttribute()realtimeclock.loadAttribute()realtimeclock.loadAttribute()realtimeclock.loadAttribute()realtimeclock.loadAttribute()realtimeclock.loadAttribute()realtimeclock→loadAttribute()realtimeclock.loadAttribute()realtimeclock.loadAttribute()realtimeclock.loadAttribute()realtimeclock.loadAttribute()
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value.
js | function loadAttribute( | attrName) |
cpp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
m | -(NSString*) loadAttribute | : (NSString*) attrName |
pas | string loadAttribute( | attrName: string): string |
vb | function loadAttribute( | ByVal attrName As String) As String |
cs | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
java | String loadAttribute( | String attrName) |
uwp | async Task<string> loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
py | loadAttribute( | attrName) |
php | function loadAttribute( | $attrName) |
ts | async loadAttribute( | attrName: string): Promise<string> |
es | async loadAttribute( | attrName) |
dnp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
cp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
Parameters :
| attrName | the name of the requested attribute |
Returns :
a string with the value of the the attribute
On failure, throws an exception or returns an empty string.
realtimeclock→load_async()realtimeclock.load_async()
Preloads the real-time clock cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version).
js | function load_async( | msValidity, callback, context) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the JavaScript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity of the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the error code (or YAPI.SUCCESS) |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
realtimeclock→muteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.muteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock→muteValueCallbacks()[realtimeclock muteValueCallbacks]realtimeclock.muteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.muteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.muteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.muteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.muteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.muteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock→muteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.muteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.muteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.muteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.muteValueCallbacks()YRealTimeClock muteValueCallbacks
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) muteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt muteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async muteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YRealTimeClock target muteValueCallbacks |
You can use this function to save bandwidth and CPU on computers with limited resources, or to prevent unwanted invocations of the HTTP callback. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
realtimeclock→nextRealTimeClock()realtimeclock.nextRealTimeClock()realtimeclock→nextRealTimeClock()[realtimeclock nextRealTimeClock]realtimeclock.nextRealTimeClock()realtimeclock.nextRealTimeClock()realtimeclock.nextRealTimeClock()realtimeclock.nextRealTimeClock()realtimeclock.nextRealTimeClock()realtimeclock.nextRealTimeClock()realtimeclock→nextRealTimeClock()realtimeclock.nextRealTimeClock()realtimeclock.nextRealTimeClock()
Continues the enumeration of real-time clocks started using yFirstRealTimeClock().
js | function nextRealTimeClock( | ) |
cpp | YRealTimeClock * nextRealTimeClock( | ) |
m | -(nullable YRealTimeClock*) nextRealTimeClock |
pas | TYRealTimeClock nextRealTimeClock( | ): TYRealTimeClock |
vb | function nextRealTimeClock( | ) As YRealTimeClock |
cs | YRealTimeClock nextRealTimeClock( | ) |
java | YRealTimeClock nextRealTimeClock( | ) |
uwp | YRealTimeClock nextRealTimeClock( | ) |
py | nextRealTimeClock( | ) |
php | function nextRealTimeClock( | ) |
ts | nextRealTimeClock( | ): YRealTimeClock | null |
es | nextRealTimeClock( | ) |
Caution: You can't make any assumption about the returned real-time clocks order. If you want to find a specific a real-time clock, use RealTimeClock.findRealTimeClock() and a hardwareID or a logical name.
Returns :
a pointer to a YRealTimeClock object, corresponding to a real-time clock currently online, or a null pointer if there are no more real-time clocks to enumerate.
realtimeclock→registerValueCallback()realtimeclock.registerValueCallback()realtimeclock→registerValueCallback()[realtimeclock registerValueCallback: ]realtimeclock.registerValueCallback()realtimeclock.registerValueCallback()realtimeclock.registerValueCallback()realtimeclock.registerValueCallback()realtimeclock.registerValueCallback()realtimeclock.registerValueCallback()realtimeclock→registerValueCallback()realtimeclock.registerValueCallback()realtimeclock.registerValueCallback()
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value.
js | function registerValueCallback( | callback) |
cpp | int registerValueCallback( | YRealTimeClockValueCallback callback) |
m | -(int) registerValueCallback | : (YRealTimeClockValueCallback _Nullable) callback |
pas | LongInt registerValueCallback( | callback: TYRealTimeClockValueCallback): LongInt |
vb | function registerValueCallback( | ByVal callback As YRealTimeClockValueCallback) As Integer |
cs | int registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
java | int registerValueCallback( | UpdateCallback callback) |
uwp | async Task<int> registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
py | registerValueCallback( | callback) |
php | function registerValueCallback( | $callback) |
ts | async registerValueCallback( | callback: YRealTimeClockValueCallback | null): Promise<number> |
es | async registerValueCallback( | callback) |
The callback is invoked only during the execution of ySleep or yHandleEvents. This provides control over the time when the callback is triggered. For good responsiveness, remember to call one of these two functions periodically. To unregister a callback, pass a null pointer as argument.
Parameters :
| callback | the callback function to call, or a null pointer. The callback function should take two arguments: the function object of which the value has changed, and the character string describing the new advertised value. |
realtimeclock→set_logicalName()
realtimeclock→setLogicalName()realtimeclock.set_logicalName()realtimeclock→set_logicalName()[realtimeclock setLogicalName: ]realtimeclock.set_logicalName()realtimeclock.set_logicalName()realtimeclock.set_logicalName()realtimeclock.set_logicalName()realtimeclock.set_logicalName()realtimeclock.set_logicalName()realtimeclock→set_logicalName()realtimeclock.set_logicalName()realtimeclock.set_logicalName()realtimeclock.set_logicalName()realtimeclock.set_logicalName()YRealTimeClock set_logicalName
Changes the logical name of the real-time clock.
js | function set_logicalName( | newval) |
cpp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setLogicalName | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_logicalName( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_logicalName( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
java | int set_logicalName( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_logicalName( | string newval) |
py | set_logicalName( | newval) |
php | function set_logicalName( | $newval) |
ts | async set_logicalName( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_logicalName( | newval) |
dnp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cmd | YRealTimeClock target set_logicalName | newval |
You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the logical name of the real-time clock. |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
realtimeclock→set_unixTime()
realtimeclock→setUnixTime()realtimeclock.set_unixTime()realtimeclock→set_unixTime()[realtimeclock setUnixTime: ]realtimeclock.set_unixTime()realtimeclock.set_unixTime()realtimeclock.set_unixTime()realtimeclock.set_unixTime()realtimeclock.set_unixTime()realtimeclock.set_unixTime()realtimeclock→set_unixTime()realtimeclock.set_unixTime()realtimeclock.set_unixTime()realtimeclock.set_unixTime()realtimeclock.set_unixTime()YRealTimeClock set_unixTime
Changes the current time.
js | function set_unixTime( | newval) |
cpp | int set_unixTime( | s64 newval) |
m | -(int) setUnixTime | : (s64) newval |
pas | integer set_unixTime( | newval: int64): integer |
vb | function set_unixTime( | ByVal newval As Long) As Integer |
cs | int set_unixTime( | long newval) |
java | int set_unixTime( | long newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_unixTime( | long newval) |
py | set_unixTime( | newval) |
php | function set_unixTime( | $newval) |
ts | async set_unixTime( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_unixTime( | newval) |
dnp | int set_unixTime( | long newval) |
cp | int set_unixTime( | s64 newval) |
cmd | YRealTimeClock target set_unixTime | newval |
Time is specifid in Unix format (number of elapsed seconds since Jan 1st, 1970).
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the current time |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
realtimeclock→set_userData()
realtimeclock→setUserData()realtimeclock.set_userData()realtimeclock→set_userData()[realtimeclock setUserData: ]realtimeclock.set_userData()realtimeclock.set_userData()realtimeclock.set_userData()realtimeclock.set_userData()realtimeclock.set_userData()realtimeclock→set_userData()realtimeclock.set_userData()realtimeclock.set_userData()
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function.
js | function set_userData( | data) |
cpp | void set_userData( | void * data) |
m | -(void) setUserData | : (id) data |
pas | set_userData( | data: Tobject) |
vb | procedure set_userData( | ByVal data As Object) |
cs | void set_userData( | object data) |
java | void set_userData( | Object data) |
py | set_userData( | data) |
php | function set_userData( | $data) |
ts | async set_userData( | data: object|null): Promise<void> |
es | async set_userData( | data) |
This attribute is never touched by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Parameters :
| data | any kind of object to be stored |
realtimeclock→set_utcOffset()
realtimeclock→setUtcOffset()realtimeclock.set_utcOffset()realtimeclock→set_utcOffset()[realtimeclock setUtcOffset: ]realtimeclock.set_utcOffset()realtimeclock.set_utcOffset()realtimeclock.set_utcOffset()realtimeclock.set_utcOffset()realtimeclock.set_utcOffset()realtimeclock.set_utcOffset()realtimeclock→set_utcOffset()realtimeclock.set_utcOffset()realtimeclock.set_utcOffset()realtimeclock.set_utcOffset()realtimeclock.set_utcOffset()YRealTimeClock set_utcOffset
Changes the number of seconds between current time and UTC time (time zone).
js | function set_utcOffset( | newval) |
cpp | int set_utcOffset( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setUtcOffset | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_utcOffset( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_utcOffset( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_utcOffset( | int newval) |
java | int set_utcOffset( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_utcOffset( | int newval) |
py | set_utcOffset( | newval) |
php | function set_utcOffset( | $newval) |
ts | async set_utcOffset( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_utcOffset( | newval) |
dnp | int set_utcOffset( | int newval) |
cp | int set_utcOffset( | int newval) |
cmd | YRealTimeClock target set_utcOffset | newval |
The timezone is automatically rounded to the nearest multiple of 15 minutes. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the number of seconds between current time and UTC time (time zone) |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
realtimeclock→unmuteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.unmuteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock→unmuteValueCallbacks()[realtimeclock unmuteValueCallbacks]realtimeclock.unmuteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.unmuteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.unmuteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.unmuteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.unmuteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.unmuteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock→unmuteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.unmuteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.unmuteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.unmuteValueCallbacks()realtimeclock.unmuteValueCallbacks()YRealTimeClock unmuteValueCallbacks
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) unmuteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YRealTimeClock target unmuteValueCallbacks |
This function reverts the effect of a previous call to muteValueCallbacks(). Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
realtimeclock→wait_async()realtimeclock.wait_async()realtimeclock.wait_async()realtimeclock.wait_async()
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function.
js | function wait_async( | callback, context) |
ts | wait_async( | callback: Function, context: object) |
es | wait_async( | callback, context) |
The callback function can therefore freely issue synchronous or asynchronous commands, without risking to block the JavaScript VM.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when all pending commands on the module are completed. The callback function receives two arguments: the caller-specific context object and the receiving function object. |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing.
11.6. Class YWakeUpMonitor
Wake-up monitor control interface, available for instance in the YoctoHub-GSM-3G-EU, the YoctoHub-GSM-3G-NA, the YoctoHub-GSM-4G or the YoctoHub-Wireless-n
The YWakeUpMonitor class handles globally all wake-up sources, as well as automated sleep mode.
In order to use the functions described here, you should include:
es | in HTML: <script src="../../lib/yocto_wakeupmonitor.js"></script> in node.js: require('yoctolib-es2017/yocto_wakeupmonitor.js'); |
js | <script type='text/javascript' src='yocto_wakeupmonitor.js'></script> |
cpp | #include "yocto_wakeupmonitor.h" |
m | #import "yocto_wakeupmonitor.h" |
pas | uses yocto_wakeupmonitor; |
vb | yocto_wakeupmonitor.vb |
cs | yocto_wakeupmonitor.cs |
java | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YWakeUpMonitor; |
uwp | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YWakeUpMonitor; |
py | from yocto_wakeupmonitor import * |
php | require_once('yocto_wakeupmonitor.php'); |
ts | in HTML: import { YWakeUpMonitor } from '../../dist/esm/yocto_wakeupmonitor.js'; in Node.js: import { YWakeUpMonitor } from 'yoctolib-cjs/yocto_wakeupmonitor.js'; |
dnp | import YoctoProxyAPI.YWakeUpMonitorProxy |
cp | #include "yocto_wakeupmonitor_proxy.h" |
vi | YWakeUpMonitor.vi |
ml | import YoctoProxyAPI.YWakeUpMonitorProxy |
| Global functions |
|---|
| YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitor(func) |
Retrieves a wake-up monitor for a given identifier. |
| YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitorInContext(yctx, func) |
Retrieves a wake-up monitor for a given identifier in a YAPI context. |
| YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitor() |
Starts the enumeration of wake-up monitors currently accessible. |
| YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitorInContext(yctx) |
Starts the enumeration of wake-up monitors currently accessible. |
| YWakeUpMonitor.GetSimilarFunctions() |
Enumerates all functions of type WakeUpMonitor available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID. |
| YWakeUpMonitor properties |
| wakeupmonitor→AdvertisedValue [read-only] |
Short string representing the current state of the function. |
| wakeupmonitor→FriendlyName [read-only] |
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| wakeupmonitor→FunctionId [read-only] |
Hardware identifier of the wake-up monitor, without reference to the module. |
| wakeupmonitor→HardwareId [read-only] |
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| wakeupmonitor→IsOnline [read-only] |
Checks if the function is currently reachable. |
| wakeupmonitor→LogicalName [writable] |
Logical name of the function. |
| wakeupmonitor→NextWakeUp [writable] |
Next scheduled wake up date/time (UNIX format). |
| wakeupmonitor→PowerDuration [writable] |
Maximal wake up time (in seconds) before automatically going to sleep. |
| wakeupmonitor→SerialNumber [read-only] |
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| YWakeUpMonitor methods |
| wakeupmonitor→clearCache() |
Invalidates the cache. |
| wakeupmonitor→describe() |
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the wake-up monitor in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_advertisedValue() |
Returns the current value of the wake-up monitor (no more than 6 characters). |
| wakeupmonitor→get_errorMessage() |
Returns the error message of the latest error with the wake-up monitor. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_errorType() |
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the wake-up monitor. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_friendlyName() |
Returns a global identifier of the wake-up monitor in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_functionDescriptor() |
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_functionId() |
Returns the hardware identifier of the wake-up monitor, without reference to the module. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_hardwareId() |
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the wake-up monitor in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_logicalName() |
Returns the logical name of the wake-up monitor. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_module() |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_module_async(callback, context) |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version). |
| wakeupmonitor→get_nextWakeUp() |
Returns the next scheduled wake up date/time (UNIX format). |
| wakeupmonitor→get_powerDuration() |
Returns the maximal wake up time (in seconds) before automatically going to sleep. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_serialNumber() |
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_sleepCountdown() |
Returns the delay before the next sleep period. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_userData() |
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_wakeUpReason() |
Returns the latest wake up reason. |
| wakeupmonitor→get_wakeUpState() |
Returns the current state of the monitor. |
| wakeupmonitor→isOnline() |
Checks if the wake-up monitor is currently reachable, without raising any error. |
| wakeupmonitor→isOnline_async(callback, context) |
Checks if the wake-up monitor is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version). |
| wakeupmonitor→isReadOnly() |
Test if the function is readOnly. |
| wakeupmonitor→load(msValidity) |
Preloads the wake-up monitor cache with a specified validity duration. |
| wakeupmonitor→loadAttribute(attrName) |
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value. |
| wakeupmonitor→load_async(msValidity, callback, context) |
Preloads the wake-up monitor cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version). |
| wakeupmonitor→muteValueCallbacks() |
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| wakeupmonitor→nextWakeUpMonitor() |
Continues the enumeration of wake-up monitors started using yFirstWakeUpMonitor(). |
| wakeupmonitor→registerValueCallback(callback) |
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value. |
| wakeupmonitor→resetSleepCountDown() |
Resets the sleep countdown. |
| wakeupmonitor→set_logicalName(newval) |
Changes the logical name of the wake-up monitor. |
| wakeupmonitor→set_nextWakeUp(newval) |
Changes the days of the week when a wake up must take place. |
| wakeupmonitor→set_powerDuration(newval) |
Changes the maximal wake up time (seconds) before automatically going to sleep. |
| wakeupmonitor→set_sleepCountdown(newval) |
Changes the delay before the next sleep period. |
| wakeupmonitor→set_userData(data) |
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function. |
| wakeupmonitor→sleep(secBeforeSleep) |
Goes to sleep until the next wake up condition is met, the RTC time must have been set before calling this function. |
| wakeupmonitor→sleepFor(secUntilWakeUp, secBeforeSleep) |
Goes to sleep for a specific duration or until the next wake up condition is met, the RTC time must have been set before calling this function. |
| wakeupmonitor→sleepUntil(wakeUpTime, secBeforeSleep) |
Go to sleep until a specific date is reached or until the next wake up condition is met, the RTC time must have been set before calling this function. |
| wakeupmonitor→unmuteValueCallbacks() |
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| wakeupmonitor→wait_async(callback, context) |
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function. |
| wakeupmonitor→wakeUp() |
Forces a wake up. |
YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitor()
YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitor()yFindWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor::FindWakeUpMonitor()[YWakeUpMonitor FindWakeUpMonitor: ]yFindWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor::FindWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitor()
Retrieves a wake-up monitor for a given identifier.
js | function yFindWakeUpMonitor( | func) |
cpp | YWakeUpMonitor* FindWakeUpMonitor( | string func) |
m | +(YWakeUpMonitor*) FindWakeUpMonitor | : (NSString*) func |
pas | TYWakeUpMonitor yFindWakeUpMonitor( | func: string): TYWakeUpMonitor |
vb | function FindWakeUpMonitor( | ByVal func As String) As YWakeUpMonitor |
cs | static YWakeUpMonitor FindWakeUpMonitor( | string func) |
java | static YWakeUpMonitor FindWakeUpMonitor( | String func) |
uwp | static YWakeUpMonitor FindWakeUpMonitor( | string func) |
py | FindWakeUpMonitor( | func) |
php | function FindWakeUpMonitor( | $func) |
ts | static FindWakeUpMonitor( | func: string): YWakeUpMonitor |
es | static FindWakeUpMonitor( | func) |
dnp | static YWakeUpMonitorProxy FindWakeUpMonitor( | string func) |
cp | static YWakeUpMonitorProxy * FindWakeUpMonitor( | string func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the wake-up monitor is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YWakeUpMonitor.isOnline() to test if the wake-up monitor is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a wake-up monitor by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
If a call to this object's is_online() method returns FALSE although you are certain that the matching device is plugged, make sure that you did call registerHub() at application initialization time.
Parameters :
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the wake-up monitor, for instance YHUBGSM3.wakeUpMonitor. |
Returns :
a YWakeUpMonitor object allowing you to drive the wake-up monitor.
YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitorInContext()
YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitorInContext()YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitorInContext()YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitorInContext()YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitorInContext()YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitorInContext()
Retrieves a wake-up monitor for a given identifier in a YAPI context.
java | static YWakeUpMonitor FindWakeUpMonitorInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, |
| String func) |
uwp | static YWakeUpMonitor FindWakeUpMonitorInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, |
| string func) |
ts | static FindWakeUpMonitorInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext, func: string): YWakeUpMonitor |
es | static FindWakeUpMonitorInContext( | yctx, func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the wake-up monitor is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YWakeUpMonitor.isOnline() to test if the wake-up monitor is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a wake-up monitor by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context |
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the wake-up monitor, for instance YHUBGSM3.wakeUpMonitor. |
Returns :
a YWakeUpMonitor object allowing you to drive the wake-up monitor.
YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitor()
YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitor()yFirstWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor::FirstWakeUpMonitor()[YWakeUpMonitor FirstWakeUpMonitor]yFirstWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor::FirstWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitor()YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitor()
Starts the enumeration of wake-up monitors currently accessible.
js | function yFirstWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
cpp | YWakeUpMonitor * FirstWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
m | +(YWakeUpMonitor*) FirstWakeUpMonitor |
pas | TYWakeUpMonitor yFirstWakeUpMonitor( | ): TYWakeUpMonitor |
vb | function FirstWakeUpMonitor( | ) As YWakeUpMonitor |
cs | static YWakeUpMonitor FirstWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
java | static YWakeUpMonitor FirstWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
uwp | static YWakeUpMonitor FirstWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
py | FirstWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
php | function FirstWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
ts | static FirstWakeUpMonitor( | ): YWakeUpMonitor | null |
es | static FirstWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
Use the method YWakeUpMonitor.nextWakeUpMonitor() to iterate on next wake-up monitors.
Returns :
a pointer to a YWakeUpMonitor object, corresponding to the first wake-up monitor currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitorInContext()
YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitorInContext()YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitorInContext()YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitorInContext()YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitorInContext()YWakeUpMonitor.FirstWakeUpMonitorInContext()
Starts the enumeration of wake-up monitors currently accessible.
java | static YWakeUpMonitor FirstWakeUpMonitorInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
uwp | static YWakeUpMonitor FirstWakeUpMonitorInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
ts | static FirstWakeUpMonitorInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext): YWakeUpMonitor | null |
es | static FirstWakeUpMonitorInContext( | yctx) |
Use the method YWakeUpMonitor.nextWakeUpMonitor() to iterate on next wake-up monitors.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context. |
Returns :
a pointer to a YWakeUpMonitor object, corresponding to the first wake-up monitor currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YWakeUpMonitor.GetSimilarFunctions()
YWakeUpMonitor.GetSimilarFunctions()YWakeUpMonitor.GetSimilarFunctions()YWakeUpMonitor.GetSimilarFunctions()
Enumerates all functions of type WakeUpMonitor available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID.
dnp | static new string[] GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
cp | static vector<string> GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
Each of these IDs can be provided as argument to the method YWakeUpMonitor.FindWakeUpMonitor to obtain an object that can control the corresponding device.
Returns :
an array of strings, each string containing the unique hardwareId of a device function currently connected.
wakeupmonitor→AdvertisedValuewakeupmonitor.AdvertisedValue
Short string representing the current state of the function.
dnp | string AdvertisedValue |
wakeupmonitor→FriendlyNamewakeupmonitor.FriendlyName
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
dnp | string FriendlyName |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the function if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the function (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
wakeupmonitor→FunctionIdwakeupmonitor.FunctionId
Hardware identifier of the wake-up monitor, without reference to the module.
dnp | string FunctionId |
For example relay1
wakeupmonitor→HardwareIdwakeupmonitor.HardwareId
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
dnp | string HardwareId |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the function (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
wakeupmonitor→IsOnlinewakeupmonitor.IsOnline
Checks if the function is currently reachable.
dnp | bool IsOnline |
If there is a cached value for the function in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the function.
wakeupmonitor→LogicalNamewakeupmonitor.LogicalName
Logical name of the function.
dnp | string LogicalName |
Writable. You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
wakeupmonitor→NextWakeUpwakeupmonitor.NextWakeUp
Next scheduled wake up date/time (UNIX format).
dnp | long NextWakeUp |
Writable. Changes the days of the week when a wake up must take place.
wakeupmonitor→PowerDurationwakeupmonitor.PowerDuration
Maximal wake up time (in seconds) before automatically going to sleep.
dnp | int PowerDuration |
Writable. Changes the maximal wake up time (seconds) before automatically going to sleep. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
wakeupmonitor→SerialNumberwakeupmonitor.SerialNumber
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
dnp | string SerialNumber |
wakeupmonitor→clearCache()wakeupmonitor.clearCache()wakeupmonitor→clearCache()[wakeupmonitor clearCache]wakeupmonitor.clearCache()wakeupmonitor.clearCache()wakeupmonitor.clearCache()wakeupmonitor.clearCache()wakeupmonitor.clearCache()wakeupmonitor→clearCache()wakeupmonitor.clearCache()wakeupmonitor.clearCache()
Invalidates the cache.
js | function clearCache( | ) |
cpp | void clearCache( | ) |
m | -(void) clearCache |
pas | clearCache( | ) |
vb | procedure clearCache( | ) |
cs | void clearCache( | ) |
java | void clearCache( | ) |
py | clearCache( | ) |
php | function clearCache( | ) |
ts | async clearCache( | ): Promise<void> |
es | async clearCache( | ) |
Invalidates the cache of the wake-up monitor attributes. Forces the next call to get_xxx() or loadxxx() to use values that come from the device.
wakeupmonitor→describe()wakeupmonitor.describe()wakeupmonitor→describe()[wakeupmonitor describe]wakeupmonitor.describe()wakeupmonitor.describe()wakeupmonitor.describe()wakeupmonitor.describe()wakeupmonitor.describe()wakeupmonitor→describe()wakeupmonitor.describe()wakeupmonitor.describe()
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the wake-up monitor in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function describe( | ) |
cpp | string describe( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) describe |
pas | string describe( | ): string |
vb | function describe( | ) As String |
cs | string describe( | ) |
java | String describe( | ) |
py | describe( | ) |
php | function describe( | ) |
ts | async describe( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async describe( | ) |
More precisely, TYPE is the type of the function, NAME it the name used for the first access to the function, SERIAL is the serial number of the module if the module is connected or "unresolved", and FUNCTIONID is the hardware identifier of the function if the module is connected. For example, this method returns Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1 if the module is already connected or Relay(BadCustomeName.relay1)=unresolved if the module has not yet been connected. This method does not trigger any USB or TCP transaction and can therefore be used in a debugger.
Returns :
a string that describes the wake-up monitor (ex: Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
wakeupmonitor→get_advertisedValue()
wakeupmonitor→advertisedValue()wakeupmonitor.get_advertisedValue()wakeupmonitor→get_advertisedValue()[wakeupmonitor advertisedValue]wakeupmonitor.get_advertisedValue()wakeupmonitor.get_advertisedValue()wakeupmonitor.get_advertisedValue()wakeupmonitor.get_advertisedValue()wakeupmonitor.get_advertisedValue()wakeupmonitor.get_advertisedValue()wakeupmonitor→get_advertisedValue()wakeupmonitor.get_advertisedValue()wakeupmonitor.get_advertisedValue()wakeupmonitor.get_advertisedValue()wakeupmonitor.get_advertisedValue()YWakeUpMonitor get_advertisedValue
Returns the current value of the wake-up monitor (no more than 6 characters).
js | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cpp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) advertisedValue |
pas | string get_advertisedValue( | ): string |
vb | function get_advertisedValue( | ) As String |
cs | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
java | String get_advertisedValue( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_advertisedValue( | ) |
py | get_advertisedValue( | ) |
php | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
ts | async get_advertisedValue( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_advertisedValue( | ) |
dnp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target get_advertisedValue |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the current value of the wake-up monitor (no more than 6 characters).
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpMonitor.ADVERTISEDVALUE_INVALID.
wakeupmonitor→get_errorMessage()
wakeupmonitor→errorMessage()wakeupmonitor.get_errorMessage()wakeupmonitor→get_errorMessage()[wakeupmonitor errorMessage]wakeupmonitor.get_errorMessage()wakeupmonitor.get_errorMessage()wakeupmonitor.get_errorMessage()wakeupmonitor.get_errorMessage()wakeupmonitor.get_errorMessage()wakeupmonitor→get_errorMessage()wakeupmonitor.get_errorMessage()wakeupmonitor.get_errorMessage()
Returns the error message of the latest error with the wake-up monitor.
js | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
cpp | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) errorMessage |
pas | string get_errorMessage( | ): string |
vb | function get_errorMessage( | ) As String |
cs | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
java | String get_errorMessage( | ) |
py | get_errorMessage( | ) |
php | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
ts | get_errorMessage( | ): string |
es | get_errorMessage( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a string corresponding to the latest error message that occured while using the wake-up monitor object
wakeupmonitor→get_errorType()
wakeupmonitor→errorType()wakeupmonitor.get_errorType()wakeupmonitor→get_errorType()[wakeupmonitor errorType]wakeupmonitor.get_errorType()wakeupmonitor.get_errorType()wakeupmonitor.get_errorType()wakeupmonitor.get_errorType()wakeupmonitor.get_errorType()wakeupmonitor→get_errorType()wakeupmonitor.get_errorType()wakeupmonitor.get_errorType()
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the wake-up monitor.
js | function get_errorType( | ) |
cpp | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
m | -(YRETCODE) errorType |
pas | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ): YRETCODE |
vb | function get_errorType( | ) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
java | int get_errorType( | ) |
py | get_errorType( | ) |
php | function get_errorType( | ) |
ts | get_errorType( | ): number |
es | get_errorType( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a number corresponding to the code of the latest error that occurred while using the wake-up monitor object
wakeupmonitor→get_friendlyName()
wakeupmonitor→friendlyName()wakeupmonitor.get_friendlyName()wakeupmonitor→get_friendlyName()[wakeupmonitor friendlyName]wakeupmonitor.get_friendlyName()wakeupmonitor.get_friendlyName()wakeupmonitor.get_friendlyName()wakeupmonitor→get_friendlyName()wakeupmonitor.get_friendlyName()wakeupmonitor.get_friendlyName()wakeupmonitor.get_friendlyName()wakeupmonitor.get_friendlyName()
Returns a global identifier of the wake-up monitor in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
js | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
cpp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) friendlyName |
cs | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
java | String get_friendlyName( | ) |
py | get_friendlyName( | ) |
php | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
ts | async get_friendlyName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_friendlyName( | ) |
dnp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
cp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the wake-up monitor if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the wake-up monitor (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the wake-up monitor using logical names (ex: MyCustomName.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpMonitor.FRIENDLYNAME_INVALID.
wakeupmonitor→get_functionDescriptor()
wakeupmonitor→functionDescriptor()wakeupmonitor.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupmonitor→get_functionDescriptor()[wakeupmonitor functionDescriptor]wakeupmonitor.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupmonitor.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupmonitor.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupmonitor.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupmonitor.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupmonitor→get_functionDescriptor()wakeupmonitor.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupmonitor.get_functionDescriptor()
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function.
js | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
cpp | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
m | -(YFUN_DESCR) functionDescriptor |
pas | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ): YFUN_DESCR |
vb | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) As YFUN_DESCR |
cs | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
java | String get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
py | get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
php | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
ts | async get_functionDescriptor( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
This identifier can be used to test if two instances of YFunction reference the same physical function on the same physical device.
Returns :
an identifier of type YFUN_DESCR.
If the function has never been contacted, the returned value is Y$CLASSNAME$.FUNCTIONDESCRIPTOR_INVALID.
wakeupmonitor→get_functionId()
wakeupmonitor→functionId()wakeupmonitor.get_functionId()wakeupmonitor→get_functionId()[wakeupmonitor functionId]wakeupmonitor.get_functionId()wakeupmonitor.get_functionId()wakeupmonitor.get_functionId()wakeupmonitor.get_functionId()wakeupmonitor→get_functionId()wakeupmonitor.get_functionId()wakeupmonitor.get_functionId()wakeupmonitor.get_functionId()wakeupmonitor.get_functionId()
Returns the hardware identifier of the wake-up monitor, without reference to the module.
js | function get_functionId( | ) |
cpp | string get_functionId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) functionId |
vb | function get_functionId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_functionId( | ) |
java | String get_functionId( | ) |
py | get_functionId( | ) |
php | function get_functionId( | ) |
ts | async get_functionId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionId( | ) |
dnp | string get_functionId( | ) |
cp | string get_functionId( | ) |
For example relay1
Returns :
a string that identifies the wake-up monitor (ex: relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpMonitor.FUNCTIONID_INVALID.
wakeupmonitor→get_hardwareId()
wakeupmonitor→hardwareId()wakeupmonitor.get_hardwareId()wakeupmonitor→get_hardwareId()[wakeupmonitor hardwareId]wakeupmonitor.get_hardwareId()wakeupmonitor.get_hardwareId()wakeupmonitor.get_hardwareId()wakeupmonitor.get_hardwareId()wakeupmonitor→get_hardwareId()wakeupmonitor.get_hardwareId()wakeupmonitor.get_hardwareId()wakeupmonitor.get_hardwareId()wakeupmonitor.get_hardwareId()
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the wake-up monitor in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
cpp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) hardwareId |
vb | function get_hardwareId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
java | String get_hardwareId( | ) |
py | get_hardwareId( | ) |
php | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
ts | async get_hardwareId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_hardwareId( | ) |
dnp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
cp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the wake-up monitor (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the wake-up monitor (ex: RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpMonitor.HARDWAREID_INVALID.
wakeupmonitor→get_logicalName()
wakeupmonitor→logicalName()wakeupmonitor.get_logicalName()wakeupmonitor→get_logicalName()[wakeupmonitor logicalName]wakeupmonitor.get_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.get_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.get_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.get_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.get_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.get_logicalName()wakeupmonitor→get_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.get_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.get_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.get_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.get_logicalName()YWakeUpMonitor get_logicalName
Returns the logical name of the wake-up monitor.
js | function get_logicalName( | ) |
cpp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) logicalName |
pas | string get_logicalName( | ): string |
vb | function get_logicalName( | ) As String |
cs | string get_logicalName( | ) |
java | String get_logicalName( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_logicalName( | ) |
py | get_logicalName( | ) |
php | function get_logicalName( | ) |
ts | async get_logicalName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_logicalName( | ) |
dnp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target get_logicalName |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the logical name of the wake-up monitor.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpMonitor.LOGICALNAME_INVALID.
wakeupmonitor→get_module()
wakeupmonitor→module()wakeupmonitor.get_module()wakeupmonitor→get_module()[wakeupmonitor module]wakeupmonitor.get_module()wakeupmonitor.get_module()wakeupmonitor.get_module()wakeupmonitor.get_module()wakeupmonitor.get_module()wakeupmonitor→get_module()wakeupmonitor.get_module()wakeupmonitor.get_module()wakeupmonitor.get_module()wakeupmonitor.get_module()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located.
js | function get_module( | ) |
cpp | YModule * get_module( | ) |
m | -(YModule*) module |
pas | TYModule get_module( | ): TYModule |
vb | function get_module( | ) As YModule |
cs | YModule get_module( | ) |
java | YModule get_module( | ) |
py | get_module( | ) |
php | function get_module( | ) |
ts | async get_module( | ): Promise<YModule> |
es | async get_module( | ) |
dnp | YModuleProxy get_module( | ) |
cp | YModuleProxy * get_module( | ) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned instance of YModule is not shown as on-line.
Returns :
an instance of YModule
wakeupmonitor→get_module_async()
wakeupmonitor→module_async()wakeupmonitor.get_module_async()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version).
js | function get_module_async( | callback, context) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned YModule object does not show as on-line.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking Firefox JavaScript VM that does not implement context switching during blocking I/O calls. See the documentation section on asynchronous JavasSript calls for more details.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the requested YModule object |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
wakeupmonitor→get_nextWakeUp()
wakeupmonitor→nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.get_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor→get_nextWakeUp()[wakeupmonitor nextWakeUp]wakeupmonitor.get_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.get_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.get_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.get_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.get_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.get_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor→get_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.get_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.get_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.get_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.get_nextWakeUp()YWakeUpMonitor get_nextWakeUp
Returns the next scheduled wake up date/time (UNIX format).
js | function get_nextWakeUp( | ) |
cpp | s64 get_nextWakeUp( | ) |
m | -(s64) nextWakeUp |
pas | int64 get_nextWakeUp( | ): int64 |
vb | function get_nextWakeUp( | ) As Long |
cs | long get_nextWakeUp( | ) |
java | long get_nextWakeUp( | ) |
uwp | async Task<long> get_nextWakeUp( | ) |
py | get_nextWakeUp( | ) |
php | function get_nextWakeUp( | ) |
ts | async get_nextWakeUp( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_nextWakeUp( | ) |
dnp | long get_nextWakeUp( | ) |
cp | s64 get_nextWakeUp( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target get_nextWakeUp |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the next scheduled wake up date/time (UNIX format)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpMonitor.NEXTWAKEUP_INVALID.
wakeupmonitor→get_powerDuration()
wakeupmonitor→powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.get_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor→get_powerDuration()[wakeupmonitor powerDuration]wakeupmonitor.get_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.get_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.get_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.get_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.get_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.get_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor→get_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.get_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.get_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.get_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.get_powerDuration()YWakeUpMonitor get_powerDuration
Returns the maximal wake up time (in seconds) before automatically going to sleep.
js | function get_powerDuration( | ) |
cpp | int get_powerDuration( | ) |
m | -(int) powerDuration |
pas | LongInt get_powerDuration( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_powerDuration( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_powerDuration( | ) |
java | int get_powerDuration( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_powerDuration( | ) |
py | get_powerDuration( | ) |
php | function get_powerDuration( | ) |
ts | async get_powerDuration( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_powerDuration( | ) |
dnp | int get_powerDuration( | ) |
cp | int get_powerDuration( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target get_powerDuration |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the maximal wake up time (in seconds) before automatically going to sleep
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpMonitor.POWERDURATION_INVALID.
wakeupmonitor→get_serialNumber()
wakeupmonitor→serialNumber()wakeupmonitor.get_serialNumber()wakeupmonitor→get_serialNumber()[wakeupmonitor serialNumber]wakeupmonitor.get_serialNumber()wakeupmonitor.get_serialNumber()wakeupmonitor.get_serialNumber()wakeupmonitor.get_serialNumber()wakeupmonitor.get_serialNumber()wakeupmonitor.get_serialNumber()wakeupmonitor→get_serialNumber()wakeupmonitor.get_serialNumber()wakeupmonitor.get_serialNumber()wakeupmonitor.get_serialNumber()wakeupmonitor.get_serialNumber()YWakeUpMonitor get_serialNumber
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
js | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
cpp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) serialNumber |
pas | string get_serialNumber( | ): string |
vb | function get_serialNumber( | ) As String |
cs | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
java | String get_serialNumber( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_serialNumber( | ) |
py | get_serialNumber( | ) |
php | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
ts | async get_serialNumber( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_serialNumber( | ) |
dnp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target get_serialNumber |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFunction.SERIALNUMBER_INVALID.
wakeupmonitor→get_sleepCountdown()
wakeupmonitor→sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.get_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor→get_sleepCountdown()[wakeupmonitor sleepCountdown]wakeupmonitor.get_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.get_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.get_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.get_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.get_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.get_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor→get_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.get_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.get_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.get_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.get_sleepCountdown()YWakeUpMonitor get_sleepCountdown
Returns the delay before the next sleep period.
js | function get_sleepCountdown( | ) |
cpp | int get_sleepCountdown( | ) |
m | -(int) sleepCountdown |
pas | LongInt get_sleepCountdown( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_sleepCountdown( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_sleepCountdown( | ) |
java | int get_sleepCountdown( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_sleepCountdown( | ) |
py | get_sleepCountdown( | ) |
php | function get_sleepCountdown( | ) |
ts | async get_sleepCountdown( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_sleepCountdown( | ) |
dnp | int get_sleepCountdown( | ) |
cp | int get_sleepCountdown( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target get_sleepCountdown |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the delay before the next sleep period
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpMonitor.SLEEPCOUNTDOWN_INVALID.
wakeupmonitor→get_userData()
wakeupmonitor→userData()wakeupmonitor.get_userData()wakeupmonitor→get_userData()[wakeupmonitor userData]wakeupmonitor.get_userData()wakeupmonitor.get_userData()wakeupmonitor.get_userData()wakeupmonitor.get_userData()wakeupmonitor.get_userData()wakeupmonitor→get_userData()wakeupmonitor.get_userData()wakeupmonitor.get_userData()
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData.
js | function get_userData( | ) |
cpp | void * get_userData( | ) |
m | -(id) userData |
pas | Tobject get_userData( | ): Tobject |
vb | function get_userData( | ) As Object |
cs | object get_userData( | ) |
java | Object get_userData( | ) |
py | get_userData( | ) |
php | function get_userData( | ) |
ts | async get_userData( | ): Promise<object|null> |
es | async get_userData( | ) |
This attribute is never touched directly by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Returns :
the object stored previously by the caller.
wakeupmonitor→get_wakeUpReason()
wakeupmonitor→wakeUpReason()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpReason()wakeupmonitor→get_wakeUpReason()[wakeupmonitor wakeUpReason]wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpReason()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpReason()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpReason()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpReason()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpReason()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpReason()wakeupmonitor→get_wakeUpReason()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpReason()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpReason()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpReason()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpReason()YWakeUpMonitor get_wakeUpReason
Returns the latest wake up reason.
js | function get_wakeUpReason( | ) |
cpp | Y_WAKEUPREASON_enum get_wakeUpReason( | ) |
m | -(Y_WAKEUPREASON_enum) wakeUpReason |
pas | Integer get_wakeUpReason( | ): Integer |
vb | function get_wakeUpReason( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_wakeUpReason( | ) |
java | int get_wakeUpReason( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_wakeUpReason( | ) |
py | get_wakeUpReason( | ) |
php | function get_wakeUpReason( | ) |
ts | async get_wakeUpReason( | ): Promise<YWakeUpMonitor_WakeUpReason> |
es | async get_wakeUpReason( | ) |
dnp | int get_wakeUpReason( | ) |
cp | int get_wakeUpReason( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target get_wakeUpReason |
Returns :
a value among YWakeUpMonitor.WAKEUPREASON_USBPOWER, YWakeUpMonitor.WAKEUPREASON_EXTPOWER, YWakeUpMonitor.WAKEUPREASON_ENDOFSLEEP, YWakeUpMonitor.WAKEUPREASON_EXTSIG1, YWakeUpMonitor.WAKEUPREASON_SCHEDULE1 and YWakeUpMonitor.WAKEUPREASON_SCHEDULE2 corresponding to the latest wake up reason
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpMonitor.WAKEUPREASON_INVALID.
wakeupmonitor→get_wakeUpState()
wakeupmonitor→wakeUpState()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpState()wakeupmonitor→get_wakeUpState()[wakeupmonitor wakeUpState]wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpState()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpState()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpState()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpState()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpState()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpState()wakeupmonitor→get_wakeUpState()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpState()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpState()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpState()wakeupmonitor.get_wakeUpState()YWakeUpMonitor get_wakeUpState
Returns the current state of the monitor.
js | function get_wakeUpState( | ) |
cpp | Y_WAKEUPSTATE_enum get_wakeUpState( | ) |
m | -(Y_WAKEUPSTATE_enum) wakeUpState |
pas | Integer get_wakeUpState( | ): Integer |
vb | function get_wakeUpState( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_wakeUpState( | ) |
java | int get_wakeUpState( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_wakeUpState( | ) |
py | get_wakeUpState( | ) |
php | function get_wakeUpState( | ) |
ts | async get_wakeUpState( | ): Promise<YWakeUpMonitor_WakeUpState> |
es | async get_wakeUpState( | ) |
dnp | int get_wakeUpState( | ) |
cp | int get_wakeUpState( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target get_wakeUpState |
Returns :
either YWakeUpMonitor.WAKEUPSTATE_SLEEPING or YWakeUpMonitor.WAKEUPSTATE_AWAKE, according to the current state of the monitor
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpMonitor.WAKEUPSTATE_INVALID.
wakeupmonitor→isOnline()wakeupmonitor.isOnline()wakeupmonitor→isOnline()[wakeupmonitor isOnline]wakeupmonitor.isOnline()wakeupmonitor.isOnline()wakeupmonitor.isOnline()wakeupmonitor.isOnline()wakeupmonitor.isOnline()wakeupmonitor→isOnline()wakeupmonitor.isOnline()wakeupmonitor.isOnline()wakeupmonitor.isOnline()wakeupmonitor.isOnline()
Checks if the wake-up monitor is currently reachable, without raising any error.
js | function isOnline( | ) |
cpp | bool isOnline( | ) |
m | -(BOOL) isOnline |
pas | boolean isOnline( | ): boolean |
vb | function isOnline( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isOnline( | ) |
java | boolean isOnline( | ) |
py | isOnline( | ) |
php | function isOnline( | ) |
ts | async isOnline( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isOnline( | ) |
dnp | bool isOnline( | ) |
cp | bool isOnline( | ) |
If there is a cached value for the wake-up monitor in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the wake-up monitor.
Returns :
true if the wake-up monitor can be reached, and false otherwise
wakeupmonitor→isOnline_async()wakeupmonitor.isOnline_async()
Checks if the wake-up monitor is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version).
js | function isOnline_async( | callback, context) |
If there is a cached value for the wake-up monitor in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the requested function.
This asynchronous version exists only in Javascript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the Javascript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the boolean result |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
wakeupmonitor→isReadOnly()wakeupmonitor→isReadOnly()[wakeupmonitor isReadOnly]wakeupmonitor.isReadOnly()wakeupmonitor.isReadOnly()wakeupmonitor.isReadOnly()wakeupmonitor.isReadOnly()wakeupmonitor.isReadOnly()wakeupmonitor.isReadOnly()wakeupmonitor→isReadOnly()wakeupmonitor.isReadOnly()wakeupmonitor.isReadOnly()wakeupmonitor.isReadOnly()wakeupmonitor.isReadOnly()YWakeUpMonitor isReadOnly
Test if the function is readOnly.
cpp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
m | -(bool) isReadOnly |
pas | boolean isReadOnly( | ): boolean |
vb | function isReadOnly( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
java | boolean isReadOnly( | ) |
uwp | async Task<bool> isReadOnly( | ) |
py | isReadOnly( | ) |
php | function isReadOnly( | ) |
ts | async isReadOnly( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isReadOnly( | ) |
dnp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target isReadOnly |
Return true if the function is write protected or that the function is not available.
Returns :
true if the function is readOnly or not online.
wakeupmonitor→load()wakeupmonitor.load()wakeupmonitor→load()[wakeupmonitor load: ]wakeupmonitor.load()wakeupmonitor.load()wakeupmonitor.load()wakeupmonitor.load()wakeupmonitor.load()wakeupmonitor→load()wakeupmonitor.load()wakeupmonitor.load()
Preloads the wake-up monitor cache with a specified validity duration.
js | function load( | msValidity) |
cpp | YRETCODE load( | int msValidity) |
m | -(YRETCODE) load | : (u64) msValidity |
pas | YRETCODE load( | msValidity: u64): YRETCODE |
vb | function load( | ByVal msValidity As Long) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE load( | ulong msValidity) |
java | int load( | long msValidity) |
py | load( | msValidity) |
php | function load( | $msValidity) |
ts | async load( | msValidity: number): Promise<number> |
es | async load( | msValidity) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity attributed to the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupmonitor→loadAttribute()wakeupmonitor.loadAttribute()wakeupmonitor→loadAttribute()[wakeupmonitor loadAttribute: ]wakeupmonitor.loadAttribute()wakeupmonitor.loadAttribute()wakeupmonitor.loadAttribute()wakeupmonitor.loadAttribute()wakeupmonitor.loadAttribute()wakeupmonitor.loadAttribute()wakeupmonitor→loadAttribute()wakeupmonitor.loadAttribute()wakeupmonitor.loadAttribute()wakeupmonitor.loadAttribute()wakeupmonitor.loadAttribute()
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value.
js | function loadAttribute( | attrName) |
cpp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
m | -(NSString*) loadAttribute | : (NSString*) attrName |
pas | string loadAttribute( | attrName: string): string |
vb | function loadAttribute( | ByVal attrName As String) As String |
cs | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
java | String loadAttribute( | String attrName) |
uwp | async Task<string> loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
py | loadAttribute( | attrName) |
php | function loadAttribute( | $attrName) |
ts | async loadAttribute( | attrName: string): Promise<string> |
es | async loadAttribute( | attrName) |
dnp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
cp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
Parameters :
| attrName | the name of the requested attribute |
Returns :
a string with the value of the the attribute
On failure, throws an exception or returns an empty string.
wakeupmonitor→load_async()wakeupmonitor.load_async()
Preloads the wake-up monitor cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version).
js | function load_async( | msValidity, callback, context) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the JavaScript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity of the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the error code (or YAPI.SUCCESS) |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
wakeupmonitor→muteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor→muteValueCallbacks()[wakeupmonitor muteValueCallbacks]wakeupmonitor.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor→muteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.muteValueCallbacks()YWakeUpMonitor muteValueCallbacks
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) muteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt muteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async muteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target muteValueCallbacks |
You can use this function to save bandwidth and CPU on computers with limited resources, or to prevent unwanted invocations of the HTTP callback. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupmonitor→nextWakeUpMonitor()wakeupmonitor.nextWakeUpMonitor()wakeupmonitor→nextWakeUpMonitor()[wakeupmonitor nextWakeUpMonitor]wakeupmonitor.nextWakeUpMonitor()wakeupmonitor.nextWakeUpMonitor()wakeupmonitor.nextWakeUpMonitor()wakeupmonitor.nextWakeUpMonitor()wakeupmonitor.nextWakeUpMonitor()wakeupmonitor.nextWakeUpMonitor()wakeupmonitor→nextWakeUpMonitor()wakeupmonitor.nextWakeUpMonitor()wakeupmonitor.nextWakeUpMonitor()
Continues the enumeration of wake-up monitors started using yFirstWakeUpMonitor().
js | function nextWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
cpp | YWakeUpMonitor * nextWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
m | -(nullable YWakeUpMonitor*) nextWakeUpMonitor |
pas | TYWakeUpMonitor nextWakeUpMonitor( | ): TYWakeUpMonitor |
vb | function nextWakeUpMonitor( | ) As YWakeUpMonitor |
cs | YWakeUpMonitor nextWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
java | YWakeUpMonitor nextWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
uwp | YWakeUpMonitor nextWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
py | nextWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
php | function nextWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
ts | nextWakeUpMonitor( | ): YWakeUpMonitor | null |
es | nextWakeUpMonitor( | ) |
Caution: You can't make any assumption about the returned wake-up monitors order. If you want to find a specific a wake-up monitor, use WakeUpMonitor.findWakeUpMonitor() and a hardwareID or a logical name.
Returns :
a pointer to a YWakeUpMonitor object, corresponding to a wake-up monitor currently online, or a null pointer if there are no more wake-up monitors to enumerate.
wakeupmonitor→registerValueCallback()wakeupmonitor.registerValueCallback()wakeupmonitor→registerValueCallback()[wakeupmonitor registerValueCallback: ]wakeupmonitor.registerValueCallback()wakeupmonitor.registerValueCallback()wakeupmonitor.registerValueCallback()wakeupmonitor.registerValueCallback()wakeupmonitor.registerValueCallback()wakeupmonitor.registerValueCallback()wakeupmonitor→registerValueCallback()wakeupmonitor.registerValueCallback()wakeupmonitor.registerValueCallback()
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value.
js | function registerValueCallback( | callback) |
cpp | int registerValueCallback( | YWakeUpMonitorValueCallback callback) |
m | -(int) registerValueCallback | : (YWakeUpMonitorValueCallback _Nullable) callback |
pas | LongInt registerValueCallback( | callback: TYWakeUpMonitorValueCallback): LongInt |
vb | function registerValueCallback( | ByVal callback As YWakeUpMonitorValueCallback) As Integer |
cs | int registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
java | int registerValueCallback( | UpdateCallback callback) |
uwp | async Task<int> registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
py | registerValueCallback( | callback) |
php | function registerValueCallback( | $callback) |
ts | async registerValueCallback( | callback: YWakeUpMonitorValueCallback | null): Promise<number> |
es | async registerValueCallback( | callback) |
The callback is invoked only during the execution of ySleep or yHandleEvents. This provides control over the time when the callback is triggered. For good responsiveness, remember to call one of these two functions periodically. To unregister a callback, pass a null pointer as argument.
Parameters :
| callback | the callback function to call, or a null pointer. The callback function should take two arguments: the function object of which the value has changed, and the character string describing the new advertised value. |
wakeupmonitor→resetSleepCountDown()wakeupmonitor.resetSleepCountDown()wakeupmonitor→resetSleepCountDown()[wakeupmonitor resetSleepCountDown]wakeupmonitor.resetSleepCountDown()wakeupmonitor.resetSleepCountDown()wakeupmonitor.resetSleepCountDown()wakeupmonitor.resetSleepCountDown()wakeupmonitor.resetSleepCountDown()wakeupmonitor.resetSleepCountDown()wakeupmonitor→resetSleepCountDown()wakeupmonitor.resetSleepCountDown()wakeupmonitor.resetSleepCountDown()wakeupmonitor.resetSleepCountDown()wakeupmonitor.resetSleepCountDown()YWakeUpMonitor resetSleepCountDown
Resets the sleep countdown.
js | function resetSleepCountDown( | ) |
cpp | int resetSleepCountDown( | ) |
m | -(int) resetSleepCountDown |
pas | LongInt resetSleepCountDown( | ): LongInt |
vb | function resetSleepCountDown( | ) As Integer |
cs | int resetSleepCountDown( | ) |
java | int resetSleepCountDown( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> resetSleepCountDown( | ) |
py | resetSleepCountDown( | ) |
php | function resetSleepCountDown( | ) |
ts | async resetSleepCountDown( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async resetSleepCountDown( | ) |
dnp | int resetSleepCountDown( | ) |
cp | int resetSleepCountDown( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target resetSleepCountDown |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds. On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupmonitor→set_logicalName()
wakeupmonitor→setLogicalName()wakeupmonitor.set_logicalName()wakeupmonitor→set_logicalName()[wakeupmonitor setLogicalName: ]wakeupmonitor.set_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.set_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.set_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.set_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.set_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.set_logicalName()wakeupmonitor→set_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.set_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.set_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.set_logicalName()wakeupmonitor.set_logicalName()YWakeUpMonitor set_logicalName
Changes the logical name of the wake-up monitor.
js | function set_logicalName( | newval) |
cpp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setLogicalName | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_logicalName( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_logicalName( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
java | int set_logicalName( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_logicalName( | string newval) |
py | set_logicalName( | newval) |
php | function set_logicalName( | $newval) |
ts | async set_logicalName( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_logicalName( | newval) |
dnp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target set_logicalName | newval |
You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the logical name of the wake-up monitor. |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupmonitor→set_nextWakeUp()
wakeupmonitor→setNextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.set_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor→set_nextWakeUp()[wakeupmonitor setNextWakeUp: ]wakeupmonitor.set_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.set_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.set_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.set_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.set_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.set_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor→set_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.set_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.set_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.set_nextWakeUp()wakeupmonitor.set_nextWakeUp()YWakeUpMonitor set_nextWakeUp
Changes the days of the week when a wake up must take place.
js | function set_nextWakeUp( | newval) |
cpp | int set_nextWakeUp( | s64 newval) |
m | -(int) setNextWakeUp | : (s64) newval |
pas | integer set_nextWakeUp( | newval: int64): integer |
vb | function set_nextWakeUp( | ByVal newval As Long) As Integer |
cs | int set_nextWakeUp( | long newval) |
java | int set_nextWakeUp( | long newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_nextWakeUp( | long newval) |
py | set_nextWakeUp( | newval) |
php | function set_nextWakeUp( | $newval) |
ts | async set_nextWakeUp( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_nextWakeUp( | newval) |
dnp | int set_nextWakeUp( | long newval) |
cp | int set_nextWakeUp( | s64 newval) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target set_nextWakeUp | newval |
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the days of the week when a wake up must take place |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupmonitor→set_powerDuration()
wakeupmonitor→setPowerDuration()wakeupmonitor.set_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor→set_powerDuration()[wakeupmonitor setPowerDuration: ]wakeupmonitor.set_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.set_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.set_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.set_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.set_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.set_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor→set_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.set_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.set_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.set_powerDuration()wakeupmonitor.set_powerDuration()YWakeUpMonitor set_powerDuration
Changes the maximal wake up time (seconds) before automatically going to sleep.
js | function set_powerDuration( | newval) |
cpp | int set_powerDuration( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setPowerDuration | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_powerDuration( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_powerDuration( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_powerDuration( | int newval) |
java | int set_powerDuration( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_powerDuration( | int newval) |
py | set_powerDuration( | newval) |
php | function set_powerDuration( | $newval) |
ts | async set_powerDuration( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_powerDuration( | newval) |
dnp | int set_powerDuration( | int newval) |
cp | int set_powerDuration( | int newval) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target set_powerDuration | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the maximal wake up time (seconds) before automatically going to sleep |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupmonitor→set_sleepCountdown()
wakeupmonitor→setSleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.set_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor→set_sleepCountdown()[wakeupmonitor setSleepCountdown: ]wakeupmonitor.set_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.set_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.set_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.set_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.set_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.set_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor→set_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.set_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.set_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.set_sleepCountdown()wakeupmonitor.set_sleepCountdown()YWakeUpMonitor set_sleepCountdown
Changes the delay before the next sleep period.
js | function set_sleepCountdown( | newval) |
cpp | int set_sleepCountdown( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setSleepCountdown | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_sleepCountdown( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_sleepCountdown( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_sleepCountdown( | int newval) |
java | int set_sleepCountdown( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_sleepCountdown( | int newval) |
py | set_sleepCountdown( | newval) |
php | function set_sleepCountdown( | $newval) |
ts | async set_sleepCountdown( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_sleepCountdown( | newval) |
dnp | int set_sleepCountdown( | int newval) |
cp | int set_sleepCountdown( | int newval) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target set_sleepCountdown | newval |
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the delay before the next sleep period |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupmonitor→set_userData()
wakeupmonitor→setUserData()wakeupmonitor.set_userData()wakeupmonitor→set_userData()[wakeupmonitor setUserData: ]wakeupmonitor.set_userData()wakeupmonitor.set_userData()wakeupmonitor.set_userData()wakeupmonitor.set_userData()wakeupmonitor.set_userData()wakeupmonitor→set_userData()wakeupmonitor.set_userData()wakeupmonitor.set_userData()
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function.
js | function set_userData( | data) |
cpp | void set_userData( | void * data) |
m | -(void) setUserData | : (id) data |
pas | set_userData( | data: Tobject) |
vb | procedure set_userData( | ByVal data As Object) |
cs | void set_userData( | object data) |
java | void set_userData( | Object data) |
py | set_userData( | data) |
php | function set_userData( | $data) |
ts | async set_userData( | data: object|null): Promise<void> |
es | async set_userData( | data) |
This attribute is never touched by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Parameters :
| data | any kind of object to be stored |
wakeupmonitor→sleep()wakeupmonitor.sleep()wakeupmonitor→sleep()[wakeupmonitor sleep: ]wakeupmonitor.sleep()wakeupmonitor.sleep()wakeupmonitor.sleep()wakeupmonitor.sleep()wakeupmonitor.sleep()wakeupmonitor.sleep()wakeupmonitor→sleep()wakeupmonitor.sleep()wakeupmonitor.sleep()wakeupmonitor.sleep()wakeupmonitor.sleep()YWakeUpMonitor sleep
Goes to sleep until the next wake up condition is met, the RTC time must have been set before calling this function.
js | function sleep( | secBeforeSleep) |
cpp | int sleep( | int secBeforeSleep) |
m | -(int) sleep | : (int) secBeforeSleep |
pas | LongInt sleep( | secBeforeSleep: LongInt): LongInt |
vb | function sleep( | ByVal secBeforeSleep As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int sleep( | int secBeforeSleep) |
java | int sleep( | int secBeforeSleep) |
uwp | async Task<int> sleep( | int secBeforeSleep) |
py | sleep( | secBeforeSleep) |
php | function sleep( | $secBeforeSleep) |
ts | async sleep( | secBeforeSleep: number): Promise<number> |
es | async sleep( | secBeforeSleep) |
dnp | int sleep( | int secBeforeSleep) |
cp | int sleep( | int secBeforeSleep) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target sleep | secBeforeSleep |
Parameters :
| secBeforeSleep | number of seconds before going into sleep mode, |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupmonitor→sleepFor()wakeupmonitor.sleepFor()wakeupmonitor→sleepFor()[wakeupmonitor sleepFor: ]wakeupmonitor.sleepFor()wakeupmonitor.sleepFor()wakeupmonitor.sleepFor()wakeupmonitor.sleepFor()wakeupmonitor.sleepFor()wakeupmonitor.sleepFor()wakeupmonitor→sleepFor()wakeupmonitor.sleepFor()wakeupmonitor.sleepFor()wakeupmonitor.sleepFor()wakeupmonitor.sleepFor()YWakeUpMonitor sleepFor
Goes to sleep for a specific duration or until the next wake up condition is met, the RTC time must have been set before calling this function.
js | function sleepFor( | secUntilWakeUp, secBeforeSleep) |
cpp | int sleepFor( | int secUntilWakeUp, int secBeforeSleep) |
m | -(int) sleepFor | : (int) secUntilWakeUp |
| : (int) secBeforeSleep |
pas | LongInt sleepFor( | secUntilWakeUp: LongInt, |
| secBeforeSleep: LongInt): LongInt |
vb | function sleepFor( | ByVal secUntilWakeUp As Integer, |
| ByVal secBeforeSleep As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int sleepFor( | int secUntilWakeUp, int secBeforeSleep) |
java | int sleepFor( | int secUntilWakeUp, int secBeforeSleep) |
uwp | async Task<int> sleepFor( | int secUntilWakeUp, int secBeforeSleep) |
py | sleepFor( | secUntilWakeUp, secBeforeSleep) |
php | function sleepFor( | $secUntilWakeUp, $secBeforeSleep) |
ts | async sleepFor( | secUntilWakeUp: number, secBeforeSleep: number): Promise<number> |
es | async sleepFor( | secUntilWakeUp, secBeforeSleep) |
dnp | int sleepFor( | int secUntilWakeUp, int secBeforeSleep) |
cp | int sleepFor( | int secUntilWakeUp, int secBeforeSleep) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target sleepFor | secUntilWakeUp secBeforeSleep |
The count down before sleep can be canceled with resetSleepCountDown.
Parameters :
| secUntilWakeUp | number of seconds before next wake up |
| secBeforeSleep | number of seconds before going into sleep mode |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupmonitor→sleepUntil()wakeupmonitor.sleepUntil()wakeupmonitor→sleepUntil()[wakeupmonitor sleepUntil: ]wakeupmonitor.sleepUntil()wakeupmonitor.sleepUntil()wakeupmonitor.sleepUntil()wakeupmonitor.sleepUntil()wakeupmonitor.sleepUntil()wakeupmonitor.sleepUntil()wakeupmonitor→sleepUntil()wakeupmonitor.sleepUntil()wakeupmonitor.sleepUntil()wakeupmonitor.sleepUntil()wakeupmonitor.sleepUntil()YWakeUpMonitor sleepUntil
Go to sleep until a specific date is reached or until the next wake up condition is met, the RTC time must have been set before calling this function.
js | function sleepUntil( | wakeUpTime, secBeforeSleep) |
cpp | int sleepUntil( | int wakeUpTime, int secBeforeSleep) |
m | -(int) sleepUntil | : (int) wakeUpTime : (int) secBeforeSleep |
pas | LongInt sleepUntil( | wakeUpTime: LongInt, |
| secBeforeSleep: LongInt): LongInt |
vb | function sleepUntil( | ByVal wakeUpTime As Integer, |
| ByVal secBeforeSleep As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int sleepUntil( | int wakeUpTime, int secBeforeSleep) |
java | int sleepUntil( | int wakeUpTime, int secBeforeSleep) |
uwp | async Task<int> sleepUntil( | int wakeUpTime, int secBeforeSleep) |
py | sleepUntil( | wakeUpTime, secBeforeSleep) |
php | function sleepUntil( | $wakeUpTime, $secBeforeSleep) |
ts | async sleepUntil( | wakeUpTime: number, secBeforeSleep: number): Promise<number> |
es | async sleepUntil( | wakeUpTime, secBeforeSleep) |
dnp | int sleepUntil( | int wakeUpTime, int secBeforeSleep) |
cp | int sleepUntil( | int wakeUpTime, int secBeforeSleep) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target sleepUntil | wakeUpTime secBeforeSleep |
The count down before sleep can be canceled with resetSleepCountDown.
Parameters :
| wakeUpTime | wake-up datetime (UNIX format) |
| secBeforeSleep | number of seconds before going into sleep mode |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupmonitor→unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor→unmuteValueCallbacks()[wakeupmonitor unmuteValueCallbacks]wakeupmonitor.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor→unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupmonitor.unmuteValueCallbacks()YWakeUpMonitor unmuteValueCallbacks
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) unmuteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target unmuteValueCallbacks |
This function reverts the effect of a previous call to muteValueCallbacks(). Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupmonitor→wait_async()wakeupmonitor.wait_async()wakeupmonitor.wait_async()wakeupmonitor.wait_async()
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function.
js | function wait_async( | callback, context) |
ts | wait_async( | callback: Function, context: object) |
es | wait_async( | callback, context) |
The callback function can therefore freely issue synchronous or asynchronous commands, without risking to block the JavaScript VM.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when all pending commands on the module are completed. The callback function receives two arguments: the caller-specific context object and the receiving function object. |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing.
wakeupmonitor→wakeUp()wakeupmonitor.wakeUp()wakeupmonitor→wakeUp()[wakeupmonitor wakeUp]wakeupmonitor.wakeUp()wakeupmonitor.wakeUp()wakeupmonitor.wakeUp()wakeupmonitor.wakeUp()wakeupmonitor.wakeUp()wakeupmonitor.wakeUp()wakeupmonitor→wakeUp()wakeupmonitor.wakeUp()wakeupmonitor.wakeUp()wakeupmonitor.wakeUp()wakeupmonitor.wakeUp()YWakeUpMonitor wakeUp
Forces a wake up.
js | function wakeUp( | ) |
cpp | int wakeUp( | ) |
m | -(int) wakeUp |
pas | LongInt wakeUp( | ): LongInt |
vb | function wakeUp( | ) As Integer |
cs | int wakeUp( | ) |
java | int wakeUp( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> wakeUp( | ) |
py | wakeUp( | ) |
php | function wakeUp( | ) |
ts | async wakeUp( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async wakeUp( | ) |
dnp | int wakeUp( | ) |
cp | int wakeUp( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpMonitor target wakeUp |
11.7. Class YWakeUpSchedule
Wake up schedule control interface, available for instance in the YoctoHub-GSM-3G-EU, the YoctoHub-GSM-3G-NA, the YoctoHub-GSM-4G or the YoctoHub-Wireless-n
The YWakeUpSchedule class implements a wake up condition. The wake up time is specified as a set of months and/or days and/or hours and/or minutes when the wake up should happen.
In order to use the functions described here, you should include:
es | in HTML: <script src="../../lib/yocto_wakeupschedule.js"></script> in node.js: require('yoctolib-es2017/yocto_wakeupschedule.js'); |
js | <script type='text/javascript' src='yocto_wakeupschedule.js'></script> |
cpp | #include "yocto_wakeupschedule.h" |
m | #import "yocto_wakeupschedule.h" |
pas | uses yocto_wakeupschedule; |
vb | yocto_wakeupschedule.vb |
cs | yocto_wakeupschedule.cs |
java | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YWakeUpSchedule; |
uwp | import com.yoctopuce.YoctoAPI.YWakeUpSchedule; |
py | from yocto_wakeupschedule import * |
php | require_once('yocto_wakeupschedule.php'); |
ts | in HTML: import { YWakeUpSchedule } from '../../dist/esm/yocto_wakeupschedule.js'; in Node.js: import { YWakeUpSchedule } from 'yoctolib-cjs/yocto_wakeupschedule.js'; |
dnp | import YoctoProxyAPI.YWakeUpScheduleProxy |
cp | #include "yocto_wakeupschedule_proxy.h" |
vi | YWakeUpSchedule.vi |
ml | import YoctoProxyAPI.YWakeUpScheduleProxy |
| Global functions |
|---|
| YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpSchedule(func) |
Retrieves a wake up schedule for a given identifier. |
| YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpScheduleInContext(yctx, func) |
Retrieves a wake up schedule for a given identifier in a YAPI context. |
| YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpSchedule() |
Starts the enumeration of wake up schedules currently accessible. |
| YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpScheduleInContext(yctx) |
Starts the enumeration of wake up schedules currently accessible. |
| YWakeUpSchedule.GetSimilarFunctions() |
Enumerates all functions of type WakeUpSchedule available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID. |
| YWakeUpSchedule properties |
| wakeupschedule→AdvertisedValue [read-only] |
Short string representing the current state of the function. |
| wakeupschedule→FriendlyName [read-only] |
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| wakeupschedule→FunctionId [read-only] |
Hardware identifier of the wake up schedule, without reference to the module. |
| wakeupschedule→HardwareId [read-only] |
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| wakeupschedule→Hours [writable] |
Hours scheduled for wake up. |
| wakeupschedule→IsOnline [read-only] |
Checks if the function is currently reachable. |
| wakeupschedule→LogicalName [writable] |
Logical name of the function. |
| wakeupschedule→MinutesA [writable] |
Minutes in the 00-29 interval of each hour scheduled for wake up. |
| wakeupschedule→MinutesB [writable] |
Minutes in the 30-59 interval of each hour scheduled for wake up. |
| wakeupschedule→MonthDays [writable] |
Days of the month scheduled for wake up. |
| wakeupschedule→Months [writable] |
Months scheduled for wake up. |
| wakeupschedule→NextOccurence [read-only] |
Date/time (seconds) of the next wake up occurrence. |
| wakeupschedule→SerialNumber [read-only] |
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| wakeupschedule→WeekDays [writable] |
Days of the week scheduled for wake up. |
| YWakeUpSchedule methods |
| wakeupschedule→clearCache() |
Invalidates the cache. |
| wakeupschedule→describe() |
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the wake up schedule in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| wakeupschedule→get_advertisedValue() |
Returns the current value of the wake up schedule (no more than 6 characters). |
| wakeupschedule→get_errorMessage() |
Returns the error message of the latest error with the wake up schedule. |
| wakeupschedule→get_errorType() |
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the wake up schedule. |
| wakeupschedule→get_friendlyName() |
Returns a global identifier of the wake up schedule in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME. |
| wakeupschedule→get_functionDescriptor() |
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function. |
| wakeupschedule→get_functionId() |
Returns the hardware identifier of the wake up schedule, without reference to the module. |
| wakeupschedule→get_hardwareId() |
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the wake up schedule in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID. |
| wakeupschedule→get_hours() |
Returns the hours scheduled for wake up. |
| wakeupschedule→get_logicalName() |
Returns the logical name of the wake up schedule. |
| wakeupschedule→get_minutes() |
Returns all the minutes of each hour that are scheduled for wake up. |
| wakeupschedule→get_minutesA() |
Returns the minutes in the 00-29 interval of each hour scheduled for wake up. |
| wakeupschedule→get_minutesB() |
Returns the minutes in the 30-59 interval of each hour scheduled for wake up. |
| wakeupschedule→get_module() |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located. |
| wakeupschedule→get_module_async(callback, context) |
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version). |
| wakeupschedule→get_monthDays() |
Returns the days of the month scheduled for wake up. |
| wakeupschedule→get_months() |
Returns the months scheduled for wake up. |
| wakeupschedule→get_nextOccurence() |
Returns the date/time (seconds) of the next wake up occurrence. |
| wakeupschedule→get_serialNumber() |
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory. |
| wakeupschedule→get_userData() |
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData. |
| wakeupschedule→get_weekDays() |
Returns the days of the week scheduled for wake up. |
| wakeupschedule→isOnline() |
Checks if the wake up schedule is currently reachable, without raising any error. |
| wakeupschedule→isOnline_async(callback, context) |
Checks if the wake up schedule is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version). |
| wakeupschedule→isReadOnly() |
Test if the function is readOnly. |
| wakeupschedule→load(msValidity) |
Preloads the wake up schedule cache with a specified validity duration. |
| wakeupschedule→loadAttribute(attrName) |
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value. |
| wakeupschedule→load_async(msValidity, callback, context) |
Preloads the wake up schedule cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version). |
| wakeupschedule→muteValueCallbacks() |
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| wakeupschedule→nextWakeUpSchedule() |
Continues the enumeration of wake up schedules started using yFirstWakeUpSchedule(). |
| wakeupschedule→registerValueCallback(callback) |
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value. |
| wakeupschedule→set_hours(newval) |
Changes the hours when a wake up must take place. |
| wakeupschedule→set_logicalName(newval) |
Changes the logical name of the wake up schedule. |
| wakeupschedule→set_minutes(bitmap) |
Changes all the minutes where a wake up must take place. |
| wakeupschedule→set_minutesA(newval) |
Changes the minutes in the 00-29 interval when a wake up must take place. |
| wakeupschedule→set_minutesB(newval) |
Changes the minutes in the 30-59 interval when a wake up must take place. |
| wakeupschedule→set_monthDays(newval) |
Changes the days of the month when a wake up must take place. |
| wakeupschedule→set_months(newval) |
Changes the months when a wake up must take place. |
| wakeupschedule→set_userData(data) |
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function. |
| wakeupschedule→set_weekDays(newval) |
Changes the days of the week when a wake up must take place. |
| wakeupschedule→unmuteValueCallbacks() |
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub. |
| wakeupschedule→wait_async(callback, context) |
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function. |
YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpSchedule()
YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpSchedule()yFindWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule::FindWakeUpSchedule()[YWakeUpSchedule FindWakeUpSchedule: ]yFindWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule::FindWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpSchedule()
Retrieves a wake up schedule for a given identifier.
js | function yFindWakeUpSchedule( | func) |
cpp | YWakeUpSchedule* FindWakeUpSchedule( | string func) |
m | +(YWakeUpSchedule*) FindWakeUpSchedule | : (NSString*) func |
pas | TYWakeUpSchedule yFindWakeUpSchedule( | func: string): TYWakeUpSchedule |
vb | function FindWakeUpSchedule( | ByVal func As String) As YWakeUpSchedule |
cs | static YWakeUpSchedule FindWakeUpSchedule( | string func) |
java | static YWakeUpSchedule FindWakeUpSchedule( | String func) |
uwp | static YWakeUpSchedule FindWakeUpSchedule( | string func) |
py | FindWakeUpSchedule( | func) |
php | function FindWakeUpSchedule( | $func) |
ts | static FindWakeUpSchedule( | func: string): YWakeUpSchedule |
es | static FindWakeUpSchedule( | func) |
dnp | static YWakeUpScheduleProxy FindWakeUpSchedule( | string func) |
cp | static YWakeUpScheduleProxy * FindWakeUpSchedule( | string func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the wake up schedule is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YWakeUpSchedule.isOnline() to test if the wake up schedule is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a wake up schedule by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
If a call to this object's is_online() method returns FALSE although you are certain that the matching device is plugged, make sure that you did call registerHub() at application initialization time.
Parameters :
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the wake up schedule, for instance YHUBGSM3.wakeUpSchedule1. |
Returns :
a YWakeUpSchedule object allowing you to drive the wake up schedule.
YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpScheduleInContext()
YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpScheduleInContext()YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpScheduleInContext()YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpScheduleInContext()YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpScheduleInContext()YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpScheduleInContext()
Retrieves a wake up schedule for a given identifier in a YAPI context.
java | static YWakeUpSchedule FindWakeUpScheduleInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, |
| String func) |
uwp | static YWakeUpSchedule FindWakeUpScheduleInContext( | YAPIContext yctx, |
| string func) |
ts | static FindWakeUpScheduleInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext, func: string): YWakeUpSchedule |
es | static FindWakeUpScheduleInContext( | yctx, func) |
The identifier can be specified using several formats:
- FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleSerialNumber.FunctionLogicalName
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionIdentifier
- ModuleLogicalName.FunctionLogicalName
This function does not require that the wake up schedule is online at the time it is invoked. The returned object is nevertheless valid. Use the method YWakeUpSchedule.isOnline() to test if the wake up schedule is indeed online at a given time. In case of ambiguity when looking for a wake up schedule by logical name, no error is notified: the first instance found is returned. The search is performed first by hardware name, then by logical name.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context |
| func | a string that uniquely characterizes the wake up schedule, for instance YHUBGSM3.wakeUpSchedule1. |
Returns :
a YWakeUpSchedule object allowing you to drive the wake up schedule.
YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpSchedule()
YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpSchedule()yFirstWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule::FirstWakeUpSchedule()[YWakeUpSchedule FirstWakeUpSchedule]yFirstWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule::FirstWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpSchedule()YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpSchedule()
Starts the enumeration of wake up schedules currently accessible.
js | function yFirstWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
cpp | YWakeUpSchedule * FirstWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
m | +(YWakeUpSchedule*) FirstWakeUpSchedule |
pas | TYWakeUpSchedule yFirstWakeUpSchedule( | ): TYWakeUpSchedule |
vb | function FirstWakeUpSchedule( | ) As YWakeUpSchedule |
cs | static YWakeUpSchedule FirstWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
java | static YWakeUpSchedule FirstWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
uwp | static YWakeUpSchedule FirstWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
py | FirstWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
php | function FirstWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
ts | static FirstWakeUpSchedule( | ): YWakeUpSchedule | null |
es | static FirstWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
Use the method YWakeUpSchedule.nextWakeUpSchedule() to iterate on next wake up schedules.
Returns :
a pointer to a YWakeUpSchedule object, corresponding to the first wake up schedule currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpScheduleInContext()
YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpScheduleInContext()YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpScheduleInContext()YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpScheduleInContext()YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpScheduleInContext()YWakeUpSchedule.FirstWakeUpScheduleInContext()
Starts the enumeration of wake up schedules currently accessible.
java | static YWakeUpSchedule FirstWakeUpScheduleInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
uwp | static YWakeUpSchedule FirstWakeUpScheduleInContext( | YAPIContext yctx) |
ts | static FirstWakeUpScheduleInContext( | yctx: YAPIContext): YWakeUpSchedule | null |
es | static FirstWakeUpScheduleInContext( | yctx) |
Use the method YWakeUpSchedule.nextWakeUpSchedule() to iterate on next wake up schedules.
Parameters :
| yctx | a YAPI context. |
Returns :
a pointer to a YWakeUpSchedule object, corresponding to the first wake up schedule currently online, or a null pointer if there are none.
YWakeUpSchedule.GetSimilarFunctions()
YWakeUpSchedule.GetSimilarFunctions()YWakeUpSchedule.GetSimilarFunctions()YWakeUpSchedule.GetSimilarFunctions()
Enumerates all functions of type WakeUpSchedule available on the devices currently reachable by the library, and returns their unique hardware ID.
dnp | static new string[] GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
cp | static vector<string> GetSimilarFunctions( | ) |
Each of these IDs can be provided as argument to the method YWakeUpSchedule.FindWakeUpSchedule to obtain an object that can control the corresponding device.
Returns :
an array of strings, each string containing the unique hardwareId of a device function currently connected.
wakeupschedule→AdvertisedValuewakeupschedule.AdvertisedValue
Short string representing the current state of the function.
dnp | string AdvertisedValue |
wakeupschedule→FriendlyNamewakeupschedule.FriendlyName
Global identifier of the function in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
dnp | string FriendlyName |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the function if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the function (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
wakeupschedule→FunctionIdwakeupschedule.FunctionId
Hardware identifier of the wake up schedule, without reference to the module.
dnp | string FunctionId |
For example relay1
wakeupschedule→HardwareIdwakeupschedule.HardwareId
Unique hardware identifier of the function in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
dnp | string HardwareId |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the function (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
wakeupschedule→Hourswakeupschedule.Hours
Hours scheduled for wake up.
dnp | int Hours |
Writable. Changes the hours when a wake up must take place. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
wakeupschedule→IsOnlinewakeupschedule.IsOnline
Checks if the function is currently reachable.
dnp | bool IsOnline |
If there is a cached value for the function in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the function.
wakeupschedule→LogicalNamewakeupschedule.LogicalName
Logical name of the function.
dnp | string LogicalName |
Writable. You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
wakeupschedule→MinutesAwakeupschedule.MinutesA
Minutes in the 00-29 interval of each hour scheduled for wake up.
dnp | int MinutesA |
Writable. Changes the minutes in the 00-29 interval when a wake up must take place. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
wakeupschedule→MinutesBwakeupschedule.MinutesB
Minutes in the 30-59 interval of each hour scheduled for wake up.
dnp | int MinutesB |
Writable. Changes the minutes in the 30-59 interval when a wake up must take place. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
wakeupschedule→MonthDayswakeupschedule.MonthDays
Days of the month scheduled for wake up.
dnp | int MonthDays |
Writable. Changes the days of the month when a wake up must take place. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
wakeupschedule→Monthswakeupschedule.Months
Months scheduled for wake up.
dnp | int Months |
Writable. Changes the months when a wake up must take place. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
wakeupschedule→NextOccurencewakeupschedule.NextOccurence
Date/time (seconds) of the next wake up occurrence.
dnp | long NextOccurence |
wakeupschedule→SerialNumberwakeupschedule.SerialNumber
Serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
dnp | string SerialNumber |
wakeupschedule→WeekDayswakeupschedule.WeekDays
Days of the week scheduled for wake up.
dnp | int WeekDays |
Writable. Changes the days of the week when a wake up must take place. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
wakeupschedule→clearCache()wakeupschedule.clearCache()wakeupschedule→clearCache()[wakeupschedule clearCache]wakeupschedule.clearCache()wakeupschedule.clearCache()wakeupschedule.clearCache()wakeupschedule.clearCache()wakeupschedule.clearCache()wakeupschedule→clearCache()wakeupschedule.clearCache()wakeupschedule.clearCache()
Invalidates the cache.
js | function clearCache( | ) |
cpp | void clearCache( | ) |
m | -(void) clearCache |
pas | clearCache( | ) |
vb | procedure clearCache( | ) |
cs | void clearCache( | ) |
java | void clearCache( | ) |
py | clearCache( | ) |
php | function clearCache( | ) |
ts | async clearCache( | ): Promise<void> |
es | async clearCache( | ) |
Invalidates the cache of the wake up schedule attributes. Forces the next call to get_xxx() or loadxxx() to use values that come from the device.
wakeupschedule→describe()wakeupschedule.describe()wakeupschedule→describe()[wakeupschedule describe]wakeupschedule.describe()wakeupschedule.describe()wakeupschedule.describe()wakeupschedule.describe()wakeupschedule.describe()wakeupschedule→describe()wakeupschedule.describe()wakeupschedule.describe()
Returns a short text that describes unambiguously the instance of the wake up schedule in the form TYPE(NAME)=SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function describe( | ) |
cpp | string describe( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) describe |
pas | string describe( | ): string |
vb | function describe( | ) As String |
cs | string describe( | ) |
java | String describe( | ) |
py | describe( | ) |
php | function describe( | ) |
ts | async describe( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async describe( | ) |
More precisely, TYPE is the type of the function, NAME it the name used for the first access to the function, SERIAL is the serial number of the module if the module is connected or "unresolved", and FUNCTIONID is the hardware identifier of the function if the module is connected. For example, this method returns Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1 if the module is already connected or Relay(BadCustomeName.relay1)=unresolved if the module has not yet been connected. This method does not trigger any USB or TCP transaction and can therefore be used in a debugger.
Returns :
a string that describes the wake up schedule (ex: Relay(MyCustomName.relay1)=RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
wakeupschedule→get_advertisedValue()
wakeupschedule→advertisedValue()wakeupschedule.get_advertisedValue()wakeupschedule→get_advertisedValue()[wakeupschedule advertisedValue]wakeupschedule.get_advertisedValue()wakeupschedule.get_advertisedValue()wakeupschedule.get_advertisedValue()wakeupschedule.get_advertisedValue()wakeupschedule.get_advertisedValue()wakeupschedule.get_advertisedValue()wakeupschedule→get_advertisedValue()wakeupschedule.get_advertisedValue()wakeupschedule.get_advertisedValue()wakeupschedule.get_advertisedValue()wakeupschedule.get_advertisedValue()YWakeUpSchedule get_advertisedValue
Returns the current value of the wake up schedule (no more than 6 characters).
js | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cpp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) advertisedValue |
pas | string get_advertisedValue( | ): string |
vb | function get_advertisedValue( | ) As String |
cs | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
java | String get_advertisedValue( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_advertisedValue( | ) |
py | get_advertisedValue( | ) |
php | function get_advertisedValue( | ) |
ts | async get_advertisedValue( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_advertisedValue( | ) |
dnp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cp | string get_advertisedValue( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target get_advertisedValue |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the current value of the wake up schedule (no more than 6 characters).
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpSchedule.ADVERTISEDVALUE_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→get_errorMessage()
wakeupschedule→errorMessage()wakeupschedule.get_errorMessage()wakeupschedule→get_errorMessage()[wakeupschedule errorMessage]wakeupschedule.get_errorMessage()wakeupschedule.get_errorMessage()wakeupschedule.get_errorMessage()wakeupschedule.get_errorMessage()wakeupschedule.get_errorMessage()wakeupschedule→get_errorMessage()wakeupschedule.get_errorMessage()wakeupschedule.get_errorMessage()
Returns the error message of the latest error with the wake up schedule.
js | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
cpp | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) errorMessage |
pas | string get_errorMessage( | ): string |
vb | function get_errorMessage( | ) As String |
cs | string get_errorMessage( | ) |
java | String get_errorMessage( | ) |
py | get_errorMessage( | ) |
php | function get_errorMessage( | ) |
ts | get_errorMessage( | ): string |
es | get_errorMessage( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a string corresponding to the latest error message that occured while using the wake up schedule object
wakeupschedule→get_errorType()
wakeupschedule→errorType()wakeupschedule.get_errorType()wakeupschedule→get_errorType()[wakeupschedule errorType]wakeupschedule.get_errorType()wakeupschedule.get_errorType()wakeupschedule.get_errorType()wakeupschedule.get_errorType()wakeupschedule.get_errorType()wakeupschedule→get_errorType()wakeupschedule.get_errorType()wakeupschedule.get_errorType()
Returns the numerical error code of the latest error with the wake up schedule.
js | function get_errorType( | ) |
cpp | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
m | -(YRETCODE) errorType |
pas | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ): YRETCODE |
vb | function get_errorType( | ) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE get_errorType( | ) |
java | int get_errorType( | ) |
py | get_errorType( | ) |
php | function get_errorType( | ) |
ts | get_errorType( | ): number |
es | get_errorType( | ) |
This method is mostly useful when using the Yoctopuce library with exceptions disabled.
Returns :
a number corresponding to the code of the latest error that occurred while using the wake up schedule object
wakeupschedule→get_friendlyName()
wakeupschedule→friendlyName()wakeupschedule.get_friendlyName()wakeupschedule→get_friendlyName()[wakeupschedule friendlyName]wakeupschedule.get_friendlyName()wakeupschedule.get_friendlyName()wakeupschedule.get_friendlyName()wakeupschedule→get_friendlyName()wakeupschedule.get_friendlyName()wakeupschedule.get_friendlyName()wakeupschedule.get_friendlyName()wakeupschedule.get_friendlyName()
Returns a global identifier of the wake up schedule in the format MODULE_NAME.FUNCTION_NAME.
js | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
cpp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) friendlyName |
cs | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
java | String get_friendlyName( | ) |
py | get_friendlyName( | ) |
php | function get_friendlyName( | ) |
ts | async get_friendlyName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_friendlyName( | ) |
dnp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
cp | string get_friendlyName( | ) |
The returned string uses the logical names of the module and of the wake up schedule if they are defined, otherwise the serial number of the module and the hardware identifier of the wake up schedule (for example: MyCustomName.relay1)
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the wake up schedule using logical names (ex: MyCustomName.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpSchedule.FRIENDLYNAME_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→get_functionDescriptor()
wakeupschedule→functionDescriptor()wakeupschedule.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupschedule→get_functionDescriptor()[wakeupschedule functionDescriptor]wakeupschedule.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupschedule.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupschedule.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupschedule.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupschedule.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupschedule→get_functionDescriptor()wakeupschedule.get_functionDescriptor()wakeupschedule.get_functionDescriptor()
Returns a unique identifier of type YFUN_DESCR corresponding to the function.
js | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
cpp | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
m | -(YFUN_DESCR) functionDescriptor |
pas | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ): YFUN_DESCR |
vb | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) As YFUN_DESCR |
cs | YFUN_DESCR get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
java | String get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
py | get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
php | function get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
ts | async get_functionDescriptor( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionDescriptor( | ) |
This identifier can be used to test if two instances of YFunction reference the same physical function on the same physical device.
Returns :
an identifier of type YFUN_DESCR.
If the function has never been contacted, the returned value is Y$CLASSNAME$.FUNCTIONDESCRIPTOR_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→get_functionId()
wakeupschedule→functionId()wakeupschedule.get_functionId()wakeupschedule→get_functionId()[wakeupschedule functionId]wakeupschedule.get_functionId()wakeupschedule.get_functionId()wakeupschedule.get_functionId()wakeupschedule.get_functionId()wakeupschedule→get_functionId()wakeupschedule.get_functionId()wakeupschedule.get_functionId()wakeupschedule.get_functionId()wakeupschedule.get_functionId()
Returns the hardware identifier of the wake up schedule, without reference to the module.
js | function get_functionId( | ) |
cpp | string get_functionId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) functionId |
vb | function get_functionId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_functionId( | ) |
java | String get_functionId( | ) |
py | get_functionId( | ) |
php | function get_functionId( | ) |
ts | async get_functionId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_functionId( | ) |
dnp | string get_functionId( | ) |
cp | string get_functionId( | ) |
For example relay1
Returns :
a string that identifies the wake up schedule (ex: relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpSchedule.FUNCTIONID_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→get_hardwareId()
wakeupschedule→hardwareId()wakeupschedule.get_hardwareId()wakeupschedule→get_hardwareId()[wakeupschedule hardwareId]wakeupschedule.get_hardwareId()wakeupschedule.get_hardwareId()wakeupschedule.get_hardwareId()wakeupschedule.get_hardwareId()wakeupschedule→get_hardwareId()wakeupschedule.get_hardwareId()wakeupschedule.get_hardwareId()wakeupschedule.get_hardwareId()wakeupschedule.get_hardwareId()
Returns the unique hardware identifier of the wake up schedule in the form SERIAL.FUNCTIONID.
js | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
cpp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) hardwareId |
vb | function get_hardwareId( | ) As String |
cs | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
java | String get_hardwareId( | ) |
py | get_hardwareId( | ) |
php | function get_hardwareId( | ) |
ts | async get_hardwareId( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_hardwareId( | ) |
dnp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
cp | string get_hardwareId( | ) |
The unique hardware identifier is composed of the device serial number and of the hardware identifier of the wake up schedule (for example RELAYLO1-123456.relay1).
Returns :
a string that uniquely identifies the wake up schedule (ex: RELAYLO1-123456.relay1)
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpSchedule.HARDWAREID_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→get_hours()
wakeupschedule→hours()wakeupschedule.get_hours()wakeupschedule→get_hours()[wakeupschedule hours]wakeupschedule.get_hours()wakeupschedule.get_hours()wakeupschedule.get_hours()wakeupschedule.get_hours()wakeupschedule.get_hours()wakeupschedule.get_hours()wakeupschedule→get_hours()wakeupschedule.get_hours()wakeupschedule.get_hours()wakeupschedule.get_hours()wakeupschedule.get_hours()YWakeUpSchedule get_hours
Returns the hours scheduled for wake up.
js | function get_hours( | ) |
cpp | int get_hours( | ) |
m | -(int) hours |
pas | LongInt get_hours( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_hours( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_hours( | ) |
java | int get_hours( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_hours( | ) |
py | get_hours( | ) |
php | function get_hours( | ) |
ts | async get_hours( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_hours( | ) |
dnp | int get_hours( | ) |
cp | int get_hours( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target get_hours |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the hours scheduled for wake up
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpSchedule.HOURS_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→get_logicalName()
wakeupschedule→logicalName()wakeupschedule.get_logicalName()wakeupschedule→get_logicalName()[wakeupschedule logicalName]wakeupschedule.get_logicalName()wakeupschedule.get_logicalName()wakeupschedule.get_logicalName()wakeupschedule.get_logicalName()wakeupschedule.get_logicalName()wakeupschedule.get_logicalName()wakeupschedule→get_logicalName()wakeupschedule.get_logicalName()wakeupschedule.get_logicalName()wakeupschedule.get_logicalName()wakeupschedule.get_logicalName()YWakeUpSchedule get_logicalName
Returns the logical name of the wake up schedule.
js | function get_logicalName( | ) |
cpp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) logicalName |
pas | string get_logicalName( | ): string |
vb | function get_logicalName( | ) As String |
cs | string get_logicalName( | ) |
java | String get_logicalName( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_logicalName( | ) |
py | get_logicalName( | ) |
php | function get_logicalName( | ) |
ts | async get_logicalName( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_logicalName( | ) |
dnp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cp | string get_logicalName( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target get_logicalName |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the logical name of the wake up schedule.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpSchedule.LOGICALNAME_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→get_minutes()
wakeupschedule→minutes()wakeupschedule.get_minutes()wakeupschedule→get_minutes()[wakeupschedule minutes]wakeupschedule.get_minutes()wakeupschedule.get_minutes()wakeupschedule.get_minutes()wakeupschedule.get_minutes()wakeupschedule.get_minutes()wakeupschedule.get_minutes()wakeupschedule→get_minutes()wakeupschedule.get_minutes()wakeupschedule.get_minutes()wakeupschedule.get_minutes()wakeupschedule.get_minutes()YWakeUpSchedule get_minutes
Returns all the minutes of each hour that are scheduled for wake up.
js | function get_minutes( | ) |
cpp | s64 get_minutes( | ) |
m | -(s64) minutes |
pas | int64 get_minutes( | ): int64 |
vb | function get_minutes( | ) As Long |
cs | long get_minutes( | ) |
java | long get_minutes( | ) |
uwp | async Task<long> get_minutes( | ) |
py | get_minutes( | ) |
php | function get_minutes( | ) |
ts | async get_minutes( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_minutes( | ) |
dnp | long get_minutes( | ) |
cp | s64 get_minutes( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target get_minutes |
wakeupschedule→get_minutesA()
wakeupschedule→minutesA()wakeupschedule.get_minutesA()wakeupschedule→get_minutesA()[wakeupschedule minutesA]wakeupschedule.get_minutesA()wakeupschedule.get_minutesA()wakeupschedule.get_minutesA()wakeupschedule.get_minutesA()wakeupschedule.get_minutesA()wakeupschedule.get_minutesA()wakeupschedule→get_minutesA()wakeupschedule.get_minutesA()wakeupschedule.get_minutesA()wakeupschedule.get_minutesA()wakeupschedule.get_minutesA()YWakeUpSchedule get_minutesA
Returns the minutes in the 00-29 interval of each hour scheduled for wake up.
js | function get_minutesA( | ) |
cpp | int get_minutesA( | ) |
m | -(int) minutesA |
pas | LongInt get_minutesA( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_minutesA( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_minutesA( | ) |
java | int get_minutesA( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_minutesA( | ) |
py | get_minutesA( | ) |
php | function get_minutesA( | ) |
ts | async get_minutesA( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_minutesA( | ) |
dnp | int get_minutesA( | ) |
cp | int get_minutesA( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target get_minutesA |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the minutes in the 00-29 interval of each hour scheduled for wake up
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpSchedule.MINUTESA_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→get_minutesB()
wakeupschedule→minutesB()wakeupschedule.get_minutesB()wakeupschedule→get_minutesB()[wakeupschedule minutesB]wakeupschedule.get_minutesB()wakeupschedule.get_minutesB()wakeupschedule.get_minutesB()wakeupschedule.get_minutesB()wakeupschedule.get_minutesB()wakeupschedule.get_minutesB()wakeupschedule→get_minutesB()wakeupschedule.get_minutesB()wakeupschedule.get_minutesB()wakeupschedule.get_minutesB()wakeupschedule.get_minutesB()YWakeUpSchedule get_minutesB
Returns the minutes in the 30-59 interval of each hour scheduled for wake up.
js | function get_minutesB( | ) |
cpp | int get_minutesB( | ) |
m | -(int) minutesB |
pas | LongInt get_minutesB( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_minutesB( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_minutesB( | ) |
java | int get_minutesB( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_minutesB( | ) |
py | get_minutesB( | ) |
php | function get_minutesB( | ) |
ts | async get_minutesB( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_minutesB( | ) |
dnp | int get_minutesB( | ) |
cp | int get_minutesB( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target get_minutesB |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the minutes in the 30-59 interval of each hour scheduled for wake up
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpSchedule.MINUTESB_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→get_module()
wakeupschedule→module()wakeupschedule.get_module()wakeupschedule→get_module()[wakeupschedule module]wakeupschedule.get_module()wakeupschedule.get_module()wakeupschedule.get_module()wakeupschedule.get_module()wakeupschedule.get_module()wakeupschedule→get_module()wakeupschedule.get_module()wakeupschedule.get_module()wakeupschedule.get_module()wakeupschedule.get_module()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located.
js | function get_module( | ) |
cpp | YModule * get_module( | ) |
m | -(YModule*) module |
pas | TYModule get_module( | ): TYModule |
vb | function get_module( | ) As YModule |
cs | YModule get_module( | ) |
java | YModule get_module( | ) |
py | get_module( | ) |
php | function get_module( | ) |
ts | async get_module( | ): Promise<YModule> |
es | async get_module( | ) |
dnp | YModuleProxy get_module( | ) |
cp | YModuleProxy * get_module( | ) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned instance of YModule is not shown as on-line.
Returns :
an instance of YModule
wakeupschedule→get_module_async()
wakeupschedule→module_async()wakeupschedule.get_module_async()
Gets the YModule object for the device on which the function is located (asynchronous version).
js | function get_module_async( | callback, context) |
If the function cannot be located on any module, the returned YModule object does not show as on-line.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking Firefox JavaScript VM that does not implement context switching during blocking I/O calls. See the documentation section on asynchronous JavasSript calls for more details.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the requested YModule object |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
wakeupschedule→get_monthDays()
wakeupschedule→monthDays()wakeupschedule.get_monthDays()wakeupschedule→get_monthDays()[wakeupschedule monthDays]wakeupschedule.get_monthDays()wakeupschedule.get_monthDays()wakeupschedule.get_monthDays()wakeupschedule.get_monthDays()wakeupschedule.get_monthDays()wakeupschedule.get_monthDays()wakeupschedule→get_monthDays()wakeupschedule.get_monthDays()wakeupschedule.get_monthDays()wakeupschedule.get_monthDays()wakeupschedule.get_monthDays()YWakeUpSchedule get_monthDays
Returns the days of the month scheduled for wake up.
js | function get_monthDays( | ) |
cpp | int get_monthDays( | ) |
m | -(int) monthDays |
pas | LongInt get_monthDays( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_monthDays( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_monthDays( | ) |
java | int get_monthDays( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_monthDays( | ) |
py | get_monthDays( | ) |
php | function get_monthDays( | ) |
ts | async get_monthDays( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_monthDays( | ) |
dnp | int get_monthDays( | ) |
cp | int get_monthDays( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target get_monthDays |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the days of the month scheduled for wake up
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpSchedule.MONTHDAYS_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→get_months()
wakeupschedule→months()wakeupschedule.get_months()wakeupschedule→get_months()[wakeupschedule months]wakeupschedule.get_months()wakeupschedule.get_months()wakeupschedule.get_months()wakeupschedule.get_months()wakeupschedule.get_months()wakeupschedule.get_months()wakeupschedule→get_months()wakeupschedule.get_months()wakeupschedule.get_months()wakeupschedule.get_months()wakeupschedule.get_months()YWakeUpSchedule get_months
Returns the months scheduled for wake up.
js | function get_months( | ) |
cpp | int get_months( | ) |
m | -(int) months |
pas | LongInt get_months( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_months( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_months( | ) |
java | int get_months( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_months( | ) |
py | get_months( | ) |
php | function get_months( | ) |
ts | async get_months( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_months( | ) |
dnp | int get_months( | ) |
cp | int get_months( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target get_months |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the months scheduled for wake up
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpSchedule.MONTHS_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→get_nextOccurence()
wakeupschedule→nextOccurence()wakeupschedule.get_nextOccurence()wakeupschedule→get_nextOccurence()[wakeupschedule nextOccurence]wakeupschedule.get_nextOccurence()wakeupschedule.get_nextOccurence()wakeupschedule.get_nextOccurence()wakeupschedule.get_nextOccurence()wakeupschedule.get_nextOccurence()wakeupschedule.get_nextOccurence()wakeupschedule→get_nextOccurence()wakeupschedule.get_nextOccurence()wakeupschedule.get_nextOccurence()wakeupschedule.get_nextOccurence()wakeupschedule.get_nextOccurence()YWakeUpSchedule get_nextOccurence
Returns the date/time (seconds) of the next wake up occurrence.
js | function get_nextOccurence( | ) |
cpp | s64 get_nextOccurence( | ) |
m | -(s64) nextOccurence |
pas | int64 get_nextOccurence( | ): int64 |
vb | function get_nextOccurence( | ) As Long |
cs | long get_nextOccurence( | ) |
java | long get_nextOccurence( | ) |
uwp | async Task<long> get_nextOccurence( | ) |
py | get_nextOccurence( | ) |
php | function get_nextOccurence( | ) |
ts | async get_nextOccurence( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_nextOccurence( | ) |
dnp | long get_nextOccurence( | ) |
cp | s64 get_nextOccurence( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target get_nextOccurence |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the date/time (seconds) of the next wake up occurrence
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpSchedule.NEXTOCCURENCE_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→get_serialNumber()
wakeupschedule→serialNumber()wakeupschedule.get_serialNumber()wakeupschedule→get_serialNumber()[wakeupschedule serialNumber]wakeupschedule.get_serialNumber()wakeupschedule.get_serialNumber()wakeupschedule.get_serialNumber()wakeupschedule.get_serialNumber()wakeupschedule.get_serialNumber()wakeupschedule.get_serialNumber()wakeupschedule→get_serialNumber()wakeupschedule.get_serialNumber()wakeupschedule.get_serialNumber()wakeupschedule.get_serialNumber()wakeupschedule.get_serialNumber()YWakeUpSchedule get_serialNumber
Returns the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
js | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
cpp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
m | -(NSString*) serialNumber |
pas | string get_serialNumber( | ): string |
vb | function get_serialNumber( | ) As String |
cs | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
java | String get_serialNumber( | ) |
uwp | async Task<string> get_serialNumber( | ) |
py | get_serialNumber( | ) |
php | function get_serialNumber( | ) |
ts | async get_serialNumber( | ): Promise<string> |
es | async get_serialNumber( | ) |
dnp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cp | string get_serialNumber( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target get_serialNumber |
Returns :
a string corresponding to the serial number of the module, as set by the factory.
On failure, throws an exception or returns YFunction.SERIALNUMBER_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→get_userData()
wakeupschedule→userData()wakeupschedule.get_userData()wakeupschedule→get_userData()[wakeupschedule userData]wakeupschedule.get_userData()wakeupschedule.get_userData()wakeupschedule.get_userData()wakeupschedule.get_userData()wakeupschedule.get_userData()wakeupschedule→get_userData()wakeupschedule.get_userData()wakeupschedule.get_userData()
Returns the value of the userData attribute, as previously stored using method set_userData.
js | function get_userData( | ) |
cpp | void * get_userData( | ) |
m | -(id) userData |
pas | Tobject get_userData( | ): Tobject |
vb | function get_userData( | ) As Object |
cs | object get_userData( | ) |
java | Object get_userData( | ) |
py | get_userData( | ) |
php | function get_userData( | ) |
ts | async get_userData( | ): Promise<object|null> |
es | async get_userData( | ) |
This attribute is never touched directly by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Returns :
the object stored previously by the caller.
wakeupschedule→get_weekDays()
wakeupschedule→weekDays()wakeupschedule.get_weekDays()wakeupschedule→get_weekDays()[wakeupschedule weekDays]wakeupschedule.get_weekDays()wakeupschedule.get_weekDays()wakeupschedule.get_weekDays()wakeupschedule.get_weekDays()wakeupschedule.get_weekDays()wakeupschedule.get_weekDays()wakeupschedule→get_weekDays()wakeupschedule.get_weekDays()wakeupschedule.get_weekDays()wakeupschedule.get_weekDays()wakeupschedule.get_weekDays()YWakeUpSchedule get_weekDays
Returns the days of the week scheduled for wake up.
js | function get_weekDays( | ) |
cpp | int get_weekDays( | ) |
m | -(int) weekDays |
pas | LongInt get_weekDays( | ): LongInt |
vb | function get_weekDays( | ) As Integer |
cs | int get_weekDays( | ) |
java | int get_weekDays( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> get_weekDays( | ) |
py | get_weekDays( | ) |
php | function get_weekDays( | ) |
ts | async get_weekDays( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async get_weekDays( | ) |
dnp | int get_weekDays( | ) |
cp | int get_weekDays( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target get_weekDays |
Returns :
an integer corresponding to the days of the week scheduled for wake up
On failure, throws an exception or returns YWakeUpSchedule.WEEKDAYS_INVALID.
wakeupschedule→isOnline()wakeupschedule.isOnline()wakeupschedule→isOnline()[wakeupschedule isOnline]wakeupschedule.isOnline()wakeupschedule.isOnline()wakeupschedule.isOnline()wakeupschedule.isOnline()wakeupschedule.isOnline()wakeupschedule→isOnline()wakeupschedule.isOnline()wakeupschedule.isOnline()wakeupschedule.isOnline()wakeupschedule.isOnline()
Checks if the wake up schedule is currently reachable, without raising any error.
js | function isOnline( | ) |
cpp | bool isOnline( | ) |
m | -(BOOL) isOnline |
pas | boolean isOnline( | ): boolean |
vb | function isOnline( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isOnline( | ) |
java | boolean isOnline( | ) |
py | isOnline( | ) |
php | function isOnline( | ) |
ts | async isOnline( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isOnline( | ) |
dnp | bool isOnline( | ) |
cp | bool isOnline( | ) |
If there is a cached value for the wake up schedule in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the wake up schedule.
Returns :
true if the wake up schedule can be reached, and false otherwise
wakeupschedule→isOnline_async()wakeupschedule.isOnline_async()
Checks if the wake up schedule is currently reachable, without raising any error (asynchronous version).
js | function isOnline_async( | callback, context) |
If there is a cached value for the wake up schedule in cache, that has not yet expired, the device is considered reachable. No exception is raised if there is an error while trying to contact the device hosting the requested function.
This asynchronous version exists only in Javascript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the Javascript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the boolean result |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
wakeupschedule→isReadOnly()wakeupschedule→isReadOnly()[wakeupschedule isReadOnly]wakeupschedule.isReadOnly()wakeupschedule.isReadOnly()wakeupschedule.isReadOnly()wakeupschedule.isReadOnly()wakeupschedule.isReadOnly()wakeupschedule.isReadOnly()wakeupschedule→isReadOnly()wakeupschedule.isReadOnly()wakeupschedule.isReadOnly()wakeupschedule.isReadOnly()wakeupschedule.isReadOnly()YWakeUpSchedule isReadOnly
Test if the function is readOnly.
cpp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
m | -(bool) isReadOnly |
pas | boolean isReadOnly( | ): boolean |
vb | function isReadOnly( | ) As Boolean |
cs | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
java | boolean isReadOnly( | ) |
uwp | async Task<bool> isReadOnly( | ) |
py | isReadOnly( | ) |
php | function isReadOnly( | ) |
ts | async isReadOnly( | ): Promise<boolean> |
es | async isReadOnly( | ) |
dnp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cp | bool isReadOnly( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target isReadOnly |
Return true if the function is write protected or that the function is not available.
Returns :
true if the function is readOnly or not online.
wakeupschedule→load()wakeupschedule.load()wakeupschedule→load()[wakeupschedule load: ]wakeupschedule.load()wakeupschedule.load()wakeupschedule.load()wakeupschedule.load()wakeupschedule.load()wakeupschedule→load()wakeupschedule.load()wakeupschedule.load()
Preloads the wake up schedule cache with a specified validity duration.
js | function load( | msValidity) |
cpp | YRETCODE load( | int msValidity) |
m | -(YRETCODE) load | : (u64) msValidity |
pas | YRETCODE load( | msValidity: u64): YRETCODE |
vb | function load( | ByVal msValidity As Long) As YRETCODE |
cs | YRETCODE load( | ulong msValidity) |
java | int load( | long msValidity) |
py | load( | msValidity) |
php | function load( | $msValidity) |
ts | async load( | msValidity: number): Promise<number> |
es | async load( | msValidity) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity attributed to the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupschedule→loadAttribute()wakeupschedule.loadAttribute()wakeupschedule→loadAttribute()[wakeupschedule loadAttribute: ]wakeupschedule.loadAttribute()wakeupschedule.loadAttribute()wakeupschedule.loadAttribute()wakeupschedule.loadAttribute()wakeupschedule.loadAttribute()wakeupschedule.loadAttribute()wakeupschedule→loadAttribute()wakeupschedule.loadAttribute()wakeupschedule.loadAttribute()wakeupschedule.loadAttribute()wakeupschedule.loadAttribute()
Returns the current value of a single function attribute, as a text string, as quickly as possible but without using the cached value.
js | function loadAttribute( | attrName) |
cpp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
m | -(NSString*) loadAttribute | : (NSString*) attrName |
pas | string loadAttribute( | attrName: string): string |
vb | function loadAttribute( | ByVal attrName As String) As String |
cs | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
java | String loadAttribute( | String attrName) |
uwp | async Task<string> loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
py | loadAttribute( | attrName) |
php | function loadAttribute( | $attrName) |
ts | async loadAttribute( | attrName: string): Promise<string> |
es | async loadAttribute( | attrName) |
dnp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
cp | string loadAttribute( | string attrName) |
Parameters :
| attrName | the name of the requested attribute |
Returns :
a string with the value of the the attribute
On failure, throws an exception or returns an empty string.
wakeupschedule→load_async()wakeupschedule.load_async()
Preloads the wake up schedule cache with a specified validity duration (asynchronous version).
js | function load_async( | msValidity, callback, context) |
By default, whenever accessing a device, all function attributes are kept in cache for the standard duration (5 ms). This method can be used to temporarily mark the cache as valid for a longer period, in order to reduce network traffic for instance.
This asynchronous version exists only in JavaScript. It uses a callback instead of a return value in order to avoid blocking the JavaScript virtual machine.
Parameters :
| msValidity | an integer corresponding to the validity of the loaded function parameters, in milliseconds |
| callback | callback function that is invoked when the result is known. The callback function receives three arguments: the caller-specific context object, the receiving function object and the error code (or YAPI.SUCCESS) |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing : the result is provided to the callback.
wakeupschedule→muteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule→muteValueCallbacks()[wakeupschedule muteValueCallbacks]wakeupschedule.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule→muteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.muteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.muteValueCallbacks()YWakeUpSchedule muteValueCallbacks
Disables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) muteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt muteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async muteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int muteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target muteValueCallbacks |
You can use this function to save bandwidth and CPU on computers with limited resources, or to prevent unwanted invocations of the HTTP callback. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupschedule→nextWakeUpSchedule()wakeupschedule.nextWakeUpSchedule()wakeupschedule→nextWakeUpSchedule()[wakeupschedule nextWakeUpSchedule]wakeupschedule.nextWakeUpSchedule()wakeupschedule.nextWakeUpSchedule()wakeupschedule.nextWakeUpSchedule()wakeupschedule.nextWakeUpSchedule()wakeupschedule.nextWakeUpSchedule()wakeupschedule.nextWakeUpSchedule()wakeupschedule→nextWakeUpSchedule()wakeupschedule.nextWakeUpSchedule()wakeupschedule.nextWakeUpSchedule()
Continues the enumeration of wake up schedules started using yFirstWakeUpSchedule().
js | function nextWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
cpp | YWakeUpSchedule * nextWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
m | -(nullable YWakeUpSchedule*) nextWakeUpSchedule |
pas | TYWakeUpSchedule nextWakeUpSchedule( | ): TYWakeUpSchedule |
vb | function nextWakeUpSchedule( | ) As YWakeUpSchedule |
cs | YWakeUpSchedule nextWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
java | YWakeUpSchedule nextWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
uwp | YWakeUpSchedule nextWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
py | nextWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
php | function nextWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
ts | nextWakeUpSchedule( | ): YWakeUpSchedule | null |
es | nextWakeUpSchedule( | ) |
Caution: You can't make any assumption about the returned wake up schedules order. If you want to find a specific a wake up schedule, use WakeUpSchedule.findWakeUpSchedule() and a hardwareID or a logical name.
Returns :
a pointer to a YWakeUpSchedule object, corresponding to a wake up schedule currently online, or a null pointer if there are no more wake up schedules to enumerate.
wakeupschedule→registerValueCallback()wakeupschedule.registerValueCallback()wakeupschedule→registerValueCallback()[wakeupschedule registerValueCallback: ]wakeupschedule.registerValueCallback()wakeupschedule.registerValueCallback()wakeupschedule.registerValueCallback()wakeupschedule.registerValueCallback()wakeupschedule.registerValueCallback()wakeupschedule.registerValueCallback()wakeupschedule→registerValueCallback()wakeupschedule.registerValueCallback()wakeupschedule.registerValueCallback()
Registers the callback function that is invoked on every change of advertised value.
js | function registerValueCallback( | callback) |
cpp | int registerValueCallback( | YWakeUpScheduleValueCallback callback) |
m | -(int) registerValueCallback | : (YWakeUpScheduleValueCallback _Nullable) callback |
pas | LongInt registerValueCallback( | callback: TYWakeUpScheduleValueCallback): LongInt |
vb | function registerValueCallback( | ByVal callback As YWakeUpScheduleValueCallback) As Integer |
cs | int registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
java | int registerValueCallback( | UpdateCallback callback) |
uwp | async Task<int> registerValueCallback( | ValueCallback callback) |
py | registerValueCallback( | callback) |
php | function registerValueCallback( | $callback) |
ts | async registerValueCallback( | callback: YWakeUpScheduleValueCallback | null): Promise<number> |
es | async registerValueCallback( | callback) |
The callback is invoked only during the execution of ySleep or yHandleEvents. This provides control over the time when the callback is triggered. For good responsiveness, remember to call one of these two functions periodically. To unregister a callback, pass a null pointer as argument.
Parameters :
| callback | the callback function to call, or a null pointer. The callback function should take two arguments: the function object of which the value has changed, and the character string describing the new advertised value. |
wakeupschedule→set_hours()
wakeupschedule→setHours()wakeupschedule.set_hours()wakeupschedule→set_hours()[wakeupschedule setHours: ]wakeupschedule.set_hours()wakeupschedule.set_hours()wakeupschedule.set_hours()wakeupschedule.set_hours()wakeupschedule.set_hours()wakeupschedule.set_hours()wakeupschedule→set_hours()wakeupschedule.set_hours()wakeupschedule.set_hours()wakeupschedule.set_hours()wakeupschedule.set_hours()YWakeUpSchedule set_hours
Changes the hours when a wake up must take place.
js | function set_hours( | newval) |
cpp | int set_hours( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setHours | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_hours( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_hours( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_hours( | int newval) |
java | int set_hours( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_hours( | int newval) |
py | set_hours( | newval) |
php | function set_hours( | $newval) |
ts | async set_hours( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_hours( | newval) |
dnp | int set_hours( | int newval) |
cp | int set_hours( | int newval) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target set_hours | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the hours when a wake up must take place |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupschedule→set_logicalName()
wakeupschedule→setLogicalName()wakeupschedule.set_logicalName()wakeupschedule→set_logicalName()[wakeupschedule setLogicalName: ]wakeupschedule.set_logicalName()wakeupschedule.set_logicalName()wakeupschedule.set_logicalName()wakeupschedule.set_logicalName()wakeupschedule.set_logicalName()wakeupschedule.set_logicalName()wakeupschedule→set_logicalName()wakeupschedule.set_logicalName()wakeupschedule.set_logicalName()wakeupschedule.set_logicalName()wakeupschedule.set_logicalName()YWakeUpSchedule set_logicalName
Changes the logical name of the wake up schedule.
js | function set_logicalName( | newval) |
cpp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
m | -(int) setLogicalName | : (NSString*) newval |
pas | integer set_logicalName( | newval: string): integer |
vb | function set_logicalName( | ByVal newval As String) As Integer |
cs | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
java | int set_logicalName( | String newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_logicalName( | string newval) |
py | set_logicalName( | newval) |
php | function set_logicalName( | $newval) |
ts | async set_logicalName( | newval: string): Promise<number> |
es | async set_logicalName( | newval) |
dnp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cp | int set_logicalName( | string newval) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target set_logicalName | newval |
You can use yCheckLogicalName() prior to this call to make sure that your parameter is valid. Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | a string corresponding to the logical name of the wake up schedule. |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupschedule→set_minutes()
wakeupschedule→setMinutes()wakeupschedule.set_minutes()wakeupschedule→set_minutes()[wakeupschedule setMinutes: ]wakeupschedule.set_minutes()wakeupschedule.set_minutes()wakeupschedule.set_minutes()wakeupschedule.set_minutes()wakeupschedule.set_minutes()wakeupschedule.set_minutes()wakeupschedule→set_minutes()wakeupschedule.set_minutes()wakeupschedule.set_minutes()wakeupschedule.set_minutes()wakeupschedule.set_minutes()YWakeUpSchedule set_minutes
Changes all the minutes where a wake up must take place.
js | function set_minutes( | bitmap) |
cpp | int set_minutes( | s64 bitmap) |
m | -(int) setMinutes | : (s64) bitmap |
pas | LongInt set_minutes( | bitmap: int64): LongInt |
vb | function set_minutes( | ByVal bitmap As Long) As Integer |
cs | int set_minutes( | long bitmap) |
java | int set_minutes( | long bitmap) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_minutes( | long bitmap) |
py | set_minutes( | bitmap) |
php | function set_minutes( | $bitmap) |
ts | async set_minutes( | bitmap: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_minutes( | bitmap) |
dnp | int set_minutes( | long bitmap) |
cp | int set_minutes( | s64 bitmap) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target set_minutes | bitmap |
Parameters :
| bitmap | Minutes 00-59 of each hour scheduled for wake up. |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupschedule→set_minutesA()
wakeupschedule→setMinutesA()wakeupschedule.set_minutesA()wakeupschedule→set_minutesA()[wakeupschedule setMinutesA: ]wakeupschedule.set_minutesA()wakeupschedule.set_minutesA()wakeupschedule.set_minutesA()wakeupschedule.set_minutesA()wakeupschedule.set_minutesA()wakeupschedule.set_minutesA()wakeupschedule→set_minutesA()wakeupschedule.set_minutesA()wakeupschedule.set_minutesA()wakeupschedule.set_minutesA()wakeupschedule.set_minutesA()YWakeUpSchedule set_minutesA
Changes the minutes in the 00-29 interval when a wake up must take place.
js | function set_minutesA( | newval) |
cpp | int set_minutesA( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setMinutesA | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_minutesA( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_minutesA( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_minutesA( | int newval) |
java | int set_minutesA( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_minutesA( | int newval) |
py | set_minutesA( | newval) |
php | function set_minutesA( | $newval) |
ts | async set_minutesA( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_minutesA( | newval) |
dnp | int set_minutesA( | int newval) |
cp | int set_minutesA( | int newval) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target set_minutesA | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the minutes in the 00-29 interval when a wake up must take place |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupschedule→set_minutesB()
wakeupschedule→setMinutesB()wakeupschedule.set_minutesB()wakeupschedule→set_minutesB()[wakeupschedule setMinutesB: ]wakeupschedule.set_minutesB()wakeupschedule.set_minutesB()wakeupschedule.set_minutesB()wakeupschedule.set_minutesB()wakeupschedule.set_minutesB()wakeupschedule.set_minutesB()wakeupschedule→set_minutesB()wakeupschedule.set_minutesB()wakeupschedule.set_minutesB()wakeupschedule.set_minutesB()wakeupschedule.set_minutesB()YWakeUpSchedule set_minutesB
Changes the minutes in the 30-59 interval when a wake up must take place.
js | function set_minutesB( | newval) |
cpp | int set_minutesB( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setMinutesB | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_minutesB( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_minutesB( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_minutesB( | int newval) |
java | int set_minutesB( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_minutesB( | int newval) |
py | set_minutesB( | newval) |
php | function set_minutesB( | $newval) |
ts | async set_minutesB( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_minutesB( | newval) |
dnp | int set_minutesB( | int newval) |
cp | int set_minutesB( | int newval) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target set_minutesB | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the minutes in the 30-59 interval when a wake up must take place |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupschedule→set_monthDays()
wakeupschedule→setMonthDays()wakeupschedule.set_monthDays()wakeupschedule→set_monthDays()[wakeupschedule setMonthDays: ]wakeupschedule.set_monthDays()wakeupschedule.set_monthDays()wakeupschedule.set_monthDays()wakeupschedule.set_monthDays()wakeupschedule.set_monthDays()wakeupschedule.set_monthDays()wakeupschedule→set_monthDays()wakeupschedule.set_monthDays()wakeupschedule.set_monthDays()wakeupschedule.set_monthDays()wakeupschedule.set_monthDays()YWakeUpSchedule set_monthDays
Changes the days of the month when a wake up must take place.
js | function set_monthDays( | newval) |
cpp | int set_monthDays( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setMonthDays | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_monthDays( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_monthDays( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_monthDays( | int newval) |
java | int set_monthDays( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_monthDays( | int newval) |
py | set_monthDays( | newval) |
php | function set_monthDays( | $newval) |
ts | async set_monthDays( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_monthDays( | newval) |
dnp | int set_monthDays( | int newval) |
cp | int set_monthDays( | int newval) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target set_monthDays | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the days of the month when a wake up must take place |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupschedule→set_months()
wakeupschedule→setMonths()wakeupschedule.set_months()wakeupschedule→set_months()[wakeupschedule setMonths: ]wakeupschedule.set_months()wakeupschedule.set_months()wakeupschedule.set_months()wakeupschedule.set_months()wakeupschedule.set_months()wakeupschedule.set_months()wakeupschedule→set_months()wakeupschedule.set_months()wakeupschedule.set_months()wakeupschedule.set_months()wakeupschedule.set_months()YWakeUpSchedule set_months
Changes the months when a wake up must take place.
js | function set_months( | newval) |
cpp | int set_months( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setMonths | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_months( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_months( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_months( | int newval) |
java | int set_months( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_months( | int newval) |
py | set_months( | newval) |
php | function set_months( | $newval) |
ts | async set_months( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_months( | newval) |
dnp | int set_months( | int newval) |
cp | int set_months( | int newval) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target set_months | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the months when a wake up must take place |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupschedule→set_userData()
wakeupschedule→setUserData()wakeupschedule.set_userData()wakeupschedule→set_userData()[wakeupschedule setUserData: ]wakeupschedule.set_userData()wakeupschedule.set_userData()wakeupschedule.set_userData()wakeupschedule.set_userData()wakeupschedule.set_userData()wakeupschedule→set_userData()wakeupschedule.set_userData()wakeupschedule.set_userData()
Stores a user context provided as argument in the userData attribute of the function.
js | function set_userData( | data) |
cpp | void set_userData( | void * data) |
m | -(void) setUserData | : (id) data |
pas | set_userData( | data: Tobject) |
vb | procedure set_userData( | ByVal data As Object) |
cs | void set_userData( | object data) |
java | void set_userData( | Object data) |
py | set_userData( | data) |
php | function set_userData( | $data) |
ts | async set_userData( | data: object|null): Promise<void> |
es | async set_userData( | data) |
This attribute is never touched by the API, and is at disposal of the caller to store a context.
Parameters :
| data | any kind of object to be stored |
wakeupschedule→set_weekDays()
wakeupschedule→setWeekDays()wakeupschedule.set_weekDays()wakeupschedule→set_weekDays()[wakeupschedule setWeekDays: ]wakeupschedule.set_weekDays()wakeupschedule.set_weekDays()wakeupschedule.set_weekDays()wakeupschedule.set_weekDays()wakeupschedule.set_weekDays()wakeupschedule.set_weekDays()wakeupschedule→set_weekDays()wakeupschedule.set_weekDays()wakeupschedule.set_weekDays()wakeupschedule.set_weekDays()wakeupschedule.set_weekDays()YWakeUpSchedule set_weekDays
Changes the days of the week when a wake up must take place.
js | function set_weekDays( | newval) |
cpp | int set_weekDays( | int newval) |
m | -(int) setWeekDays | : (int) newval |
pas | integer set_weekDays( | newval: LongInt): integer |
vb | function set_weekDays( | ByVal newval As Integer) As Integer |
cs | int set_weekDays( | int newval) |
java | int set_weekDays( | int newval) |
uwp | async Task<int> set_weekDays( | int newval) |
py | set_weekDays( | newval) |
php | function set_weekDays( | $newval) |
ts | async set_weekDays( | newval: number): Promise<number> |
es | async set_weekDays( | newval) |
dnp | int set_weekDays( | int newval) |
cp | int set_weekDays( | int newval) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target set_weekDays | newval |
Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Parameters :
| newval | an integer corresponding to the days of the week when a wake up must take place |
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS if the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupschedule→unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule→unmuteValueCallbacks()[wakeupschedule unmuteValueCallbacks]wakeupschedule.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule→unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.unmuteValueCallbacks()wakeupschedule.unmuteValueCallbacks()YWakeUpSchedule unmuteValueCallbacks
Re-enables the propagation of every new advertised value to the parent hub.
js | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cpp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
m | -(int) unmuteValueCallbacks |
pas | LongInt unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): LongInt |
vb | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) As Integer |
cs | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
java | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
uwp | async Task<int> unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
py | unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
php | function unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
ts | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ): Promise<number> |
es | async unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
dnp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cp | int unmuteValueCallbacks( | ) |
cmd | YWakeUpSchedule target unmuteValueCallbacks |
This function reverts the effect of a previous call to muteValueCallbacks(). Remember to call the saveToFlash() method of the module if the modification must be kept.
Returns :
YAPI.SUCCESS when the call succeeds.
On failure, throws an exception or returns a negative error code.
wakeupschedule→wait_async()wakeupschedule.wait_async()wakeupschedule.wait_async()wakeupschedule.wait_async()
Waits for all pending asynchronous commands on the module to complete, and invoke the user-provided callback function.
js | function wait_async( | callback, context) |
ts | wait_async( | callback: Function, context: object) |
es | wait_async( | callback, context) |
The callback function can therefore freely issue synchronous or asynchronous commands, without risking to block the JavaScript VM.
Parameters :
| callback | callback function that is invoked when all pending commands on the module are completed. The callback function receives two arguments: the caller-specific context object and the receiving function object. |
| context | caller-specific object that is passed as-is to the callback function |
Returns :
nothing.
12. Troubleshooting
12.1. Where to start?
If it is the first time that you use a Yoctopuce module and you do not really know where to start, have a look at the Yoctopuce blog. There is a section dedicated to beginners 22.
12.2. Programming examples don't seem to work
Most of Yoctopuce API programming examples are command line programs and require some parameters to work properly. You have to start them from your operating system command prompt, or configure your IDE to run them with the proper parameters. 23.
12.3. Linux and USB
To work correctly under Linux, the the library needs to have write access to all the Yoctopuce USB peripherals. However, by default under Linux, USB privileges of the non-root users are limited to read access. To avoid having to run the VirtualHub as root, you need to create a new udev rule to authorize one or several users to have write access to the Yoctopuce peripherals.
To add a new udev rule to your installation, you must add a file with a name following the "##-arbitraryName.rules" format, in the "/etc/udev/rules.d" directory. When the system is starting, udev reads all the files with a ".rules" extension in this directory, respecting the alphabetical order (for example, the "51-custom.rules" file is interpreted AFTER the "50-udev-default.rules" file).
The "50-udev-default" file contains the system default udev rules. To modify the default behavior, you therefore need to create a file with a name that starts with a number larger than 50, that will override the system default rules. Note that to add a rule, you need a root access on the system.
In the udev_conf directory of the VirtualHub for Linux24 archive, there are two rule examples which you can use as a basis.
Example 1: 51-yoctopuce.rules
This rule provides all the users with read and write access to the Yoctopuce USB peripherals. Access rights for all other peripherals are not modified. If this scenario suits you, you only need to copy the "51-yoctopuce_all.rules" file into the "/etc/udev/rules.d" directory and to restart your system.
# udev rules to allow write access to all users # for Yoctopuce USB devices SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="24e0", MODE="0666"
Example 2: 51-yoctopuce_group.rules
This rule authorizes the "yoctogroup" group to have read and write access to Yoctopuce USB peripherals. Access rights for all other peripherals are not modified. If this scenario suits you, you only need to copy the "51-yoctopuce_group.rules" file into the "/etc/udev/rules.d" directory and restart your system.
# udev rules to allow write access to all users of "yoctogroup" # for Yoctopuce USB devices SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="24e0", MODE="0664", GROUP="yoctogroup"
12.4. ARM Platforms: HF and EL
There are two main flavors of executable on ARM: HF (Hard Float) binaries, and EL (EABI Little Endian) binaries. These two families are not compatible at all. The compatibility of a given ARM platform with of one of these two families depends on the hardware and on the OS build. ArmHL and ArmEL compatibility problems are quite difficult to detect. Most of the time, the OS itself is unable to make a difference between an HF and an EL executable and will return meaningless messages when you try to use the wrong type of binary.
All pre-compiled Yoctopuce binaries are provided in both formats, as two separate ArmHF et ArmEL executables. If you do not know what family your ARM platform belongs to, just try one executable from each family.
12.5. Powered module but invisible for the OS
If your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is connected by USB, if its blue led is on, but if the operating system cannot see the module, check that you are using a true USB cable with data wires, and not a charging cable. Charging cables have only power wires.
12.6. Another process named xxx is already using yAPI
If when initializing the Yoctopuce API, you obtain the "Another process named xxx is already using yAPI" error message, it means that another application is already using Yoctopuce USB modules. On a single machine only one process can access Yoctopuce modules by USB at a time. You can easily work around this limitation by using a VirtualHub and the network mode 25.
12.7. Disconnections, erratic behavior
If you YoctoHub-Wireless-SR behaves erratically and/or disconnects itself from the USB bus without apparent reason, check that it is correctly powered. Avoid cables with a length above 2 meters. If needed, insert a powered USB hub 26 27.
12.8. Registering a VirtualHub disconnect an other one
If, when performing a call to RegisterHub() with an VirtualHub address, an other previously registered VirtualHub disconnects, make sure the machine running theses VirtualHubs don't have the same Hostname. Same Hostname can happen very easily when the operating system is installed from a monolithic image, Raspberry-PI are the best example. The Yoctopuce API uses serial numbers to communicate with devices and VirtualHub serial number are created on the fly based the hostname of the machine running the VirtualHub.
12.9. Dropped commands
If, after sending a bunch of commands to a Yoctopuce device, you are under the impression that the last ones have been ignored, typical example is a quick and dirty program meant to configure a device, make sure you used a YAPI.FreeAPI() at the end of the program. Commands are sent to Yoctopuce modules asynchronously thanks to a background thread. When the main program terminates, that thread is killed no matter if some command are left to be sent. However API.FreeAPI() will wait until there is no more commands to send before freeing the API resources and returning.
12.10. Can't contact sub devices by USB
The point of the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is to provide network access to connected sub-devices, it does not behave like a common USB hub. The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR's USB port is just meant for power and Hub configuration. Access to sub device is only possible through a network connection.
12.11. Network Readiness stuck at 3- LAN ready
Check your outbound Internet connectivity and make sure you don't have an invalid callback set in the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR configuration
12.12. Damaged device
Yoctopuce strives to reduce the production of electronic waste. If you believe that your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR is not working anymore, start by contacting Yoctopuce support by e-mail to diagnose the failure. Even if you know that the device was damaged by mistake, Yoctopuce engineers might be able to repair it, and thus avoid creating electronic waste.
 Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
If you really want to get rid of your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR, do not throw it
away in a trash bin but bring it to your local WEEE recycling point. In this
way, it will be disposed properly by a specialized WEEE recycling center.
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
If you really want to get rid of your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR, do not throw it
away in a trash bin but bring it to your local WEEE recycling point. In this
way, it will be disposed properly by a specialized WEEE recycling center.
13. Characteristics
You can find below a summary of the main technical characteristics of your YoctoHub-Wireless-SR module.
| Product ID | YHUBWLN2 |
| Hardware release† | Rev. C |
| USB connector | micro-B |
| Thickness | 8.1 mm |
| Width | 58 mm |
| Length | 60 mm |
| Weight | 30 g |
| Channels | 3 ports |
| Max Current (continuous) | 2 A |
| Protection class, according to IEC 61140 | class III |
| Normal operating temperature | 5...40 °C |
| Extended operating temperature‡ | -30...85 °C |
| USB consumption | 110 mA |
| Network connection | 802.11b |
| RoHS compliance | RoHS III (2011/65/UE+2015/863) |
| USB Vendor ID | 0x24E0 |
| USB Device ID | 0x003A |
| Suggested enclosure | YoctoBox-HubWlan-Transp |
| Harmonized tariff code | 9032.9000 |
| Made in | Switzerland |
† These specifications are for the current hardware revision. Specifications for earlier revisions may differ.
‡ The extended temperature range is defined based on components specifications and has been tested during a limited duration (1h). When using the device in harsh environments for a long period of time, we strongly advise to run extensive tests before going to production.
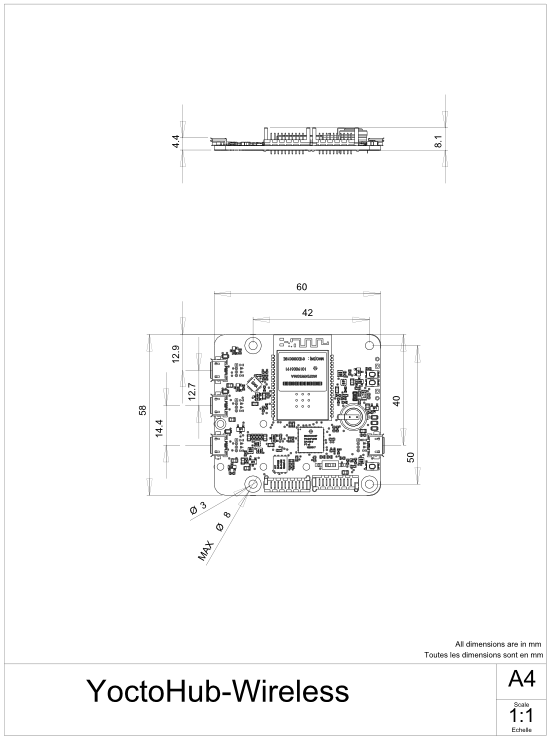
14. Index
AadhocNetwork AdminPassword AdvertisedValue API C
CallbackCredentials CallbackEncoding CallbackInitialDelay callbackLogin CallbackMaxDelay CallbackMethod CallbackMinDelay CallbackSchedule CallbackUrl clearCache D
DefaultPage describe Discoverable download download_async E
Enabled F
fileExist FilesCount FindFiles FindFilesInContext FindHubPort FindHubPortInContext FindNetwork FindNetworkInContext FindRealTimeClock FindRealTimeClockInContext FindWakeUpMonitor FindWakeUpMonitorInContext FindWakeUpSchedule FindWakeUpScheduleInContext FindWireless FindWirelessInContext FirstFiles FirstFilesInContext FirstHubPort FirstHubPortInContext FirstNetwork FirstNetworkInContext FirstRealTimeClock FirstRealTimeClockInContext FirstWakeUpMonitor FirstWakeUpMonitorInContext FirstWakeUpSchedule FirstWakeUpScheduleInContext FirstWireless FirstWirelessInContext format_fs FriendlyName FunctionId G
get_adminPassword get_advertisedValue get_baudRate get_callbackCredentials get_callbackEncoding get_callbackInitialDelay get_callbackMaxDelay get_callbackMethod get_callbackMinDelay get_callbackSchedule get_callbackUrl get_channel get_dateTime get_defaultPage get_detectedWlans get_discoverable get_enabled get_errorMessage get_errorType get_filesCount get_freeSpace get_friendlyName get_functionDescriptor get_functionId get_hardwareId get_hours get_httpPort get_ipAddress get_ipConfig get_linkQuality get_list get_logicalName get_macAddress get_message get_minutes get_minutesA get_minutesB get_module get_module_async get_monthDays get_months get_nextOccurence get_nextWakeUp get_ntpServer get_poeCurrent get_portState get_powerDuration get_primaryDNS get_readiness get_router get_secondaryDNS get_security get_serialNumber get_sleepCountdown get_ssid get_subnetMask get_timeSet get_unixTime get_userData get_userPassword get_utcOffset get_wakeUpReason get_wakeUpState get_weekDays get_wlanState get_wwwWatchdogDelay GetSimilarFunctions H
HardwareId Hours HTTPCallbacks HttpPort I
IpAddress IsOnline isOnline isOnline_async isReadOnly J
joinNetwork L
LinkQuality load load_async loadAttribute LogicalName M
MacAddress MinutesA MinutesB MonthDays Months muteValueCallbacks N
nextFiles nextHubPort nextNetwork NextOccurence nextRealTimeClock NextWakeUp nextWakeUpMonitor nextWakeUpSchedule nextWireless NtpServer P
ping PortState PowerDuration PrimaryDNS R
Readiness registerValueCallback remove resetSleepCountDown S
SecondaryDNS SerialNumber set_adminPassword set_callbackCredentials set_callbackEncoding set_callbackInitialDelay set_callbackMaxDelay set_callbackMethod set_callbackMinDelay set_callbackSchedule set_callbackUrl set_defaultPage set_discoverable set_enabled set_hours set_httpPort set_logicalName set_minutes set_minutesA set_minutesB set_monthDays set_months set_nextWakeUp set_ntpServer set_periodicCallbackSchedule set_powerDuration set_primaryDNS set_secondaryDNS set_sleepCountdown set_unixTime set_userData set_userPassword set_utcOffset set_weekDays set_wwwWatchdogDelay sleep sleepFor sleepUntil softAPNetwork Ssid startWlanScan T
techspec triggerCallback U
unmuteValueCallbacks upload useDHCP useDHCPauto UserPassword useStaticIP UtcOffset W
wait_async wakeUp WeekDays WwwWatchdogDelay Y
YFiles YHubPort YNetwork YRealTimeClock YWakeUpMonitor YWakeUpSchedule YWireless
- http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/virtualhub.php ←
- support@yoctopuce.com ←
- short-short-short long-long-long short-short-short ←
- su
pport @yoct opuce .com ← - The Yoctopuce Micro-USB-Hub is a standard USB hub and does not work either. ←
- www.yoctopuce.com/FR/products/yoctohub-shield ←
- http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/virtualhub.php ←
- http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/libraries.php ←
- http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/products/accessories-and-connectors/fix-2-5mm ←
- http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/products/accessories-and-connectors/board2board-127 ←
- The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR interface is regularly tested with Internet Explorer 6+, Firefox 3.5+, Chrome, and Safari. It does not work with Opera. ←
- The YoctoHub-Wireless-SR does not need to be more recent than the module you want to test and configure: all the elements specific to the module interfaces are kept in the module ROM, and not in the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR. ←
- Never trust people telling you that their software does not have bugs :-) ←
- www.yoctopuce.com ←
- On the condition that the interface could access the Yoctopuce web site. ←
- http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/virtualhub.php ←
- http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/article/using-emoncms-on-a-private-server ←
- http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/article/using-yoctopuce-sensors-with-influxdb-and-grafana ←
- http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/article/new-prtg-support-in-the-yoctohubs ←
- http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/article/a-gateway-to-remotely-access-yoctohubs ←
- Advertised values are the ones you can see on the YoctoHub-Wireless-SR main interface when you click on the show functions button. ←
- see: http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/blog_by_categories/for-the-beginners ←
- see: http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/article/about-programming-examples ←
- http://www.yoctopuce.com/FR/virtualhub.php ←
- see: http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/article/error-message-another-process-is-already-using-yapi ←
- see: http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/article/usb-cables-size-matters ←
- see: http://www.yoctopuce.com/EN/article/how-many-usb-devices-can-you-connect ←

